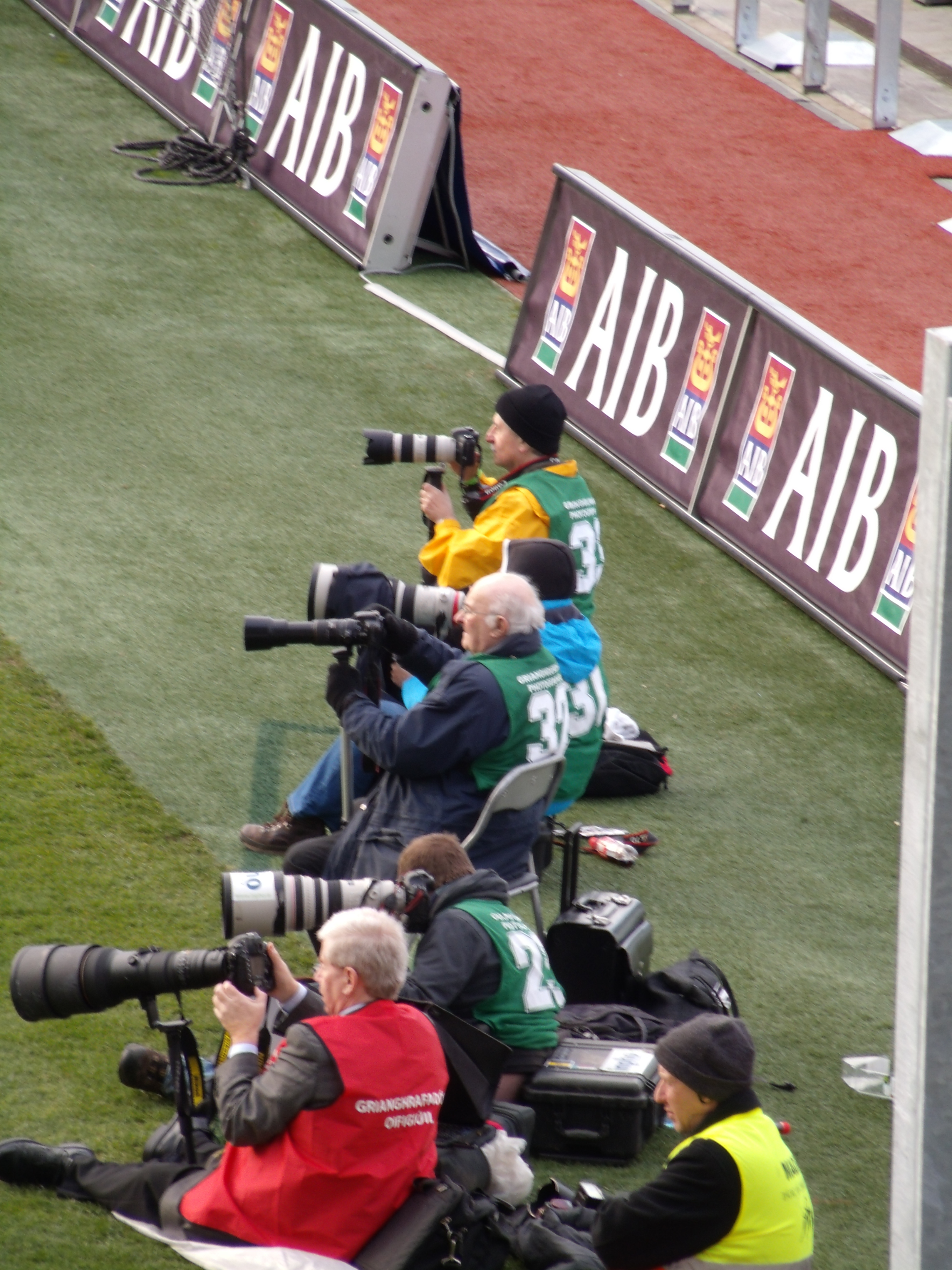|
Open School Of Journalism
The Open School of Journalism is an independent journalism school with branches in Berlin and New York City. OSJ is a member of the Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication (AEJMC), the International Communication Association (ICA, sections ''Journalism Studies'' and ''Public Relations''), and the Journalism Education Association (JEA). Certificate in Journalism OSJ offers a distance and online program in journalism with a recommended duration of one year which can be extended to two years. The course leads to a Certificate in Journalism according to ISCED Level 4. The journalism program is authorized by the ZFU, a German state agency for distance education. Curriculum The curriculum can be personalized by selecting course modules based on the student's prior experience and occupational objectives. The course offers modules in the following areas: * Journalistic working techniques: investigation/research, interviews, writing style for print media, radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journalism School
A journalism school is a school or department, usually part of an established university, where journalists are trained. 'J-School' is an increasingly used term for a journalism department at a school or college. Journalists in most parts of the world must first complete university-level training, which incorporates both technical skills such as research skills, interviewing technique and shorthand and academic studies in media theory, cultural studies and ethics. Africa In 2007, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) named what it terms the Potential Centres of Excellence in Journalism Training in Africa. After thorough research there were 12 journalism and media training institutions named on the list and they were not placed in any order. These twelve UNESCO Potential Centres of Excellence in Journalism Training in Africa are the Department of Journalism at the Tshwane University of Technology in Pretoria in South Africa (TUT),, Mass C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arts Journalism
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both highly dynamic and a characteristically constant feature of human life, they have developed into innovative, stylized and sometimes intricate forms. This is often achieved through sustained and deliberate study, training and/or theorizing within a particular tradition, across generations and even between civilizations. The arts are a vehicle through which human beings cultivate distinct social, cultural and individual identities, while transmitting values, impressions, judgments, ideas, visions, spiritual meanings, patterns of life and experiences across time and space. Prominent examples of the arts include: * visual arts (including architecture, ceramics, drawing, filmmaking, painting, photography, and sculpting), * literary arts (incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Journalism
Database journalism or structured journalism is a principle in information management whereby news content is organized around structured pieces of data, as opposed to news stories. See also Data journalism Communication scholar Wiebke Loosen defines database journalism as "supplying databases with raw material - articles, photos and other content - by using medium-agnostic Content management system, publishing systems and then making it available for different gadget, devices." History and development of database journalism Computer programmer Adrian Holovaty wrote what is now considered the manifesto of database journalism in September 2006. In this article, Holovaty explained that most material collected by journalists is "structured information: the type of information that can be sliced-and-diced, in an automated fashion, by computers". For him, a key difference between database journalism and traditional journalism is that the latter produces Article (publishing), articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comics Journalism
Comics journalism is a form of journalism that covers news or nonfiction events using the framework of comics, a combination of words and drawn images. Typically, sources are actual people featured in each story, and word balloons are actual quotes. The term "comics journalism" was coined by one of its most notable practitioners, Joe Sacco. Other terms for the practice include "graphic journalism,"Hodara, Susan"Graphic Journalism,"''Communication Arts'' (March 2020). "comic strip journalism", "cartoon journalism", "cartoon reporting", "comics reportage",Cavna, Michael"COMICS: Meet the man who’s creating a space for longform journalism — in graphic novel form,"''Washington Post'' (September 16, 2016). "journalistic comics", and "sketchbook reports".McGee, Kathleen"SPIEGELMAN SPEAKS: Art Spiegelman is the author of Maus for which he won a special Pulitzer in 1992. Kathleen McGee interviewed him when he visited Minneapolis in 1998,"''Conduit'' (1998). Visual narrative storytelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collaborative Journalism
Collaborative journalism is a growing practice in the field of journalism. One definition is "a cooperative arrangement (formal or informal) between two or more news and information organizations, which aims to supplement each organization’s resources and maximize the impact of the content produced." It is practiced by both professional and amateur reporters. It is not to be confused with citizen journalism. Further definition Collaborative journalism can take many forms. One way to categorize collaborations is by duration (either temporary or ongoing), or by the level of integration among collaborators (from no integration to top-level organizational integration). Most collaborations can be placed within a matrix defined by these two variables, as here: Depending on the system of collaboration, individuals may also provide feedback or vote on whether an article is newsworthy. A single collaborative news story, therefore, may encompass multiple authors, varying articles, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizen Journalism
Citizen journalism, also known as collaborative media, participatory journalism, democratic journalism, guerrilla journalism or street journalism, is based upon public citizens "playing an active role in the process of collecting, reporting, analyzing, and disseminating news and information."Bowman, S. and Willis, C.We Media: How Audiences are Shaping the Future of News and Information. 2003, ''The Media Center at the American Press Institute''. Similarly, Courtney C. Radsch defines citizen journalism "as an alternative and activist form of news gathering and reporting that functions outside mainstream media institutions, often as a response to shortcomings in the professional journalistic field, that uses similar journalistic practices but is driven by different objectives and ideals and relies on alternative sources of legitimacy than traditional or mainstream journalism". Jay Rosen offers a simpler definition: "When the people formerly known as the audience employ the press t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advocacy Journalism
Advocacy journalism is a genre of journalism that adopts a non-objective viewpoint, usually for some social or political purpose. Some advocacy journalists reject that the traditional ideal of objectivity is possible or practical, in part due to the perceived influence of corporate sponsors in advertising. Proponents of advocacy journalism feel that the public interest is better served by a diversity of media outlets with varying points of view, or that advocacy journalism serves a similar role to that of muckraking. Perspectives from advocacy journalists In an April 2000 address to the Canadian Association of Journalists, Sue Careless gave the following commentary and advice to advocacy journalists, which seeks to establish a common view of what journalistic standards the genre should follow."Advocacy journalism" by Sue Careless. ''The Interim, May 2000.'' Rules and advice for advocacy journalists. * Acknowledge your perspective up front. * Be truthful, accurate, and credible. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports Journalism
Sports journalism is a form of writing that reports on matters pertaining to sporting topics and competitions. Sports journalism started in the early 1800s when it was targeted to the social elite and transitioned into an integral part of the news business with newspapers having dedicated sports sections. The increased popularity of sports amongst the middle and lower class led to the more coverage of sports content in publications. The appetite for sports resulted in sports-only media such as ''Sports Illustrated'' and ESPN. There are many different forms of sports journalism, ranging from play-by-play and game recaps to analysis and investigative journalism on important developments in the sport. Technology and the internet age has massively changed the sports journalism space as it is struggling with the same problems that the broader category of print journalism is struggling with, mainly not being able to cover costs due to falling subscriptions. New forms of internet blog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Journalism
Science journalism conveys reporting about science to the public. The field typically involves interactions between scientists, journalists, and the public. Origins Modern science journalism dates back to ''Digdarshan'' (means showing the direction) that was an educational monthly magazine started publication in 1818 from Srirampore, Bengal, India. ''Digdarshan'' carried articles on different aspects of science, such as plants, steam boat, etc. It was available in Bengali, Hindi and English languages. One of the occasions an article was attributed to a "scientific correspondent" was "A Gale in the Bay of Biscay" by William Crookes which appeared in ''The Times'' on 18 January 1871, page 7. Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895) and John Tyndall (1820–1893) were scientists who were greatly involved in journalism and Peter Chalmers Mitchell (1864–1945) was Scientific Correspondent for ''The Times'' from 1918 to 1935.Gristock, J. (2006"J.G. Crowther, Kuhn and Systems of Mediatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Journalism
Political journalism is a broad branch of journalism that includes coverage of all aspects of politics and political science, although the term usually refers specifically to coverage of civil governments and political power. Political journalism aims to provide voters with the information to formulate their own opinion and participate in community, local or national matters that will affect them. According to Edward Morrissey in an opinion article from theweek.com, political journalism frequently includes opinion journalism, as current political events can be biased in their reporting. The information provided includes facts, its perspective is subjective and leans towards one viewpoint. Brendan Nyhan and John M. Sides argue that "Journalists who report on politics are frequently unfamiliar with political science research or question its relevance to their work". Journalists covering politics who are unfamiliar with information that would provide context to their stories can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Journalism
Medical journalism is news reporting (as opposed to peer-review publication) of medical news and features. Medical journalism is diverse, and reflects its audience. The main division is into (1) medical journalism for the general public, which includes medical coverage in general news publications and in specialty medical publications, and (2) medical journalism for doctors and other professionals, which often appears in peer-reviewed journals. The accuracy of medical journalism varies widely. Reviews of mass media publications have graded most stories unsatisfactory, although there were examples of excellence. Other reviews have found that most errors in mass media publications were the result of repeating errors in the original journal articles or their press releases. Some web sites, such as Columbia Journalism Review and Hippocrates Med Review, publish and review medical journalism. Sources Medical journalism can come from a variety of sources including: * Television news prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)