|
Open System Environment
Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties. This reference model is meant as an environment model, complementary to the POSIX architecture for open systems. It offers an extensible framework that allows services, interfaces, protocols, and supporting data formats to be defined in terms of nonproprietary specifications that evolve through open (public), consensus-based forums. This reference model served in the 1990s as a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architectures. In 1996 this reference model was standardized in the ISO/IEC TR 14252 titled "Information technology -- Guide to the POSIX Open System Environment (OSE)". History The development of the open-system environment reference m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open System Environment Reference Model
Open-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or ''OSE reference model'' (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties. This reference model is meant as an environment model, complementary to the POSIX architecture for open systems. It offers an extensible framework that allows services, interfaces, protocols, and supporting data formats to be defined in terms of nonproprietary specifications that evolve through open (public), consensus-based forums. This reference model served in the 1990s as a basic building block of several technical reference models and technical architectures. In 1996 this reference model was standardized in the ISO/IEC TR 14252 titled "Information technology -- Guide to the POSIX Open System Environment (OSE)". History The development of the open-system environment reference mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into the software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
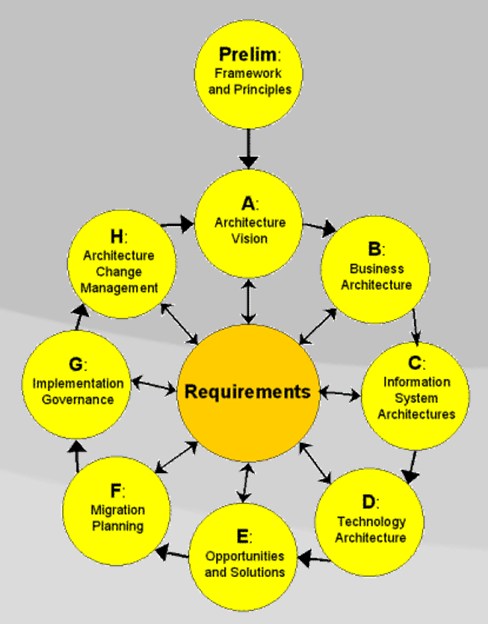
TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOGAF is a high-level approach to design. It is typically modeled at four levels: Business, Application, Data, and Technology. It relies heavily on modularization, standardization, and already existing, proven technologies and products. TOGAF was developed starting 1995 by The Open Group, based on United States Department of Defense's TAFIM and Capgemini's Integrated Architecture Framework (IAF). As of 2016, The Open Group claims that TOGAF is employed by 80% of Global 50 companies and 60% of Fortune 500 companies. Overview An architecture framework is a set of tools which can be used for developing a broad range of different architectures. It should: * describe a method for defining an information system in terms of a set of building bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAFIM
Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM) was a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture by and for the United States Department of Defense (DoD). TAFIM provided enterprise-level guidance for the evolution of the DoD Technical infrastructure. It identifies the services, standards, concepts, components, and configurations that can be used to guide the development of technical architectures that meet specific mission requirements.NHSITRC (2005)Consolidated References IT Planning and Management Guides, List of Resources. Last Updated: May 4, 2005. Accessed 12 Dec 2008. TAFIM has been developed by the United States Department of Defense from 1986 until 1999. Parallel in 1994 they started the development of the C4ISR Architecture Framework, which evolved into the Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) in the new millennium. TAFIM concepts are further developed in TOGAF, which first version in 1995 was based on the TAFIM framework. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
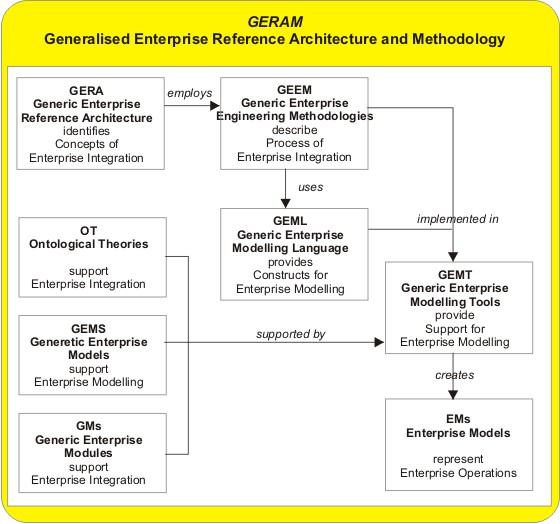
GERAM
Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering. J.G. Nell, NIST (1997).An Overview of GERAM ICEIMT'97 International Conference on Enterprise Integration Modelling Technology 1997. Updated 30 January 1997 This framework was developed in the 1990s by a joint task force of both the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC) and the International Federation of Information Processing (IFIP) on enterprise architectures for enterprise integration. The development started with the evaluation of then-existing frameworks for enterprise application integration, which was developed into an overall definition of a so-called "generalised architecture". P. Bernus, and L. Nemes (1994). "A Framework to Define a Generic Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology". In: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Architecture Framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models - typically matrices and diagrams - for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support. Overview Enterprise architecture regards the enterprise as a large and complex system or system of systems. To manage the scale and complexity of this system, an architectural framework provides tools and approaches that help architects abstract from the level of detail at which builders work, to bring enterprise design tasks into focus and produce valuable architecture description docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
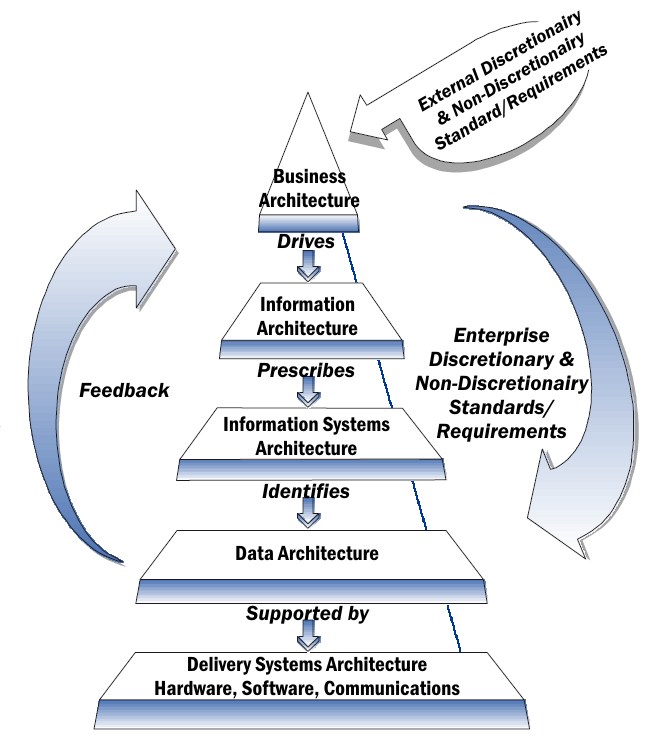
Technical Architecture
Information technology architecture is the process of development of methodical information technology specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of information technology notations, for example Unified Modeling Language (UML), within a coherent information technology architecture framework, following formal and informal information technology solution, enterprise, and infrastructure architecture processes. These processes have been developed in the past few decades in response to the requirement for a coherent, consistent approach to delivery of information technology capabilities. They have been developed by information technology product vendors and independent consultancies, such as for example the Open Group, based on real experiences in the information technology marketplace and collaboration amongst industry stakeholders. Best practice information technology architecture encourages the use of open technology standards and global technology interoperability. Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Stores
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development. A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term '' programmer'' is sometimes used as a synonym, but may also lack connotations of engineering education or skills. Engineering techniques are used to inform the software development process which involves the definition, implementation, assessment, measurement, management, change, and improvement of the software life cycle process itself. It heavily uses software configuration management which is about systematically controlling changes to the configuration, and maintaining the integrity and traceability of the configuration and code throughout the system life cycle. Modern processes use software versioning. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was seen as its own type of engineering. Additionally, the development of soft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)