|
Operation Barak
Operation Barak ( he, מבצע ברק, ''Mivtza Barak'', lit. ''Operation Lightning'') was a Haganah offensive launched just before the end of the British Mandate in Palestine. It was part of Plan Dalet. Its objective was to capture villages North of Gaza in anticipation of the arrival of the Egyptian army. It was undertaken by the newly formed Giv'ati brigade, commanded by Shimon Avidan. Background Operational orders defined the Giv'ati brigades objectives as: "To deny the enemy a base ... creating general panic and breaking his morale ... cause the flight of the inhabitants of the smaller settlements in the area." Commander Avidan's instructions were: "You will determine alone, in consultation with your Arab affair advisers and Intelligence Service officer, the villages in your zone that should be occupied, cleaned up or destroyed." According to historian Benny Morris, Avidan preferred the latter option.As a prelude, the Giv'ati brigade's first action took place on 4 May 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haganah
Haganah ( he, הַהֲגָנָה, lit. ''The Defence'') was the main Zionist paramilitary organization of the Jewish population ("Yishuv") in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and its disestablishment in 1948, when it became the core of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Formed out of previous existing militias, its original purpose was to defend Jewish settlements from Arab attacks, such as the riots of 1920, 1921, 1929 and during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. It was under the control of the Jewish Agency, the official governmental body in charge of Palestine's Jewish community during the British Mandate. Until the end of the Second World War, Haganah's activities were moderate, in accordance with the policy of havlaga ("self-restraint"), which caused the splitting of the more radical Irgun and Lehi. The group received clandestine military support from Poland. Haganah sought cooperation with the British in the event of an Axis invasion of Palestine through North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev Brigade
The 12th Negev Brigade ( he, חטיבת הנגב, ''Hativat HaNegev'') is an Israeli reserve infantry brigade under the Sinai Division, that originally served in the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. History Founding and organization The brigade was founded in March 1948 with two battalions, the 2nd and 8th. The 7th Battalion was created in April, with the 9th Battalion being the last of the four. Yisrael Galili, the Haganah Chief of Staff, and Yigal Allon, the Palmach commander, chose Sarig to command the brigade in December 1947, although the residents of the Negev and David Ben-Gurion appointed Shaul Avigur instead, without Sarig's knowledge. After Avigur toured the Negev, he told Ben-Gurion that he would not be able to command the brigade, citing deteriorating health, and praised Sarig. It was commanded by Nahum "Sergei" Sarig (which is why it was also called ''Sergei Brigade'') and consisted of four Palmach battalions. The Negev Brigade participated in many operations in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walid Khalidi
Walid Khalidi ( ar, وليد خالدي, born 1925 in Jerusalem) is an Oxford University-educated Palestinian historian who has written extensively on the Palestinian exodus. He is a co-founder of the Institute for Palestine Studies, established in Beirut in December 1963 as an independent research and publishing center focusing on the Palestine problem and the Arab–Israeli conflict, and was its General Secretary until 2016. Khalidi's first teaching post was at Oxford, a position he resigned from in 1956 in protest at the British invasion of Suez. He was Professor of Political Studies at the American University of Beirut until 1982 and thereafter a research fellow at the Harvard Center for International Affairs. He has also taught at Princeton University. He is a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He has been influential in scholarship, institutional development and diplomacy. His academic work in particular, according to Rashid Khalidi, has played a ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Maghar
al-Maghar was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. It was depopulated by the Givati Brigade during Operation Barak on 18 May 1948. It was located 12 km southwest of Ramla, situated north of Wadi al-Maghar. History An inscription which was in Greek, and dated to a Christian period was found here. In the 8th century, the village was the birthplace of the Islamic jurist Abu al-Hasan Muhammad al-Maghari.Khalidi, 1992, p. 394 Ottoman era In 1517, Al-Maghar, like the rest of Palestine, was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire, and in the 1596 tax registers the village appeared under the name of ''Imgar'', as being in the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Gaza under the Liwa of Gaza, with a population was 22 households, all Muslim. The villagers paid a fixed tax rate of 33,3% on various agricultural products, such as wheat, barley, summer crops, fruit trees, olive trees, and sesame; a total of 6,400 akçe. In 1838, ''el Mughar'' was noted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simsim, Gaza
Simsim ( ar, سمسم), known to the Crusaders as Semsem, was a Palestinian village, located northeast of Gaza. It was depopulated just prior to the outbreak of 1948 Arab-Israeli war. On 12 May 1948, pre-state Israeli forces expelled the villagers, along with those of the neighboring village of Najd.Morris, 2004, p.258/ref> History Simsim contained two archaeological sites known locally as ar-Ras and Sha'fat al-Mughur (the latter of which contained a Roman cemetery). Byzantine ceramics have been found here. The village was known as ''Semsem'' to the Crusaders. Ottoman period Simsim was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517 with all of Palestine, and by 1596 it was part of the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Gaza under the ''liwa''' (district) of Sanjak of Gaza, and it had 20 Muslim households, an estimated population of 110. They paid a fixed tax rate of 33,3% on a number of crops, including wheat, barley and fruit trees, as well as on goats and beehives; a total of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qubab
Al-Qubab ( ar, القباب) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict. It was depopulated in July 1948 during the Operation Dani led by the Yiftach Brigade. History Remains, possibly dating from the Roman era have been found here.Clermont-Ganneau, 1896, vol 2, pp8385 Archeological excavations have revealed tombs and cisterns dating to the Roman and Byzantine eras,Lupu, 2010El-Qubab/ref>Shachar, 2019El-Qubab/ref> and addition to pottery remains from the same eras. Pottery remains from the early Islamic era, including a glazed bowl from the Abbasid period have also been found here. Mamluk era During the late Mamluk era, Mujir al-Din wrote that al-Qubab was a village within the administrative jurisdiction of al-Ramla in 1483.Khalidi, 1992, p. 406 Mujir al-Din further noted that In 898 A. H., or 1492 C.E. the fellahin rebelled against the governor of Jerusalem. They were then caught between the governors of Gaza and Jerusalem, about in whose jurisdiction Al-Qubab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Na'ani
Al-Na'ani, also called Al-Ni'ana, was a Palestinian people, Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on May 14, 1948, by the Givati Brigade during Operation Barak. It was located 6 km south of Ramle. History In 1838, it was noted as a Muslim village in Er-Ramleh district. The village was at the site of a historic Roman site of Tel Na'na' ( he, תל נענע), where excavations have resulted in discovery of tombs and items dating to the Roman, Byzantine, and early Arab era. An Ottoman Empire, Ottoman village list from about 1870 counted 92 houses and a population of 265, though the population count included men, only. In 1882, the Palestine Exploration Fund, PEF's ''PEF Survey of Palestine, Survey of Western Palestine'' described the place as: "A small adobe, mud village on low ground, identified with Naamah (near Makkedah), by Captain Charles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Shusha
Abu Shusha ( ar, أبو شوشة) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine, located 8 km southeast of Ramle. It was depopulated in May 1948. Abu Shusha was located on the slope of Tell Jezer/Tell el-Jazari, which is commonly identified with the ancient city of Gezer. In April–May 1948, during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Abu Shusha was attacked several times. The final assault began on May 13, one day prior to Israel's declaration of independence. Abu Shusha residents attempted to defend the village, but the village was occupied on May 14. Those residents who had not already died or fled were expelled by May 21. With their descendants, they numbered about 6,198 in 1998. Name Abu Shusheh is said to derive its name from a derwish who prayed for rain in a time of drought, and was told by a sand-diviner that he would perish if it came. The water came out of the earth (probably at Et Tannur) and formed a pool, into which he stepped and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
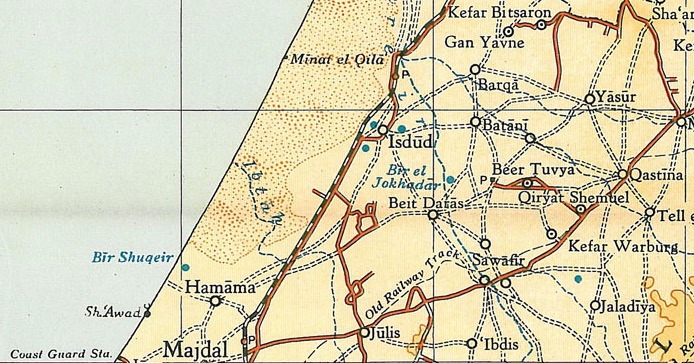
Al-Batani Al-Sharqi
Al-Batani al-Sharqi ( ar, البطاني الشرقي) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza situated in the flat terrain on the southern coastal plain of Palestine. It had a population of 650 in 1945. Al-Batani al-Sharqi was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, pp.84-85. History Ceramics from the Byzantine era have been found here, together with coins from reigns of Phocas and Constantine IV. One mention of al-Batani indicates that it was founded as a ranch by the Umayyad caliph Mu'awiyah I in the 8th century CE. Ottoman era Al-Batani al-Sharqi, like the rest of Palestine, was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517, and in the tax registers of 1596, it was a village in the ''nahiya'' of Gaza, east of Isdud, north of Bayt Daras and part of the Sanjak of Gaza with a population of 39. Al-Batani paid taxes on wheat, barley, fruit, beehives, goats, and vineyards. The whole population was Muslim. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irgun
Irgun • Etzel , image = Irgun.svg , image_size = 200px , caption = Irgun emblem. The map shows both Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan, which the Irgun claimed in its entirety for a future Jewish state. The acronym "Etzel" is written above the map, and "raq kach" ("only thus") is written below. , dates = 1931–1948 , country = Yishuv, Mandatory Palestine Israel , type = Paramilitary (pre-independence) Unified armed forces (post-independence) , role = , size = , battles = Arab Revolt in PalestineWorld War II *Anglo-Iraqi War *Syria–Lebanon Campaign Jewish Revolt in Palestine Palestine Civil War1948 Arab–Israeli War , disbanded = 11 June 1948 , commander1 = , commander1_label = , commander2 = , commander2_label = , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = Ze'ev Jabotinsky, Avraham Tehomi, Menachem Begin , identification_symbol = , identification_symbol_label = , identification_symbol_2 = , identification_symbol_2_labe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khubbayza
Khubbayza ( ar, خبْيزة) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Haifa Subdistrict, located southeast of Haifa. It was situated on hilly terrain, south of Wadi al-Sindiyana, between the Jezreel Valley with the Mediterranean coast. In 1945, it had a population of 290.Khalidi, 1992, p.172. Khubbayza was depopulated during the 1948 War on May 12, 1948, in the Battle of Mishmar HaEmek.Khalidi, 1992, p.173. History The village is named after the Arabic term for mallow, a wild plant used in Palestinian cuisine, particularly in rural areas. To the north of Khubbayza laid the ruins of Khirbat Kalba, named after Banu Kalb, the Arab tribe. It contained traces of human settlement. In 1859, Khubbayza had an estimated 270 inhabitants who cultivated 24 feddans of land,Conder and Kitchener, 1882, SWP II, p42/ref> while Victor Guérin, who visited in 1870, found the village to have 400 inhabitant. In 1882 the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' described Khobbeizeh as a "village of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |