|
Operation Pearl Harbour
Italian-occupied Corsica refers to the military (and administrative) occupation by the Kingdom of Italy of the island of Corsica during the Second World War, from November 1942 to September 1943. After an initial period of increased control over the island, by early spring 1943 the had begun to occupy the hinterland. In the aftermath of the Armistice of Cassibile, the Italian capitulation to the Allies, some Italian units sided with German troops sent to replace the Italian garrison and some defected to the and Free French Forces. Background Operation Torch On 8 November 1942, the western Allies landed in North Africa in Operation Torch. The Germans implemented a contingency plan, Case Anton to occupy the the part of France not occupied in 1940. The plan included (11 November) an Italian occupation of the French island of Corsica and mainland France up to the Rhone. The Italian occupation of Corsica had been strongly promoted by Italian irredentism by the Fascist regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligurian Sea Map
Ligurian may refer to: * Ligurian, pertaining to modern Liguria in Italy * Ligurian, pertaining to the ancient Ligures * Ligurian language, a modern Romance language spoken in parts of Italy, France, Monaco and Argentina * Ligurian (ancient language), an extinct language spoken by the ancient Ligures * Ligurian Sea, an arm of the Mediterranean Sea * Ligurian bee, a type of Italian bee ''Apis mellifera ligustica'' is the Italian bee which is a subspecies of the western honey bee (''Apis mellifera''). Origin The Italian honey bee is thought to originate from the continental part of Italy, south of the Alps, and north of Sicily ... (''Apis mellifera ligustica'') {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
225th Coastal Division (Italy)
The 225th Coastal Division ( it, 225ª Divisione Costiera) was an infantry division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II. Royal Italian Army coastal divisions were second line divisions formed with reservists and equipped with second rate materiel. They were often commanded by officers called out of retirement.Jowett p 6 History In November 1942 Axis forces invaded Southern France and divided it into a German and an Italian occupation zone. For the coastal defense of the island of Corsica Italy raised on 20 January 1943 the 225th Coastal Division in Pisa and the 226th Coastal Division in Florence. Both divisions were assigned to VII Army Corps and transferred to Corsica in March 1943. The 225th Coastal Division was based in Corbara and responsible for the northwestern coast of Corsica. After the announcement of the Armistice of Cassibile on 8 September 1943 the division fought, together with the 225th Coastal Division, 20th Infantry Division "Friuli", 44th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefect (France)
A prefect (french: préfet, plural ''préfets'') in France is the state's representative in a department or region. Subprefects (French: ''sous-préfets'') are responsible for the subdivisions of departments, known as arrondissements. The office of a prefect is known as a prefecture and that of a subprefect as a subprefecture. Regional prefects are ''ex officio'' the departmental prefects of the regional prefecture. Prefects are tasked with upholding the law in the department they serve in, including controlling the actions of local authorities to ensure adhesion to national guidelines. They are authorised to sue local collectivities in the name of the state. Prefects are appointed by a decree of the President of France when presiding the Government's Council of Ministers, following a proposal by the Prime Minister and the Minister of the Interior. They serve at the Government's discretion and can be replaced at any meeting of the Council of Ministers. From 1982 to 1988, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Germany, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan. The Axis were united in their opposition to the Allies, but otherwise lacked comparable coordination and ideological cohesion. The Axis grew out of successive diplomatic efforts by Germany, Italy, and Japan to secure their own specific expansionist interests in the mid-1930s. The first step was the protocol signed by Germany and Italy in October 1936, after which Italian leader Benito Mussolini declared that all other European countries would thereafter rotate on the Rome–Berlin axis, thus creating the term "Axis". The following November saw the ratification of the Anti-Comintern Pact, an anti-communist treaty between Germany and Japan; Italy joined the Pact in 1937, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 1943, and "Duce" of Italian Fascism from the establishment of the Italian Fasces of Combat in 1919 until his execution in 1945 by Italian partisans. As dictator of Italy and principal founder of fascism, Mussolini inspired and supported the international spread of fascist movements during the inter-war period. Mussolini was originally a socialist politician and a journalist at the ''Avanti!'' newspaper. In 1912, he became a member of the National Directorate of the Italian Socialist Party (PSI), but he was expelled from the PSI for advocating military intervention in World War I, in opposition to the party's stance on neutrality. In 1914, Mussolini founded a new journal, ''Il Popolo d'Italia'', and served in the Royal Italian Army durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
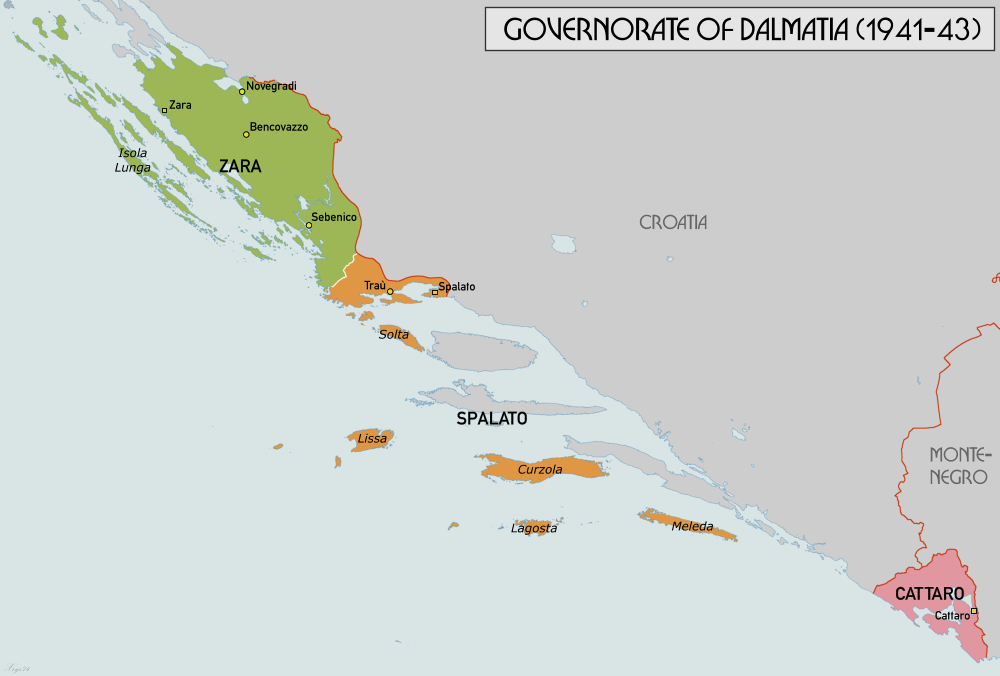
Governatorate Of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia ( it, Governatorato di Dalmazia) was a territory divided into three provinces of Italy during the Italian Kingdom and Italian Empire epoch. It was created later as an entity in April 1941 at the start of World War II in Yugoslavia, by uniting the existing Province of Zara together with occupied Yugoslav territory annexed by Italy after the invasion of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers and the signing of the Rome Treaties. Background Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente Allies in 1915 upon agreeing to the London Pact that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5 to 6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Lissa, Lagosta, Sebenico, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. At the end of hostilities in November 1918, the Italian m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petru Giovacchini
Petru Giovacchini (french: Pierre Giovacchini, it, Pietro Giovacchini; 1 February 1910 – 29 September 1955) was a Corsican activist, born in Canale-di-Verde to an old family of the Corsican nobility with deep-rooted pro-Italian feelings. Giovacchini was the most renowned of the Corsican Italians, who actively promoted the unification of Corsica to the Kingdom of Italy during the Fascist years. Life Since young he collaborated with writings to the literary newspaper ''A Muvra''. In 1927 he was expelled from the "Liceo National" of Bastia and founded the pro-Italian magazine "Primavera", where he published the poems "Musa canalinca" and "Rime notturne". Giovacchini was disappointed with the moderate positions of the ''Movimento Autonomista Corso'' and decided to move to Italy in 1930 to study medicine at the Pisa University. In Italy Giovacchini entered in contact with the Italian irredentism movement and because of this was harshly attacked by the French authorities when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maquis (World War II)
The Maquis () were rural guerrilla bands of French and Belgian Resistance fighters, called ''maquisards'', during the Nazi occupation of France in World War II. Initially, they were composed of young, mostly working-class, men who had escaped into the mountains and woods to avoid conscription into Vichy France's ''Service du travail obligatoire'' ("Compulsory Work Service" or ''STO'') to provide forced labor for Germany. To avoid capture and deportation to Germany, they became increasingly organized into active resistance groups. They had an estimated to members in autumn of 1943 and approximately members in June 1944. Meaning Originally the word came from the kind of terrain in which the armed resistance groups hid, high ground in southeastern France covered with scrub growth called ''maquis'' (scrubland). from Dictionary.com Although strictly speaking it means thicket, ''maquis'' could be roughly translated as "the bush"; in Corsica, the saying ''prendre le maquis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Italian Army (1940–1946)
This article is about the Royal Italian Army (''Regio Esercito'') which participated in the Second World War. The Royal Italian Army was reformed in 1861 and existed until 1946. The Royal Army started with the unification of Italy (''Risorgimento'') and the formation of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia''). It ended with the dissolution of the monarchy. The Royal Army was preceded by the individual armies of the independent Italian states and was followed by the Italian Army (''Esercito Italiano'') of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''). Organization The Italian Army of World War II was a "Royal" army. The nominal Commander-in-Chief of the Italian Royal Army was His Majesty King Vittorio Emanuele III. As Commander-in-Chief of all Italian armed forces, Vittorio Emanuele also commanded the Royal Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica'') and the Royal Navy (''Regia Marina''). However, in reality, most of the King's military responsibilities were assumed by the Italia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Petru Cristofini
Simon Petru Cristofini (1903–1943), also known as Pietro Simone Cristofini (french: Pierre Simon Cristofini), was a Corsican soldier who commanded the Phalange Africaine during World War II and was executed for treason by the French authorities because of his support to Italian irredentism in Corsica during the Italian occupation of Corsica. Biography Early life Cristofini was born in Calenzana, Haute-Corse on 26 May 1903. World War II In 1939 became a Captain of the 3rd Algerian Tirailleurs Regiment. He was initially a supporter of Marshal Philippe Pétain. Allied forces landed in French Morocco and Algeria in November 1942. Immediately, German and Italian reinforcements landed in French Tunisia and on 14 November the idea of an '' African Phalange'' was mooted in Paris with the support of the Third Reich Ambassador Otto Abetz. In December, German authorities approved the plan and 330 volunteers were recruited under the command of Cristofini. The troops trained at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Magli
Giovanni Magli ( Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto, 27 June 1884 – Bari, 28 January 1969) was an Italian general during World War II. Biography Magli was born in Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto on June 27, 1884, the son of Diomede Magli and Antonia Calcagno. After attending the three-year course at the Royal Military Academy of Infantry and Cavalry of Modena, in 1908, he graduated as infantry second lieutenant as the first of his course, and was assigned to the 47th Infantry Regiment "Ferrara". In 1911 he fought in Libya during the Italo-Turkish War; he remained there even after the end of the hostilities against Turkey, participating in counterguerrilla operational and receiving, in 1913, a decoration for valor. In the same year he briefly taught at the Infantry Application School. In April 1915 he was captain in the 10th Infantry Regiment "Regina" and with this unit, after the Kingdom of Italy entered the war on 24 May following, he took part in the Second Battle of the Isonzo ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giacomo Carboni
Giacomo Carboni (29 April 1889 – 2 December 1973) was an Italian general who was the commander of ''Corpo d'armata motocorazzato'' deployed around Rome in the early days of September 1943. Life and career Born in Reggio Emilia he joined the Modena Military Academy where he was commissioned Sottotenente. Then he fought in the Libyan war. During World War I he was an officer of the Alpini. In 1936–37 he was commander of the 81st infantry regiment during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, in 1939 he was Vice Commander of Cacciatori delle Alpi division. From September 1939 to June 1940 he was the chief of SIM. As chief of the Italian military secret service he wrote a series of reports to Mussolini wherein the Italian preparation to the war was described as inadequate. Carboni was dismissed from his post at SIM and was made commander of the Modena Military Academy. From December 1941 until November 1942, he was commander of the 20 Infantry Division Friuli and in the first h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |