|
Omo Sebua
The Omo sebua is a traditional house style of the Nias people from Nias island, Indonesia. They are built only for the houses of village's chiefs. Situated in the centre of a village, ''omo sebua'' are built on massive ironwood piles and have towering roofs. Nias culture, with former frequent inter-village warfare, has made the design of ''omo sebua'' impregnable to attack. The houses' sole access is through a narrow staircase with a small trap door above. The steeply pitched roofs can reach 16 metres (50 feet) in height. Apart from a strong defense against enemies, ''omo sebua'' have proven earthquake resistance. Background Nias ( id, Pulau Nias, Nias language: ''Tanö Niha'') is a rugged island 140 km off the mainland port of Sibolga at the western coast of Sumatra, separated by the Mentawai Strait. Nias is part of the North Sumatra province with Gunungsitoli as its administrative center. The island covers an area of 4,771 km²; the largest of its 131 chain of islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maison Nias
Maison (French for "house") may refer to: People * Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress * Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist * Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837 * Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Marshal of France and Minister of War * René Maison (1895–1962), Belgian operatic tenor * Rudolf Maison (1854–1904), German sculptor * Maison-Feyne, a commune in the Creuse department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine * Maison-Maugis, a former commune in the Orne department, Normandy * Maison-Ponthieu * Maison-Roland, a commune in the Somme department, Hauts-de-France * Maison-Rouge, a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department, Île-de-France Music Songs * "Maison", by Dreamcatcher from '' Apocalypse: Save Us'' See also * Valérie Grand'Maison (born 1988), Canadian Paralympic swimmer * Zoé De Grand Maison (born 1995), Canadian actress * Maisons (other) * Mason (other) Mason may refer to: Occupations * Mason, bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that salvation comes by divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, but disagree among themselves regarding the number of sacraments, the real presence of Christ in the Eucharist, and matters of ecclesiast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the mid-1600s. Galleons generally carried three or more masts with a lateen fore-and-aft rig on the rear masts, were carvel built with a prominent squared off raised stern, and used square-rigged sail plans on their fore-mast and main-masts. Such ships were the mainstay of maritime commerce into the early 19th century, and were often drafted into use as auxiliary naval war vessels—indeed, were the mainstay of contending fleets through most of the 150 years of the Age of Exploration—before the Anglo-Dutch wars brought purpose-built ship-rigged warships, ships of the line, that thereafter dominated war at sea during the remainder of the age of sail. Etymology The word ''galleon'' 'large ship' comes from Old French ''galion'' 'arme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
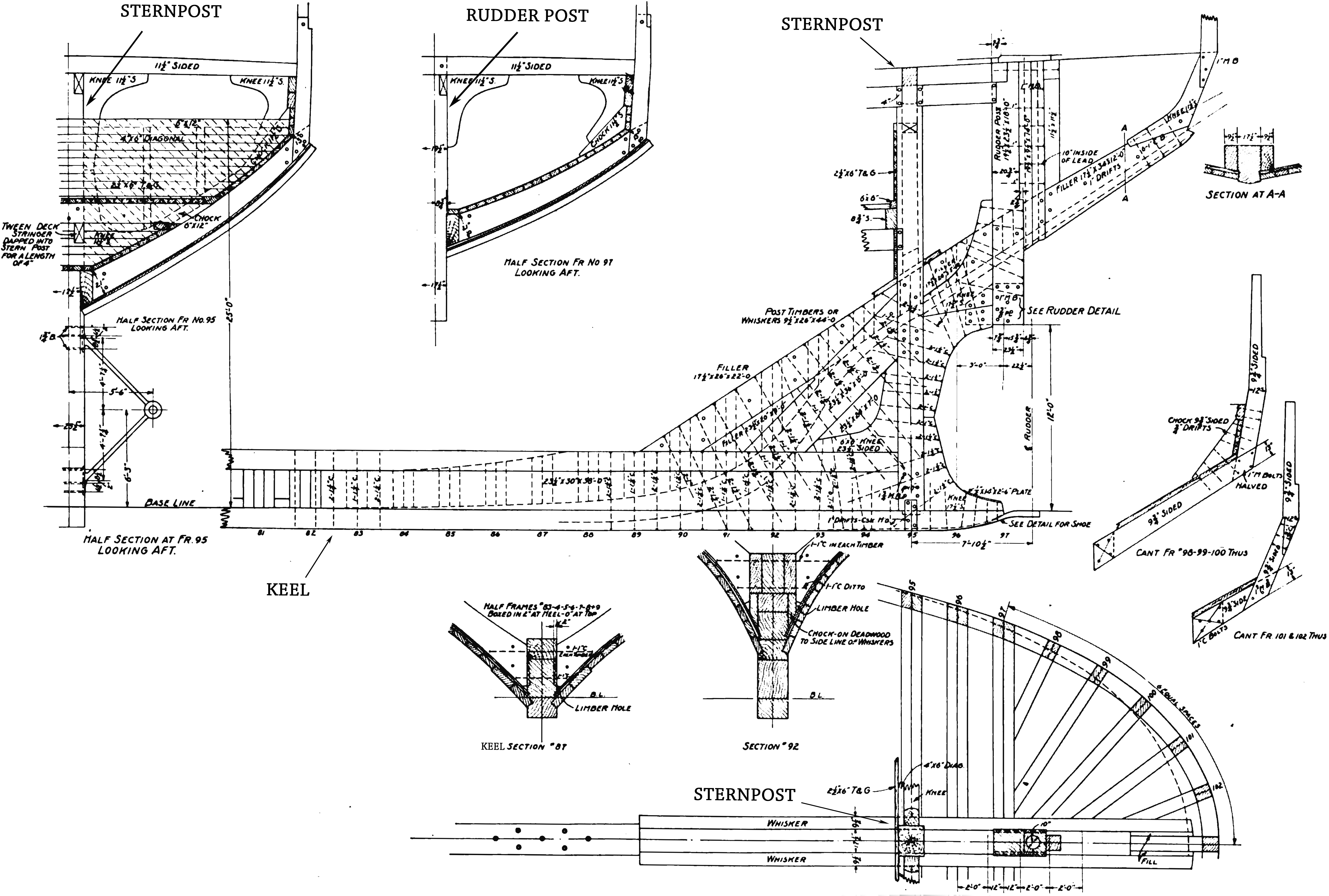
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eave
The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural style, such as the Chinese dougong bracket systems. Etymology and usage According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', ''eaves'' is derived from the Old English (singular), meaning "edge", and consequently forms both the singular and plural of the word. This Old English word is itself of Germanic origin, related to the German dialect ''Obsen'', and also probably to ''over''. The Merriam-Webster dictionary lists the word as ''eave'' but notes that it is "usually used in plural". Function The primary function of the eaves is to keep rain water off the walls and to prevent the ingress of water at the junction where the roof meets the wall. The eaves may also protect a pathway around the building from the rain, prevent erosion of the footin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesthetic concerns. The term gable wall or gable end more commonly refers to the entire wall, including the gable and the wall below it. Some types of roof do not have a gable (for example hip roofs do not). One common type of roof with gables, the gable roof, is named after its prominent gables. A parapet made of a series of curves (Dutch gable) or horizontal steps (crow-stepped gable) may hide the diagonal lines of the roof. Gable ends of more recent buildings are often treated in the same way as the Classic pediment form. But unlike Classical structures, which operate through trabeation, the gable ends of many buildings are actually bearing-wall structures. Gable style is also used in the design of fabric structures, with varying degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (structure)
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists Structural load, loads applied laterally to the beam's axis (an element designed to carry primarily axial load would be a strut or column). Its mode of Deflection (engineering), deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam's support points. The total effect of all the forces acting on the beam is to produce shear forces and bending moments within the beams, that in turn induce internal stresses, strains and deflections of the beam. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile (shape of cross-section), equilibrium conditions, length, and their material. Beams are traditionally descriptions of building or civil engineering structural elements, where the beams are horizontal and carry vertical loads. However, any structure may contain beams, for instance automobile frames, aircraft components, machine frames, and other mechanical or structural systems. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Slab
A stone slab is a big stone, flat and relatively thin, often of rectangular or almost rectangular form. They are generally used for paving floors, for covering walls or as headstones. In dolmens Most dolmen constructions were built using stone slabs of big dimensions. Their architecture often includes a corridor of access that can be constructed using stone slabs or dry stones. The burial chamber, with variable shapes (e.g. rectangular, polygonal, oval, circular) can also be preceded by an anteroom. In some dolmens, the entrance has a door cut into one or more vertical stone slabs. In construction The main applications of the slabs as material of construction are for pavings and in the construction of roofs. They can be employed for other uses, among them: * Balconies formed from a slab * Dry stone constructions of: walls, caves, rooms. * The base of some fireplaces are built with stone slabs (a big one or some smaller together). * In religious altars, the ''altar stone'' ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omo Sebua, South Nias, Indonesia
Omo or OMO may refer to: Geography Ethiopia * Omo River (Ethiopia), in southern Ethiopia is the largest Ethiopian river outside the Nile Basin and namesake for all the topics below * Omo Nada, one of the woredas in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia * South Omo Zone, a zone in the Ethiopian Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples' Region (SNNPR) * Omo National Park, Ethiopia * Omo Kibish Formation, an East African rock formation * Omo remains, a collection of hominid bones Elsewhere * Omo River(Yamanashi) * Omø, an island in Denmark *Omo River (Quebec), a tributary of Maicasagi River in Quebec, Canada People * Omo Osaghae (born 1988), American hurdler * Suleiman Omo (born 1985), Nigerian footballer for clubs in southeastern Europe Acronyms and codes * Open market operation, by the Federal Reserve or other central banks * Open Market Option allows someone approaching retirement to ‘shop around’ * One-man operation (OMO), a bus or tram on which the driver collects the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terraced House
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house ( UK) or townhouse ( US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings share side walls. In the United States and Canada they are also known as row houses or row homes, found in older cities such as Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Toronto. Terrace housing can be found throughout the world, though it is in abundance in Europe and Latin America, and extensive examples can be found in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, and Australia. The Place des Vosges in Paris (1605–1612) is one of the early examples of the style. Sometimes associated with the working class, historical and reproduction terraces have increasingly become part of the process of gentrification in certain inner-city areas. Origins and nomenclature Though earlier Gothic ecclesiastical examples, such as Vicars' Close, Wells, are known, the practice of building new domestic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruciform
Cruciform is a term for physical manifestations resembling a common cross or Christian cross. The label can be extended to architectural shapes, biology, art, and design. Cruciform architectural plan Christian churches are commonly described as having a cruciform architecture. In Early Christian, Byzantine and other Eastern Orthodox forms of church architecture this is likely to mean a tetraconch plan, a Greek cross, with arms of equal length or, later, a cross-in-square plan. In the Western churches, a cruciform architecture usually, though not exclusively, means a church built with the layout developed in Gothic architecture. This layout comprises the following: *An east end, containing an altar and often with an elaborate, decorated window, through which light will shine in the early part of the day. *A west end, which sometimes contains a baptismal font, being a large decorated bowl, in which water can be firstly, blessed (dedicated to the use and purposes of God) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobblestone
Cobblestone is a natural building material based on cobble-sized stones, and is used for pavement roads, streets, and buildings. Setts, also called Belgian blocks, are often casually referred to as "cobbles", although a sett is distinct from a cobblestone by being quarried or shaped to a regular form, whereas cobblestone is generally of a naturally occurring form and is less uniform in size. Use in roading Cobblestones are typically either set in sand or similar material, or are bound together with mortar. Paving with cobblestones allows a road to be heavily used all year long. It prevents the build-up of ruts often found in dirt roads. It has the additional advantage of immediately draining water, and not getting muddy in wet weather or dusty in dry weather. Shod horses are also able to get better traction on stone cobbles, pitches or setts than tarmac or asphalt. The fact that carriage wheels, horse hooves and even modern automobiles make a lot of noise when rolling ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |