|
Ontology For Media Resources
Ontology for Media Resources is a W3C recommendation from 2012 that aims to define "a core set of metadata properties for media resources, along with their mappings to elements from a set of existing metadata formats"{{Cite web, url=https://www.w3.org/TR/mediaont-10/, title = Ontology for Media Resources 1.0 In addition to defining vocabulary terms to annotate multimedia objects, the document also provides a mapping to common multimedia metadata formats, including ID3, XMP, IPTC, Dublin core, OGG, Exif, Media RSS, and others, as well as mapping to several container formats, including 3GP, MP4, WebM, and others. See also Ontology for Media Resources 1.0 * Multimedia Web Ontology Language Machine interpretation of documents and services in Semantic Web environment is primarily enabled by (a) the capability to mark documents, document segments and services with semantic tags and (b) the ability to establish contextual relations bet ... References Bibliography * Van Deu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensible Metadata Platform
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets. XMP standardizes a data model, a serialization format and core properties for the definition and processing of extensible metadata. It also provides guidelines for embedding XMP information into popular image, video and document file formats, such as JPEG and PDF, without breaking their readability by applications that do not support XMP. Therefore, the non-XMP metadata have to be reconciled with the XMP properties. Although metadata can alternatively be stored in a sidecar file, embedding metadata avoids problems that occur when metadata is stored separately. The XMP data model, serialization format and core properties is published by the International Organization for Standardization as ISO 16684-1:2012 standard. Data model The defined XMP data model can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPTC
The International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC), based in London, United Kingdom, is a consortium of the world's major news agencies, other news providers and news industry vendors and acts as the global standards body of the news media. Currently more than 50 companies and organizations from the news industry are members of the IPTC, including global players like Associated Press (AP), Agence France-Presse (AFP), Deutsche Presse-Agentur (dpa), BBC, Getty Images, Press Association (PA), Reuters and ''The New York Times''. IPTC aims at simplifying the distribution of information. To achieve this technical standards are developed to improve the management and exchange of information between content providers, intermediaries and consumers. IPTC is committed to open standards and makes all standards freely available to its members and the wider community. The IPTC was established in 1965 by a group of news organisations including the Alliance Européenne des Agences de Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Core
220px, Logo image of DCMI, which formulates Dublin Core The Dublin Core, also known as the Dublin Core Metadata Element Set (DCMES), is a set of fifteen "core" elements (properties) for describing resources. This fifteen-element Dublin Core has been formally standardized as ISO 15836, ANSI/NISO Z39.85, and IETF RFC 5013. The Dublin Core Metadata Initiative (DCMI), which formulates the Dublin Core, is a project of the Association for Information Science and Technology (ASIS&T), a non-profit organization. The core properties are part of a larger set of DCMI Metadata Terms. "Dublin Core" is also used as an adjective for Dublin Core metadata, a style of metadata that draws on multiple Resource Description Framework (RDF) vocabularies, packaged and constrained in Dublin Core application profiles. The resources described using the Dublin Core may be digital resources (video, images, web pages, etc.) as well as physical resources such as books or works of art. Dublin Core metadata may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
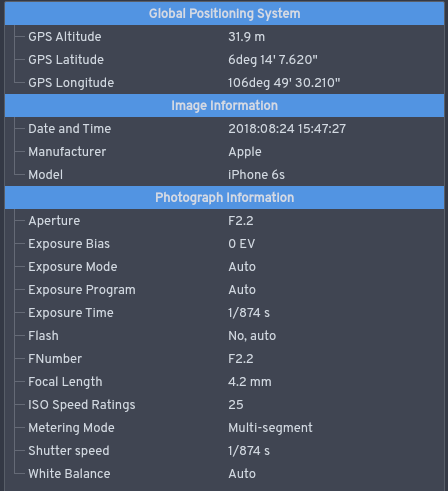
Exif
Exchangeable image file format (officially Exif, according to JEIDA/JEITA/CIPA specifications) is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smartphones), scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing encoding formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG lossy coding for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 (RGB or YCbCr) for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files (linear PCM or ITU-T G.711 μ-law PCM for uncompressed audio data, and IMA-ADPCM for compressed audio data). It does not support JPEG 2000 or GIF encoded images. This standard consists of the Exif image file specification and the Exif audio file specification. Background Exif is supported by almost all camera manufacturers. The metadata tags defined in the Exif standard cover a broad spectrum: * Camera settings: This includes static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media RSS
Media RSS (MRSS) is an RSS extension that adds several enhancements to RSS enclosures, and is used for syndicating multimedia files (audio, video, image) in RSS feeds. It was originally designed by Yahoo! and the Media RSS community in 2004, but in 2009 its development has been moved to the RSS Advisory Board. One example of enhancements is specification of thumbnails for each media enclosure, and the possibility to enclose multiple versions of the same content (e.g. different file formats). The format can be used for podcasting, which uses the RSS format as a means of delivering content to media-playing devices, as well as Smart TVs. Media RSS allows for a much more detailed description of the content to be delivered to the subscriber than the RSS standard. The standard is also used by content publishers to feed media files into Yahoo! Video Search, which is a feature of Yahoo! Search that allows users to search for video files. Applications supporting MRSS * Adobe Media Playe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 14
MPEG-4 Part 14 or MP4 is a digital multimedia container format most commonly used to store video and audio, but it can also be used to store other data such as subtitles and still images. Like most modern container formats, it allows streaming over the Internet. The only filename extension for MPEG-4 Part 14 files as defined by the specification is .mp4. MPEG-4 Part 14 (formally ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003) is a standard specified as a part of MPEG-4. Portable media players are sometimes advertised as "MP4 players", although some are simply MP3 players that also play AMV video or some other video format, and do not necessarily play the MPEG-4 Part 14 format. History MPEG-4 Part 14 is an instance of the more general ISO/IEC 14496-12:2004 (MPEG-4 Part 12: ISO base media file format) which is directly based upon the QuickTime File Format which was published in 2001. MPEG-4 Part 14 is essentially identical to the QuickTime File Format, but formally specifies support for Initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebM
WebM is an audiovisual media file format. It is primarily intended to offer a royalty-free alternative to use in the HTML5 video and the HTML5 audio elements. It has a sister project, WebP, for images. The development of the format is sponsored by Google, and the corresponding software is distributed under a BSD license. The WebM container is based on a profile of Matroska. WebM initially supported VP8 video and Vorbis audio streams. In 2013, it was updated to accommodate VP9 video and Opus audio. It also supports the new AV1 codec. Vendor support Software Native WebM support by Mozilla Firefox, Opera, and Google Chrome was announced at the 2010 Google I/O conference. Internet Explorer 9 requires third-party WebM software. In 2021, Apple released Safari 14.1 for macOS, which added native WebM support to the browser. , QuickTime does not natively support WebM, but does with a suitable third-party plug-in. In 2011, the Google WebM Project Team released plugins for Internet E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multimedia Web Ontology Language
Machine interpretation of documents and services in Semantic Web environment is primarily enabled by (a) the capability to mark documents, document segments and services with semantic tags and (b) the ability to establish contextual relations between the tags with a domain model, which is formally represented as ontology. Human beings use natural languages to communicate an abstract view of the world. Natural language constructs are symbolic representations of human experience and are close to the conceptual model that Semantic Web technologies deal with. Thus, natural language constructs have been naturally used to represent the ontology elements. This makes it convenient to apply Semantic Web technologies in the domain of textual information. In contrast, multimedia documents are perceptual recording of human experience. An attempt to use a conceptual model to interpret the perceptual records gets severely impaired by the semantic gap that exists between the perceptual media fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |