|
Openmoko Linux
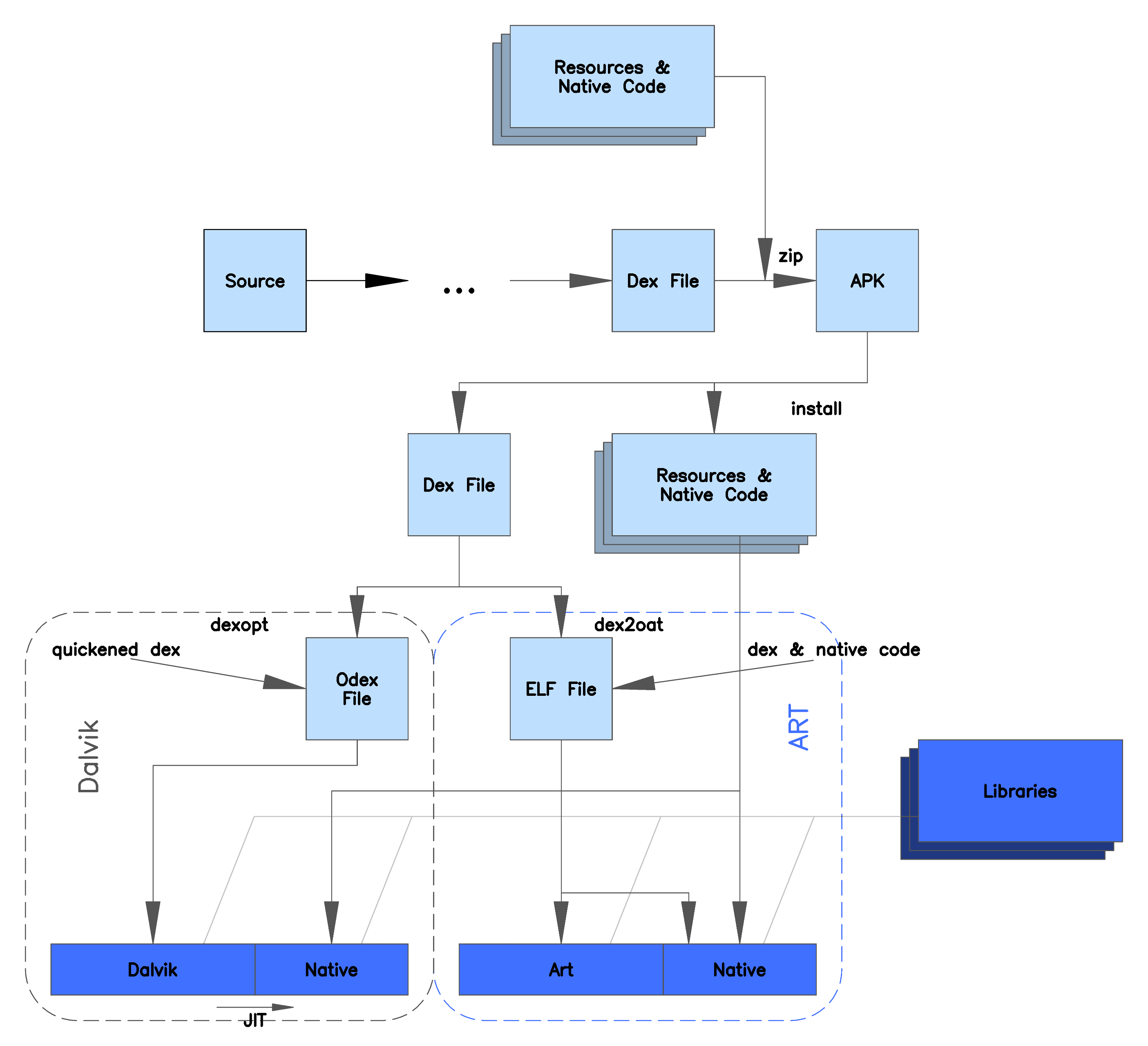
Openmoko Linux is an operating system for smartphones developed by the Openmoko project. It is based on the Ångström distribution, comprising various pieces of free software. The main targets of Openmoko Linux were the Openmoko Neo 1973 and the Neo FreeRunner. Furthermore, there were efforts to port the system to other mobile phones. Openmoko Linux was developed from 2007 to 2009 by Openmoko Inc. The development was discontinued because of financial problems. Afterwards the development of software for the Openmoko phones was taken over by the community and continued in various projects, including SHR, QtMoko and Hackable1. Components Openmoko Linux uses the Linux kernel, GNU libc, the X.Org Server plus their own graphical user environment built using the EFL toolkit, GTK+ toolkit, Qt toolkit and the illume window manager (previously Matchbox window manager). The OpenEmbedded build framework and opkg package management system, are used to create and maintain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Openmoko Logo 2
Openmoko is a discontinued project to create a family of open source mobile phones, including the hardware specification, the operating system ( Openmoko Linux), and actual smartphone development implementation like the Neo 1973 and Neo FreeRunner. The whole project was sponsored by Openmoko Inc. The first sub-project was Openmoko Linux, a Linux-based operating system designed for mobile phones, built using free software. The second sub-project was developing hardware devices on which Openmoko Linux runs. The first device released was the Neo 1973, in 2007, which was followed up by the Neo FreeRunner on 25 June 2008. On 2 April 2009, Openmoko suspended development of their third device, codenamed GTA03, to focus on the FreeRunner. In 2010, development of the GTA03 was continued by Golden Delicious Computers under the new codename GTA04, which includes major hardware revision, and the first unit was shipped on 10 October 2011. Unlike most other mobile phone platforms, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Environment
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows User (computing), users to Human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through graphical icon (computing), icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs (command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through Direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution User ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Interface Device
A human interface device or HID is a type of computer device usually used by humans that takes input from humans and gives output to humans. The term "HID" most commonly refers to the USB-HID specification. The term was coined by Mike Van Flandern of Microsoft when he proposed that the USB committee create a Human Input Device class working group. The working group was renamed as the Human Interface Device class at the suggestion of Tom Schmidt of DEC because the proposed standard supported bi-directional communication. HID standard The HID standard was adopted primarily to enable innovation in PC input devices and to simplify the process of installing such devices. Prior to the introduction of the HID concept, devices usually conformed to strictly defined protocols for mouse, keyboards and joysticks; for example, the standard mouse protocol at the time supported relative X- and Y-axis data and binary input for up to two buttons, with no legacy support. All hardware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Buffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor. In computing, a screen buffer is a part of computer memory used by a computer application for the representation of the content to be shown on the computer display. The screen buffer may also be called the video buffer, the regeneration buffer, or regen buffer for short. Screen buffers should be distinguished from video memory. To this end, the term off-screen buffer is also used. The information in the buffer typically consists of color values for every pixel to be shown on the display. Color values are commonly stored in 1-bit binary (monochrome), 4-bit palettized, 8-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' ( WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. , Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub, particularly for client–server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers. Java was originally de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalvik Virtual Machine
Dalvik is a discontinued process virtual machine#Process_virtual_machines, process virtual machine (VM) in the Android (operating system), Android operating system that executes applications written for Android. (Dalvik bytecode format is still used as a distribution format, but no longer at runtime in newer Android versions.) Dalvik was an integral part of the Android software stack in the (now unsupported) Android version history, Android versions Android KitKat, 4.4 "KitKat" and earlier, which were commonly used on mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers, and more in some devices such as smart TVs and wearables. Dalvik is open-source software, originally written by Dan Bornstein, who named it after the fishing village of Dalvík in Eyjafjörður, Iceland. Computer program, Programs for Android are commonly written in Java programming language, Java and compiled to bytecode for the Java virtual machine, Java Virtual Machine, which is then translated to Dalvik by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Package (installation)
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opkg
opkg (''open package management'') is a lightweight package management system based upon ipkg. It is written in C and resembles Advanced Package Tool (APT)/dpkg in operation. It is intended for use on embedded Linux devices and is used in this capacity in the OpenEmbedded and OpenWrt projects. Opkg was originally forked from ipkg by the Openmoko project. More recently, development of opkg has moved from its old Google Code repository to Yocto Project The Yocto Project is a Linux Foundation collaborative open source project whose goal is to produce tools and processes that enable the creation of Linux distributions for embedded and IoT software that are independent of the underlying architectu ... where it is actively maintained again. Opkg packages usually use either .ipk or .opk extension. References External links * Free package management systems Free software programmed in C Linux package management-related software Linux-only free software {{Linux-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenEmbedded
OpenEmbedded is a build automation framework and cross-compile environment used to create Linux distributions for embedded devices. The OpenEmbedded framework is developed by the OpenEmbedded community, which was formally established in 2003. OpenEmbedded is the recommended build system of the Yocto Project, which is a Linux Foundation workgroup that assists commercial companies in the development of Linux-based systems for embedded products. The build system is based on BitBake "recipes", which specify how a particular package is built but also include lists of dependencies and source code locations, as well as for instructions on how to install and remove a compiled package. OpenEmbedded tools use these recipes to fetch and patch source code, compile and link binaries, produce binary packages (ipk, deb, rpm), and create bootable images. Historically, OpenEmbedded's collection of recipes was stored in a single repository, and the metadata was structured in a form now called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matchbox (window Manager)
Matchbox is a free and open source window manager for the X Window System. It is mainly intended for embedded systems and differs from most other window managers in that it only shows one window at a time. It is used by Maemo on Nokia Internet Tablets, the Neo 1973 smartphone based on Openmoko, thVernier LabQuesthandheld data acquisition device for science education, as well as on the XO-1 XO-1 is a magnitude 11 G-type main-sequence star located approximately 536 light-years away in the constellation Corona Borealis. XO-1 has a mass and radius similar to the Sun. In 2006 the extrasolar planet An exoplanet or extras ... of the One Laptop Per Child Project. before being replaced by Metacity. Matchbox 2 Matchbox Window Manager II is a complete rewrite of the original m-w-m. It is in early stages of development. * See also * Comparison of window managers References External links * * * {{X desktop environments and window managers Embedded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlightenment (window Manager)
Enlightenment, also known simply as E, is a compositing window manager for the X Window System. Since version 20, Enlightenment is also a Wayland compositor. Enlightenment developers have referred to it as "the original eye-candy window manager." Enlightenment includes functions to provide a graphical shell and can be used in conjunction with programs written for GNOME or KDE. When used together with the Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL), Enlightenment can refer to an entire desktop environment. History The first version of Enlightenment was released by Rasterman ( Carsten Haitzler) in 1997. Version 0.17, also referred to as E17, was in development for 12 years starting in December 2000 until 21 December 2012 when it was officially released as stable. During the development period it was also referred to as DR17 (Development Release 17). It is a complete rewrite on DR16 and was designed to be a full-fledged desktop shell, based on the new Enlightenment Foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |