|
Operation Ezra And Nehemiah
From 1951 to 1952, Operation Ezra and Nehemiah airlifted between 120,000 and 130,000 Iraqi Jews to Israel via Iran and Cyprus. The massive emigration of Iraqi Jews was among the most climactic events of the Jewish exodus from the Muslim World. The operation is named after Ezra and Nehemiah, who led the Jewish people from exile in Babylonia to return to Israel in the 5th century BC, as recorded in the books of the Hebrew Bible that bear their names. Most of the $4 million cost of the operation was financed by the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee. Background 1940s A change in Iraqi Jewish identity occurred after the violent ''Farhud'' against the Jews of Baghdad, on June 1–2, 1941 following the collapse of the pro-Nazi ''Golden Square'' regime of Rashid Ali al-Kaylani, during which at least 180 Jews were killed during two days of pogrom mob attacks in the community. In some accounts the Farhud marked the turning point for Iraq's Jews. Other historians, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Jews
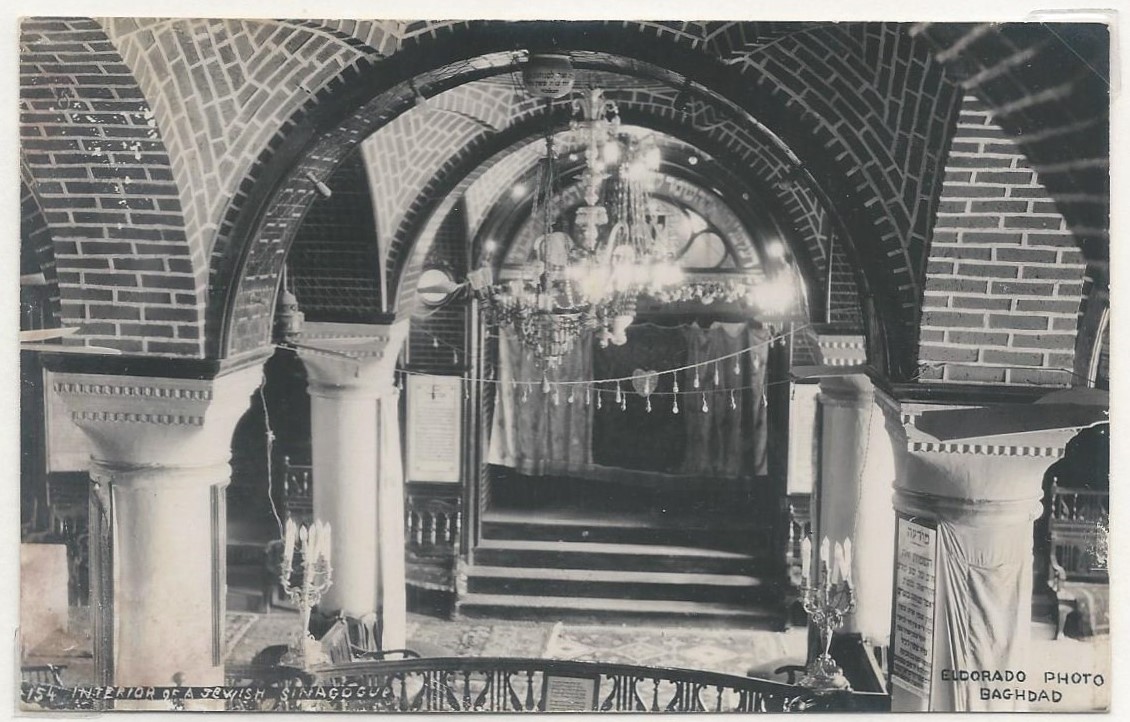
The history of the Jews in Iraq ( he, יְהוּדִים בָּבְלִים, ', ; ar, اليهود العراقيون, ) is documented from the time of the Babylonian captivity c. 586 BC. Iraqi Jews constitute one of the world's oldest and most historically significant Jewish communities. The Jewish community of what is termed in Jewish sources "Babylon" or "Babylonia" included Ezra the scribe, whose return to Judea in the late 6th century BCE is associated with significant changes in Jewish ritual observance and the rebuilding of the Temple in Jerusalem. The Babylonian Talmud was compiled in "Babylonia", identified with modern Iraq. From the biblical Babylonian period to the rise of the Islamic caliphate, the Jewish community of "Babylon" thrived as the center of Jewish learning. The Mongol invasion and Islamic discrimination in the Middle Ages led to its decline. Under the Ottoman Empire, the Jews of Iraq fared better. The community established modern schools in the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuri Al-Said
Nuri Pasha al-Said CH (December 1888 – 15 July 1958) ( ar, نوري السعيد) was an Iraqi politician during the British mandate in Iraq and the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq. He held various key cabinet positions and served eight terms as the prime minister of Iraq. From his first appointment as prime minister under the British mandate in 1930, Nuri was a major political figure in Iraq under the monarchy. During his many terms in office, he was involved in some of the key policy decisions that shaped the modern Iraqi state. In 1930, during his first term, he signed the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty, which, as a step toward greater independence, granted Britain the unlimited right to station its armed forces in and transit military units through Iraq and also gave legitimacy to British control of the country's oil industry. The treaty nominally reduced British involvement in Iraq's internal affairs but only to the extent that Iraq did not conflict with British economic or military i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas Shiblak
Abbas Shiblak (born 6 January 1944) is a Palestinian academic, historian, Research Associate at the Refugee Studies Centre (RSC), University of Oxford (a post he has held since 1992), free-lance writer, former diplomat and an advocate of human rights. Shiblak specializes in refugee-host country relationships and international humanitarian law. For the last few years, he has been working on a paper on the topic of statelessness in the Arab region. Shiblak founded Shaml, the Palestinian Refugee and Diaspora Centre in Ramallah, and also served as its first director. Shiblak was also a member of the Palestinian delegation to the peace talks on the "Working Group on Refugees". Personal life Shiblak was born in Palestine on 6 January 1944 and, after completing his schooling in Jordan, his university education in Egypt and working in Lebanon, he moved to Britain in 1975, where he completed his postgraduate education in international relations. Shiblak then pursued a career in free-la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Mack (diplomat)
Sir William Henry Bradshaw Mack (21 August 1894 - 9 March 1974) was a British diplomat. He was Ambassador to Austria from 1945 to 1948, Ambassador to Iraq from 1948 to 1951, and Ambassador to Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ... from 1951 to 1955. References Ambassadors of the United Kingdom to Austria Ambassadors of the United Kingdom to Iraq Ambassadors of the United Kingdom to Argentina Knights Commander of the Order of St Michael and St George Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the British Empire 1894 births 1974 deaths {{UK-diplomat-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Refugees
Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country over the course of the 1947–49 Palestine war (1948 Palestinian exodus) and the Six-Day War (1967 Palestinian exodus). Most Palestinian refugees live in or near 68 Palestinian refugee camps across Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. In 2019 more than 5.6 million Palestinian refugees were registered with the United Nations. In 1949, the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) defined Palestinian refugees to refer to the original "Palestine refugees" as well as their patrilineal descendants. However, UNRWA's assistance is limited to Palestine refugees residing in UNRWA's areas of operation in the Palestinian Territories, Lebanon, Jordan and Syria. As of 2019, more than 5.6 million Palestinians were registered with UNRWA as refugees, of which more than 1.5 million live in UNRWA-run camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Exchange
Population transfer or resettlement is a type of mass migration, often imposed by state policy or international authority and most frequently on the basis of ethnicity or religion but also due to economic development. Banishment or exile is a similar process, but is forcibly applied to individuals and groups. Population transfer differs more than simply technically from individually motivated migration, but at times of war, the act of fleeing from danger or famine often blurs the differences. If a state can preserve the fiction that migrations are the result of innumerable "personal" decisions, the state may be able to claim that it is not to blame for the displacement. Often the affected population is transferred by force to a distant region, perhaps not suited to their way of life, causing them substantial harm. In addition, the process implies the loss of immovable property and substantial amounts of movable property when rushed. This transfer may be motivated by the more p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Palestinian Exodus
In 1948 Estimates of the Palestinian Refugee flight of 1948, more than 700,000 Palestinians, Palestinian Arabs – about half of prewar Mandatory Palestine, Palestine's Arab population – Causes of the 1948 Palestinian exodus, were expelled or fled from their homes, during the 1948 Palestine war. The exodus was a central component of the fracturing, dispossession and displacement of Palestinian society, known as the Nakba, in which between Depopulated Palestinian locations in Israel, 400 and 600 Palestinian villages were destroyed, village wells were poisoned in a biological warfare programme to prevent Palestinians returning, and other sites subject to Hebraization of Palestinian place names, and also refers to the wider period of war itself and the subsequent oppression up to the present day. The precise number of Palestinian refugees, refugees, many of whom settled in Palestinian refugee camps, refugee camps in neighboring states, is a matter of dispute but around 80 perc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eliahu Eilat
Eliahu Elath (Hebrew: אליהו אילת, born ''Ilya Menakhemovich Epstein''; 16 July 1903 – 21 June 1990) was an Israeli diplomat and Orientalist. In 1948 he became the first Israeli ambassador to the United States, and between 1950 and 1959, he was Israel's ambassador to the United Kingdom. He was the President of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem from 1962 to 1968. Biography Eliahu Eilat immigrated from Russia to Palestine in 1924, and spent a decade in Beirut as a student and journalist. Diplomatic career From 1934 to 1945 he worked for the Jewish Agency, which evolved into the government of Israel (as described by V. Jacobson in 1934 in “Report on my trip to Eretz Israel and Syria”, 12 May 1933). That same year he came to the United States as the agency's representative in Washington, D.C., and from 1948 to 1950 he served as the first Israeli ambassador to the United States. Following that appointment he served as the Israeli ambassador to the United Kingdom f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, Eastern Africa, and Western Asia. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945, initially with six members: Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt, Kingdom of Iraq (1932–1958), Iraq, Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan (renamed Jordan in 1949), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has member states of the Arab League, 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011. The League's main goal is to "draw closer the relations between member states and co-ordinate collaboration between them, to safeguard their independence and sovereignty, and to consider in a general way the affairs and interests of the Arab countries". The organization has received a relatively l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is handled at the port of Umm Qasr. However, there is ongoing constuction of Grand Faw Port on the coast of Basra, which is considered a national project for Iraq and will become one of the largest ports in the world and the largest in the Middle East, in addition, the port will strengthen Iraq’s geopolitical position in the region and the world. Furthermore, Iraq is planning to establish large naval base in the Al-Faw peninsula, Faw peninsula. Historically, the city is one of the ports from which the fictional Sinbad the Sailor journeyed. The city was built in 636 and has played an important role in Islamic Golden Age. Basra is consistently one of the hottest cities in Iraq, with summer temperatures regularly exceeding . In April 2017, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shafiq Ades
Shafiq Ades ( ar, شفيق عدس, he, שפיק עדס; born in 1900, died on 23 September 1948) was a wealthy Iraqi-Jewish businessman of Syrian origins. After a short show trial in 1948, he was executed by hanging on charges of selling weapons to Israel and supporting the Iraqi Communist Party.www.ajds.org.au Early life and career Ades was born to a wealthy family based in , . He migrated to Iraq and based himself in . His main business activity was the establishment and manage ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |