|
Onerahi Branch
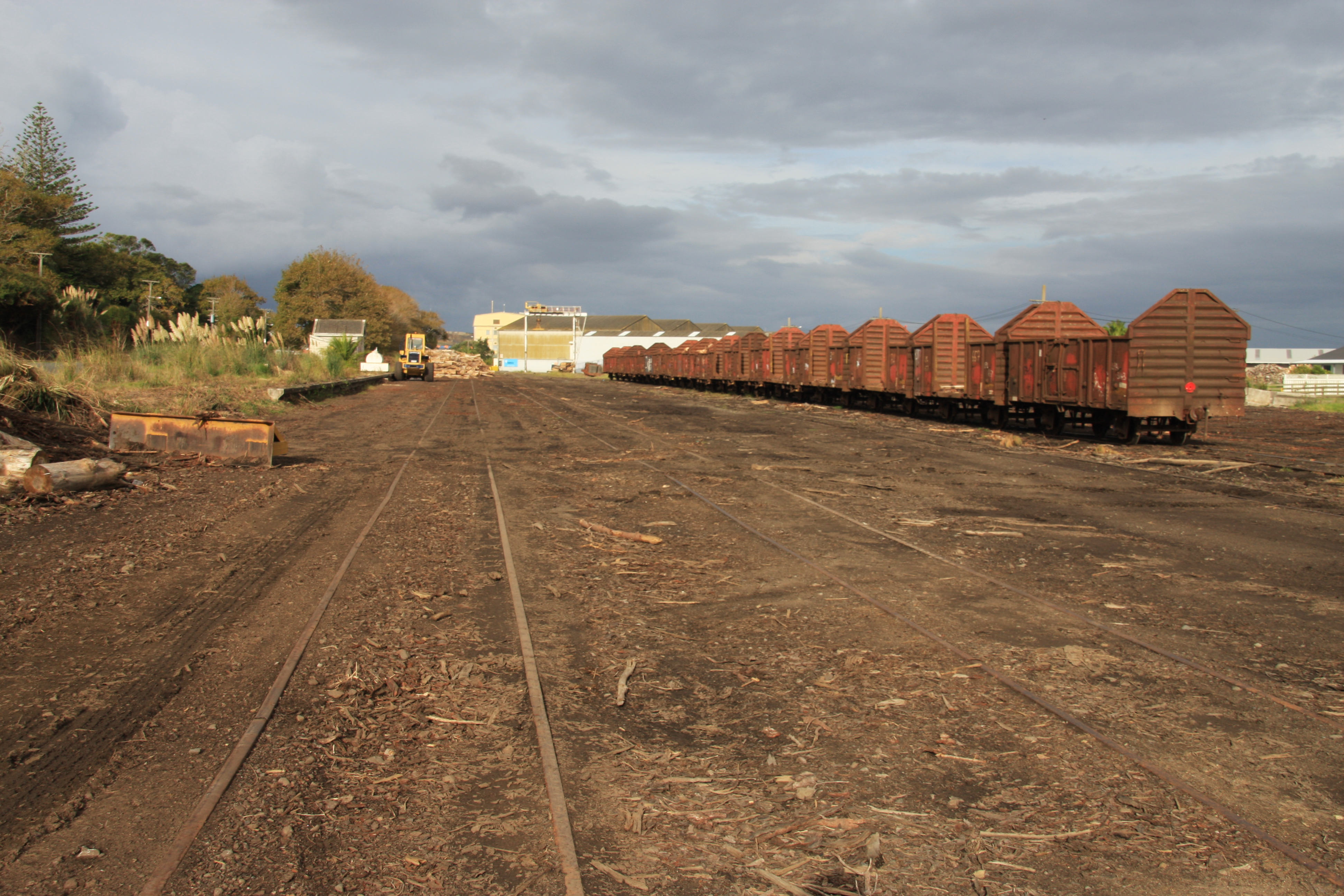
The Onerahi Branch, sometimes known as the Grahamstown Railway, was a branch line railway in the Northland Region of New Zealand. It operated from 1911 until 1933 and linked the city of Whangārei to the nearby harbour in Onerahi. History In the early 1880s, a wharf was established at Whangārei in the tidal part of the Hātea River, in the upper reaches of Whangārei Harbour. Roughly 20 years later the maintenance bill was rising and the wharf's inadequacies were being revealed as it was too shallow for some vessels to access. The deep-water wharves in nearby Onerahi were considerably more desirable, and in 1899 approval was granted to extend the railway from Whangārei to Onerahi. It took until July 1901 for construction to get underway, and in May 1902 a contract was let to build a bridge across the Hātea River. It was 323 metres long with a central lifting span, and completed in 1904. It was not long before the bridge was nicknamed the Gull Roost, for obvious r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas: Rapid transit A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid acceleration. It uses passenger railcars operating singly or in multiple unit trains on fixed rails. It operates on separate rights-of-way from which all other vehicular and foot traffic are excluded (i.e. is fully grade-separated from other traffic). It uses sophisticated signaling systems, and high platform loading. Originally, the term ''rapid transit'' was used in the 1800s to describe new forms of quick urban public transportation that had a right-of-way separated from street traffic. This set rapid transit apart from horsecars, trams, streetcars, omnibuses, and other forms of public transport. A variant of the term, ''mass rapid transit (MRT)'', is also used for metro systems in Southeast Asia and Taiwan. Though the term was almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S (for 'Screw Steamer') or PS (for 'Paddle Steamer'); however, these designations are most often used for steamships. The term ''steamboat'' is used to refer to smaller, insular, steam-powered boats working on lakes and rivers, particularly riverboats. As using steam became more reliable, steam power became applied to larger, ocean-going vessels. Background Limitations of the Newcomen steam engine Early steamboat designs used Newcomen atmospheric engine, Newcomen steam engines. These engines were large, heavy, and produced little power, which resulted in an unfavorable power-to-weight ratio. The Newcomen engine also produced a reciprocating or rocking motion because it was designed for pumping. The piston stroke was caused by a water jet i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines Opened In 1911
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In The Northland Region
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters *Rail (rail transport) A railway track (British English and UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, railroad ties (sleepers, ... or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film *Rails (film), ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini *Rail (1967 film), ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films *''Mirattu'' or ''Rail'', a Tamil-language film and its Telugu dub Magazines *Rail (magazine), ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical *Rails (magazine), ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts *The Rails, a British folk-rock band *Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology *Rails f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines In New Zealand
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsden Point Branch
The Marsden Point Branch is a branch line railway, which is to be built in the Northland Region of New Zealand's North Island. It will diverge from the North Auckland Line at Oakleigh, south of Whangārei, and serve Northport at Marsden Point. The proposal has existed since the 1970s and land for the rail corridor is being actively purchased. In October 2017, the new Labour–NZ First coalition government announced that it would spend $600 million on rehabilitating the North Auckland Line and building the branch at a cost of $200 million, the total works to cost $800 million. In June 2021 it was announced that the line would be built and was expected to take about 5 years. Early 20th century The Marsden Point proposal has been preceded by two earlier lines: the Onerahi Branch of 1911–33, and a proposed Waipu Branch that was partially built and then abandoned. The former was built for the same purpose as the Marsden Point Branch: better harbour access for Whangarei. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnellys Crossing Section
The Donnellys Crossing Section (later the Donnellys Crossing Branch), also known as the Kaihu Valley Railway or Kaihu Branch, was a railway line in Northland, New Zealand. Initially an isolated line of , it became a branch line when the Dargaville Branch was opened and connected it with the North Auckland Line and the rest of the national rail network in 1943. The branch was closed in 1959. The name of the line is often given as the ''Donnelly's'' Crossing Section or Branch. Although grammatically accurate, this is incorrect as the locality's name is officially recognised as ''Donnellys'' Crossing with no apostrophe. Construction The Kaihu Valley Railway Company Limited (KVRC) formed in 1882 under the provisions of the Railways Construction and Land Act of 1881 to build a railway linking lumber mills in the Kaihu Valley with the port in Dargaville. The Railways Construction and Land Act authorised settlers to build railways instead of waiting for the government to do it, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dargaville Branch
The Dargaville Branch is a branch line railway that leaves the North Auckland Line not far south of Whangarei and runs westward to Dargaville. Construction of this relatively short line took approximately two decades, and when it was completed, it linked the now closed Donnellys Crossing Section with the national rail network. The branch has been closed to all traffic since 2014 and is currently used by a tourist railcart operation. Construction The Dargaville Branch was built relatively late in comparison to most railway lines in New Zealand. Construction from Waiotira on the North Auckland Line commenced in 1922. Dargaville, however, was not reached for another eighteen years. The first twenty-two kilometres through unstable country took six years to build, with the line not opened to Kirikopuni until 15 May 1928. In January 1931, the line was open to Tangowahine, sixteen kilometres from Dargaville, but construction ceased for five years due to the Great Depression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northland Regional Council
The Northland Region ( mi, Te Tai Tokerau) is the northernmost of New Zealand's 16 local government regions. New Zealanders sometimes refer to it as the Winterless North because of its mild climate all throughout the year. The main population centre is the city of Whangārei, and the largest town is Kerikeri. At the 2018 New Zealand census, Northland recorded a population growth spurt of 18.1% since the previous 2013 census, placing it as the fastest growing region in New Zealand, ahead of other strong growth regions such as the Bay of Plenty (2nd with 15%) and Waikato (3rd with 13.5%). Geography The Northland Region occupies the northern 80% (265 km) of the 330 km Northland Peninsula, the southernmost part of which is in the Auckland Region. Stretching from a line at which the peninsula narrows to a width of just 15 km a little north of the town of Wellsford, Northland Region extends north to the tip of the Northland Peninsula, covering an area of 13,940&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupō District, and parts of Rotorua District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council. The region stretches from Coromandel Peninsula in the north, to the north-eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu in the south, and spans the North Island from the west coast, through the Waikato and Hauraki to Coromandel Peninsula on the east coast. Broadly, the extent of the region is the Waikato River catchment. Other major catchments are those of the Waihou, Piako, Awakino and Mokau rivers. The region is bounded by Auckland on the north, Bay of Plenty on the east, Hawke's Bay on the south-east, and Manawatū-Whanganui and Taranaki on the south. Waikato Region is the fourth largest region in the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
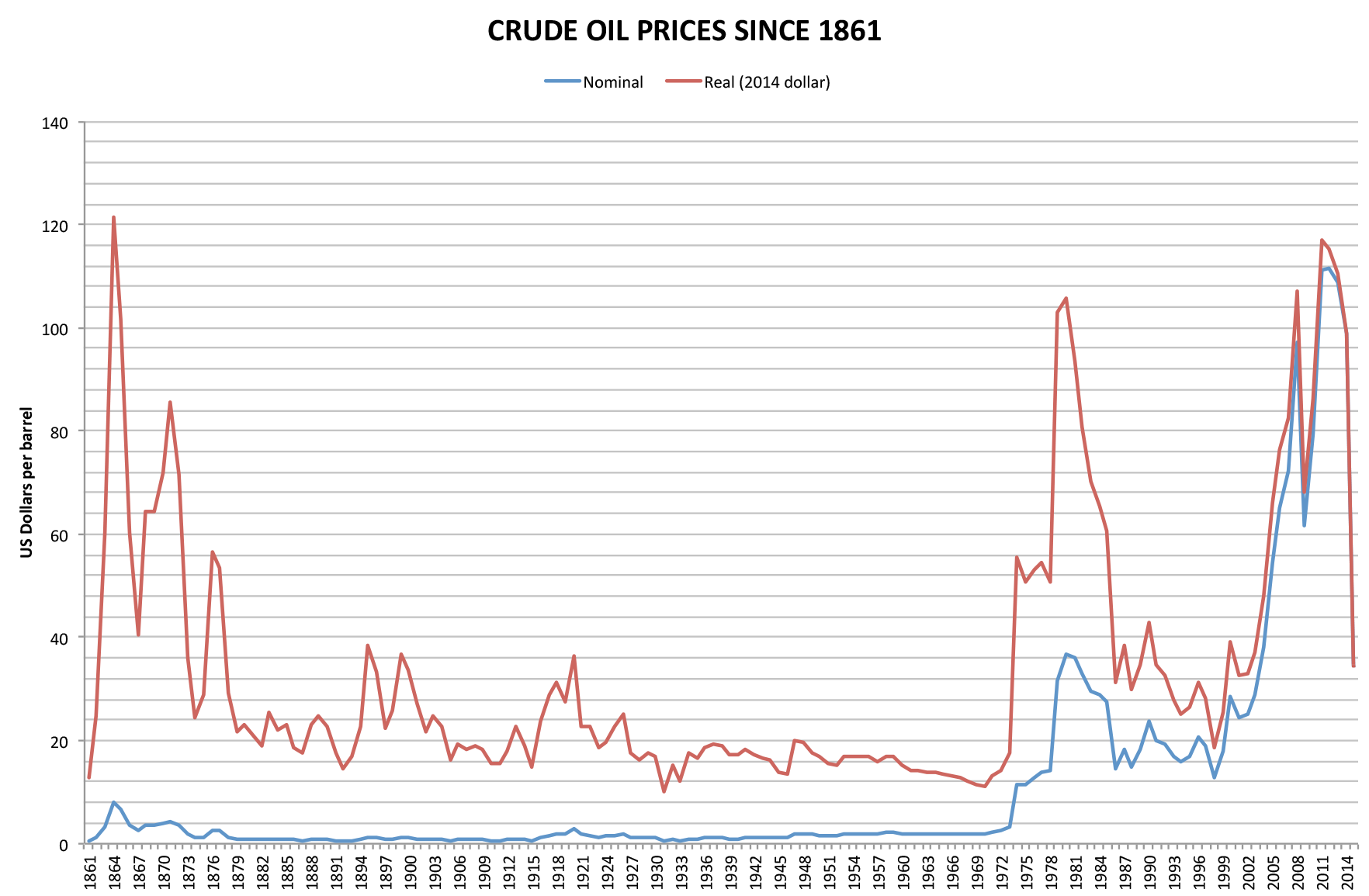
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsden Point
Marsden Point is a broad, flat peninsula that is the southern head of the Whangārei Harbour entrance on the east coast of Northland, New Zealand, southeast of the city of Whangārei. It is the location of Marsden Point Oil Refinery and the Northport cargo port. Geography The point is a broad, flat barrier spit, a peninsula of sand dunes, alluvium and estuarine deposits, that forms the southern head of the Whangārei Harbour entrance. It is southeast of Whangārei and around from Auckland's CBD. The flat, developed terrain contrasts starkly with the forest-covered peaks and pinnacles of the mountains across the channel on the northern head, including the 420-metre Mount Manaia. The point is at the northern end of the 22-kilometre long Bream Bay, which has mostly white-sand beaches. Easy access to beaches and recreational fishing grounds, with a climate of warm summers and mild winters, make the area a popular holiday spot and residential location. It is in the Whangarei D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |