|
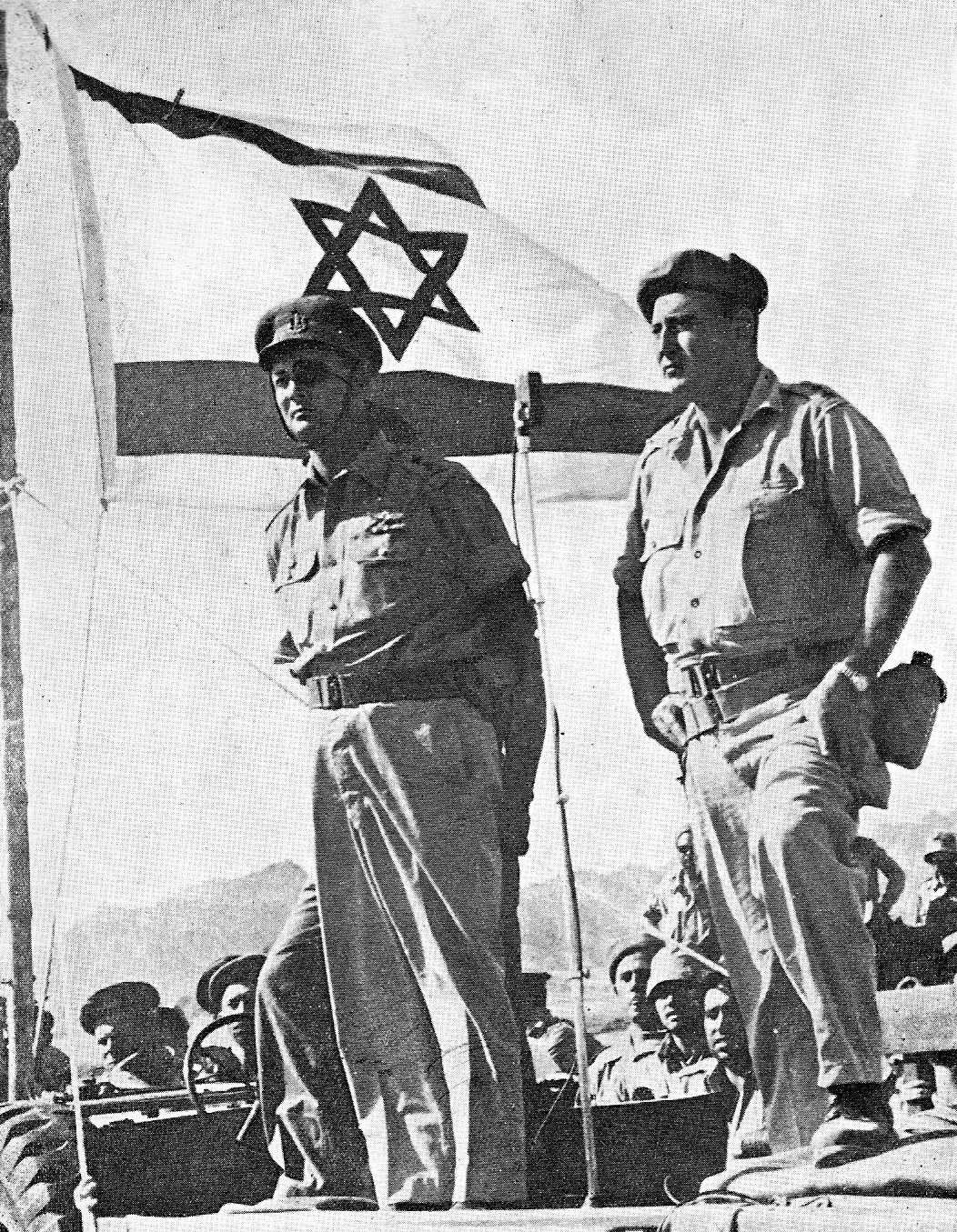
Operation Samaria
The Negev desert road ambush was a terrorist attack which occurred on Thursday, 4 October 1956. The attack During the afternoon of 4 October 1956, a squad of 10 armed Palestinian Fedayeen militants infiltrated Israel from Jordan. In broad daylight, the militants swooped down on two jeeps on the Sodom–Beer Sheva road ( Highway 25), which were traveling on the road section which goes through the southern part of the Dead Sea, 7 miles west of the Jordanian border with Israel. The vehicles were carrying employees of the Solel Boneh company. The militants began by attacking the first vehicle with machine gun fire, killing all four of the passengers in the car. Afterwards the militants attacked the second vehicle. One of the passengers in the second car jumped out in an attempt to escape the militants and save his life. The militants killed him as well with machine-gun fire. Only one person, an American engineer who was driving the second car, managed to escape the incident. Fatal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Fedayeen Insurgency
The Palestinian Fedayeen insurgency refers to the armed cross-border conflict, which peaked between 1949 and 1956, involving Israel and Palestinians, Palestinian militants, mainly based in the Gaza Strip, under the nominal control, of the All-Palestine Protectorate a Palestinian client-state of Egypt declared in October 1948, which became the focal point of the Palestinian fedayeen activity. The conflict was parallel to the Palestinian return to Israel, Palestinian infiltration phenomenon. Hundreds were killed in the course of the conflict, which declined after the 1956 Suez War. Emerging from among the Palestinian refugees who fled or were expelled from their villages as a result of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War,Almog, 2003, p. 20. in the mid-1950s the fedayeen began mounting cross-border operations into Israel from Syria, Egypt and Jordan. The earliest infiltrations were often made in order to access the lands and agricultural products, which Palestinians had lost as a result of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Military
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and the Israeli Navy. It is the sole military wing of the Israeli security apparatus, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel. The IDF is headed by the Chief of the General Staff, who is subordinate to the Israeli Defense Minister. On the orders of David Ben-Gurion, the IDF was formed on 26 May 1948 and began to operate as a conscript military, drawing its initial recruits from the already-existing paramilitaries of the Yishuv—namely Haganah, the Irgun, and Lehi. Since its formation shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independence, the IDF has participated in every armed conflict involving Israel. While it originally operated on three major fronts—against Lebanon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrorist Incidents In Asia In 1956
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States. There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Murder In 1956
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrorist Attacks Attributed To Palestinian Militant Groups
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States. There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 In Israel
Events in the year 1956 in Israel. Incumbents * Prime Minister of Israel – David Ben-Gurion (Mapai) * President of Israel – Yitzhak Ben-Zvi * President of the Supreme Court – Yitzhak Olshan * Chief of General Staff – Moshe Dayan * Government of Israel – 7th Government of Israel Events * 2 February – The IDF prevents the Egyptian delegation from attending the Egypt-Israel Mixed Armistice Commission meeting at al-Auja, in the de-militarized zone. * 29 March – After 15 months in the Syrian captivity, four IDF soldiers of the Golani Brigade return to Israel in exchange for 41 Syrian prisoners. A fifth IDF soldier, Uri Ilan, had committed suicide in captivity. Uri Ilan's remains are later returned to Israel. * 5 April – IDF launch an intensive 120mm mortar attack on Gaza town centre killing 58 civilians. 33 men, 15 women and 10 children. * 1 May – Finance Minister, Levi Eshkol, approves the establishment of the city of Ashdod. * 8 May – Israel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrorist Attacks Against Israeli Civilians Before 1967
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States. There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
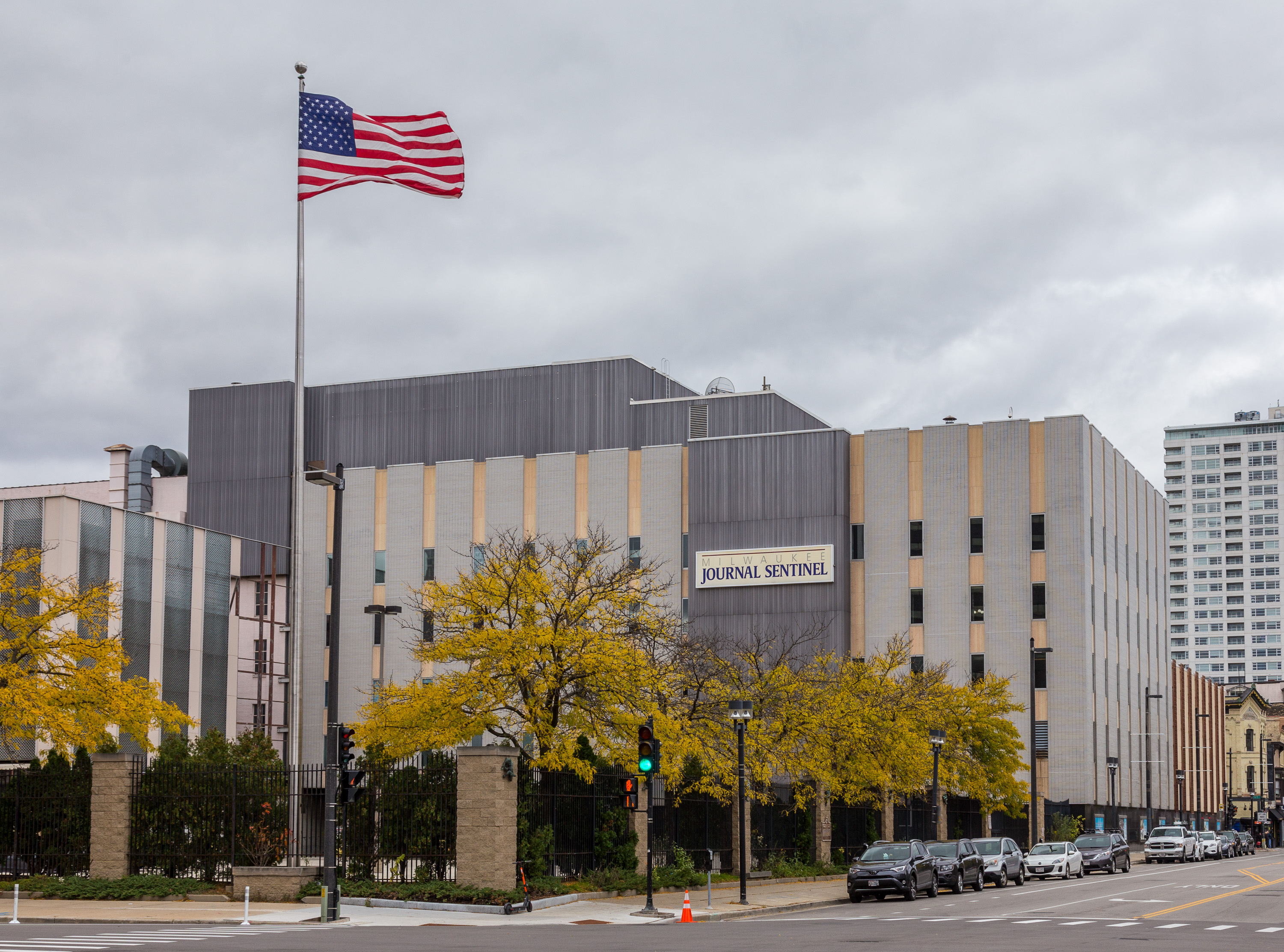
Milwaukee Journal
The ''Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'' is a daily morning broadsheet printed in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, where it is the primary newspaper. It is also the largest newspaper in the state of Wisconsin, where it is widely distributed. It is currently owned by the Gannett Company.Gannett Completes Acquisition of Journal Media Group . ''USA Today'', April 11, 2016. In early 2003, the ''Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'' began printing operations at a new printing facility in West Milwaukee. In September 2006, the ''Journal Sentinel'' announced it had "signed a five-year agreement to print the national edition of '' |
Tegart Fort
A Tegart fort is a type of militarized police fort constructed throughout Palestine during the British Mandatory period, initiated as a measure against the 1936–1939 Arab Revolt. Etymology The forts are named after their designer, British police officer and engineer Sir Charles Tegart. In Israel, the name is often pronounced "Taggart". This is probably due to the transliteration of the name to Hebrew and then back to Latin alphabet, along with the translator's wrong assumption that the most common way of writing this anglicised Scottish surname has to be applied ("Taggart" is far more widespread than "Tegart"). History Mandate Palestine Sir Charles Tegart designed the forts in 1938 based on his experiences in the Indian insurgency. They were built of reinforced concrete with water systems that would allow them to withstand a month-long siege. Two types of forts were erected. Five structures were built to reinforce the so-called " Tegart's wall" of the northern border wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalqilya
Qalqilya or Qalqiliya ( ar, قلقيلية, Qalqīlyaḧ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank which serves as the administrative center of the Qalqilya Governorate of the State of Palestine. In the 2007 census, the city had a population of 41,739. Qalqilya is surrounded by the Israeli West Bank wall, with a narrow gap in the east controlled by the Israeli military and a tunnel to the Palestinian town of Hableh. Qalqilya is under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority (as part of Area A), while remaining under Israeli military occupation. Oranges are a major part of the city's economy. Etymology Qalqilya was known as ''Calecailes'' in the Roman period, and ''Calcelie'' in the Frankish sources from the early Medieval times. The word "Qalqilya" might be derived from a Canaanite term which means "rounded stones or hills".According to E.H. Palmer, the name came from "a type of pomegranate", or "gurgling of water".Palmer, 1881, p183/ref> History The vicinity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retribution Operations
Reprisal operations ( he, פעולות התגמול, ') were raids carried out by the Israel Defense Forces in the 1950s and 1960s in response to frequent fedayeen attacks during which armed Arab militants infiltrated Israel from Syria, Egypt, and Jordan to carry out attacks on Israeli civilians and soldiers. Most of the reprisal operations followed raids that resulted in Israeli fatalities. The goal of these operations was to create deterrence and prevent future attacks. Two other factors behind the raids were restoring public morale and training newly formed army units. Background: 1949–1956 Reprisal operations were carried out following raids by armed infiltrators into Israel during the entire period from 1948 Arab–Israeli War until October 1956. Most of Reprisal operations followed raids that resulted in Israeli fatalities. From 1949 to 1954 the reprisal operations were directed against Jordan. In 1954 the Jordanian authorities decided to curb the infiltration due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even Yehuda
Even Yehuda ( he, אֶבֶן יְהוּדָה) is a town in the central Sharon region of Israel east of Netanya. In it had a population of . History The area of Even Yehuda has been inhabited intermittently since the Middle Paleolithic age, with peak periods of settlement during the Byzantine (4th - 7th centuries CE) and Late Ottoman periods (19- early 20th centuries CE). Before the 20th century, the territory of Even Yehuda formed part of the Forest of Sharon, a hallmark of the region’s historical landscape. It was an open woodland dominated by Mount Tabor Oak (Quercus ithaburensis), which extended from Kfar Yona in the north to Ra’ananna in the south. The local Arab inhabitants traditionally used the area for pasture, firewood and intermittent cultivation. The intensification of settlement and agriculture in the coastal plain during the 19th century led to deforestation and subsequent environmental degradation known from Hebrew sources. Even Yehuda is named for E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |