|
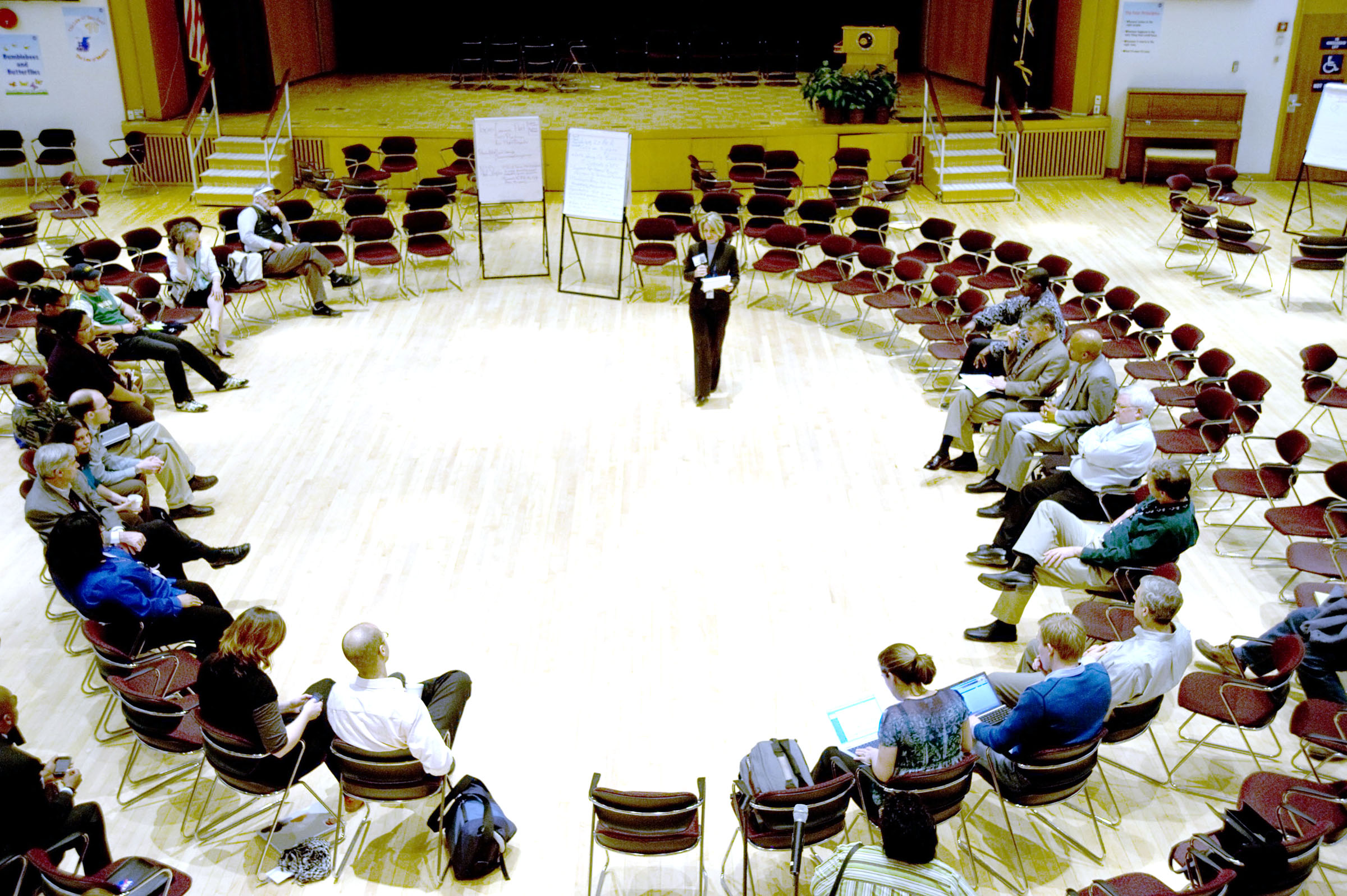
Open Space Technology
Open space technology (OST) is a method for organizing and running a meeting or multi-day conference where participants are invited to focus on a specific, important task or purpose. The agenda and schedule of presentations are partly or mostly unknown until people begin arriving. The scheduling of speakers, topics, and locations is created by people attending once they arrive. A debriefing document is created at the end of each OST meeting, summarizing what worked and what did not. Harrison Owen created the method in the early 1980s as an alternative to pre-planned conferences, where conference organizers predetermined speakers and time was often scheduled months in advance. OST instead relies on decisions made by participants once they are physically present at the live event venue. OST was among the top ten organizational development tools cited between 2004 and 2013. History The approach was originated by Harrison Owen, an Episcopal priest whose academic background and traini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Development
Organization development (OD) is the study and implementation of practices, systems, and techniques that affect organizational change. The goal of which is to modify a group's/organization's performance and/or culture. The organizational changes are typically initiated by the group's Stakeholder (corporate), stakeholders. OD emerged from human relations studies in the 1930s, during which psychologists realized that organizational structures and processes influence worker behavior and motivation. Organization Development allows businesses to construct and maintain a brand new preferred state for the whole agency. Key concepts of OD theory include: Organisation climate, organizational climate (the mood or unique "personality" of an organization, which includes attitudes and beliefs that influence members' collective behavior), organizational culture (the deeply-seated norms, values, and behaviors that members share) and organizational strategies (how an organization identifies p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tim O'Reilly
Timothy O'Reilly (born 6 June 1954) is an Irish-American author and publisher, who is the founder of O'Reilly Media (formerly O'Reilly & Associates). He popularised the terms open source and Web 2.0. Education and early life Born in County Cork, Ireland, Tim O'Reilly moved to San Francisco, California with his family when he was a baby. He has three brothers and three sisters. As a teenager, encouraged by his older brother Sean, O'Reilly became a follower of George Simon, a writer and adherent of the general semantics program. Through Simon, O'Reilly became acquainted with the work of Alfred Korzybski, which he has cited as a formative experience. In 1973, O'Reilly enrolled at Harvard College to study classics and graduated ''cum laude'' with a Bachelor of Arts degree in 1975. During O'Reilly's first year at Harvard, George Simon died in an accident. Career After graduating, O'Reilly completed an edition of Simon's ''Notebooks, 1965–1973''. He also wrote a well-received b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Decision-making
Group decision-making (also known as collaborative decision-making or collective decision-making) is a situation faced when individuals collectively make a choice from the alternatives before them. The decision is then no longer attributable to any single individual who is a member of the group. This is because all the individuals and social group processes such as social influence contribute to the outcome. The decisions made by groups are often different from those made by individuals. In workplace settings, collaborative decision-making is one of the most successful models to generate buy-in from other stakeholders, build consensus, and encourage creativity. According to the idea of synergy, decisions made collectively also tend to be more effective than decisions made by a single individual. In this vein, certain collaborative arrangements have the potential to generate better net performance outcomes than individuals acting on their own. Under normal everyday conditions, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of A Feather (computing)
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, a non-profit organization with local chapters around the world. Organization There is no membership in the IETF. Anyone can participate by signing up to a working group mailing list, or registering for an IETF meeting. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by working groups. Each working group normally has appointed two co-chairs (occasionally three); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open to all who want to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Of Hosting
“The Art of Hosting” is a method of participatory leadership for facilitating group processes, as used by a loose-knit community of practitioners. In their method, people are invited into structured conversation about matters they are concerned about while facilitators act as hosts. This community group understands “hosting” as a certain way of facilitation that is supposed to have the capacity of making emerge the collective intelligence that people possess. As an approach to facilitation, The Art of Hosting is focused on “improved, conscious, and kind ways of growing a capacity to support a deliberate wisdom, unique to being together,” and also relies on a specific attitude to process organization. The practitioners see this methodology of engagement as a way to bring people in complex, social systems into convergence on collective actions, with the participants discovering and proposing their own solutions. Approach The Art of Hosting is a specific approach and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GV (company)
GV Management Company, L.L.C. (file no. 4726690) is a venture capital investment arm of Alphabet Inc., founded by Bill Maris, that provides seed, venture, and growth stage funding to technology companies. Founded as Google Ventures in 2010, the firm has operated independently of Google, Alphabet's search and advertising division, since 2015. GV invests in startup companies in a variety of fields ranging from the Internet, software, and hardware to life science, healthcare, artificial intelligence, transportation, cyber security and agriculture. It has helped finance more than 300 companies that include Uber, Nest, Slack, and Flatiron Health. History The group was founded on March 31, 2010, with a $100 million capital commitment, by Bill Maris who also became GV's first CEO. In 2012, that commitment was raised to $300 million annually, and the fund has $2 billion under management. In 2014, the group announced $125 million to invest in promising European startups. By 2014, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Thinking
Design thinking refers to the set of Cognition, cognitive, strategic and practical procedures used by designers in the process of designing, and to the body of knowledge that has been developed about how people reason when engaging with design problems. Design thinking is also associated with prescriptions for the innovation of products and services within business and social contexts. Background Design thinking has a history extending from the 1950s and '60s, with roots in the study of design cognition and design methods. It has also been referred to as "designerly ways of knowing, thinking and acting" and as "designerly thinking". Many of the key concepts and aspects of design thinking have been identified through studies, across different design domains, of design cognition and design activity in both laboratory and natural contexts. The term ''design thinking'' has been used to refer to a specific cognitive style (thinking like a designer), a general theory of design (a way of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Sprint
A design sprint is a time-constrained, five-phase process that uses design thinking with the aim of reducing the risk when bringing a new product, service or a feature to the market. The process aims to help teams to clearly define goals, validate assumptions and decide on a product roadmap before starting development. It seeks to address Business strategy, strategic issues using interdisciplinary expertise, rapid Software prototyping, prototyping, and usability testing. This design process is similar to Sprint (software development), Sprints in an Agile software development, Agile development cycle. How it started There are multiple origins to the concept of mixing Agile software development, Agile and Design Thinking. The most popular was developed by a multi-disciplinary team working out of Google Ventures. The initial iterations of the approach were created by Jake Knapp, and popularised by a series of blog articles outlining the approach and reporting on its successes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BarCamp
BarCamp is an international network of user-generated conferences primarily focused on technology and the web. They are open, participatory workshop-events, the content of which is provided by participants. The first BarCamps focused on early stage web applications, and were related to open-source technologies, social software, and open data formats. The format has also been used for a variety of other topics, including public transit, health care, education, and political organizing. The BarCamp format has also been adapted for specific industries like banking, education, real estate and social media. History The name ''BarCamp'' is a playful allusion to the event's origins, with reference to the programmer slang term, foobar: BarCamp arose as an open-to-the-public alternative to Foo Camp, which is an annual invitation-only participant-driven conference hosted by Tim O'Reilly. The first BarCamp was held in Palo Alto, California, from August 19–21, 2005, in the offices o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episcopal Church (United States)
The Episcopal Church (TEC), also known as the Protestant Episcopal Church in the United States of America (PECUSA), is a member of the worldwide Anglican Communion, based in the United States. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is divided into nine Ecclesiastical provinces and dioceses of the Episcopal Church, provinces. The current presiding bishop of the Episcopal Church is Sean Rowe, Sean W. Rowe. In 2023, the Episcopal Church had 1,547,779 members. it was the 14th largest denomination in the United States. Note: The number of members given here is the total number of baptized members in 2012 (cf. #refBaptizedMembers2012, Baptized Members by Province and Diocese 2002–2013). In 2025, Pew Research Center, Pew Research estimated that 1 percent of the adult population in the United States, or 2.6 million people, self-identify as mainline Episcopalians. The church has declined in membership and Sunday attendance since the 1960s, particularly in the Northeastern Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FooCamp
Foo Camp is an annual hacker event hosted by publisher O'Reilly Media. Event O'Reilly describes it as "the wiki of conferences", where the program is developed by the attendees at the event, using big whiteboard schedule templates that can be rewritten or overwritten by attendees to optimize the schedule; this type of event is sometimes called an unconference. The event started as a joke between Tim O'Reilly and Sara Winge, O'Reilly's VP of Corporate Communications. Sara had always wanted to run a ''foo bar'', an open bar for ''Friends of O'Reilly'', at one of O'Reilly's conferences. That joke morphed into a brainstorm after the dot com bust left O'Reilly with much unused office space in its new buildings, creating the opportunity for Foo Camp. The first Foo Camp was held in October 2003, and had approximately 200 attendees. There was eventually a Foo Bar at the camp. Tim O'Reilly describes the goal of his company as "changing the world by spreading the knowledge of innovators. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconference
An unconference is a participant-driven meeting. The term "unconference" has been applied to a wide range of gatherings that try to avoid hierarchical aspects of a conventional conference, such as sponsored presentations and top-down organization. History According to Tim O'Reilly, a predecessor of an unconference was a gathering organized by Alexander von Humboldt in 1828, which had a reduced emphasis on formal speeches and instead emphasized informal connections. The term "unconference" first appeared in an announcement for the annual XML developers conference in 1998. Unconferences often use variations on Open Space Technology, the format/method developed by Harrison Owen in 1985. Owen's 1993 book ''Open Space Technology: a User's Guide'' discussed many of the techniques now associated with unconferences, although his book does not use that term. The term was used by Lenn Pryor when discussing BloggerCon (a series of conferences organized by Dave Winer and first he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |