|
Omnidens Amplus
''Omnidens amplus'', meaning "large all-tooth", is an extinct species of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian ''Pambdelurion'', indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, with which it may be synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of , ''Omnidens'' is suggested to have been the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. ''Omnidens'' fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales. Description ''Omnidens'' is only known from mouthparts. The preserved mouthparts would have formed a short muscular, potentially protrusible pharynx surrounded by circles of spiny sclerites, which were reminiscent of the scalids of priapulids, kinorhynchs, and loriciferans. The inside of the pharynx wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megadictyon
''Megadictyon'' is a genus of Cambrian lobopodian with similarities to ''Jianshanopodia'' and '' Siberion''. Occasionally mis-spelt ''Magadictyon''. Megadictyon is a large lobopodian, with body length (excluding appendages) possibly up to 20 centimeters in total. The head has a pair of robust frontal appendages associated with rows of spine and terminal claws. Underside the head is a radiodont-like mouthpart forming by multiple layers of plates and teeth-like structures. The trunk is wide and annulated, with a pair of well-developed lobopodous limbs on each body segment. Only 8 segment/limb pairs are countable in the incomplete fossil materials which lacking posterior region, so it may have had more (possibly up to 11 to 13) in nature. It also has pairs of digestive glands similar to those of basal arthropod Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Animals
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
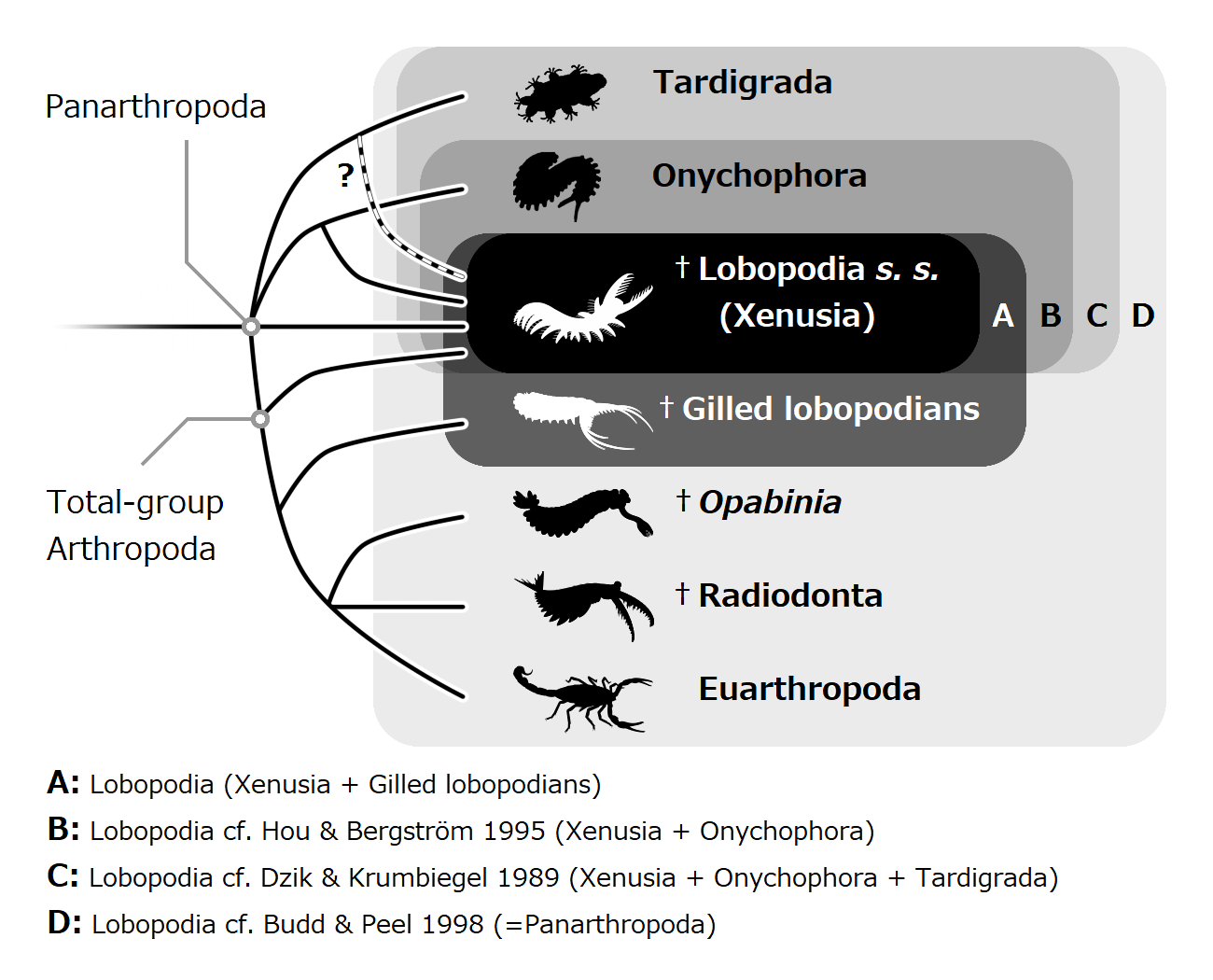
Lobopodian
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek language, Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as small carbonaceous fossil, carbonaceous or Small Shelly Fossils, mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 In Paleontology
Plants Ferns and fern allies Angiosperms Arthropods Insects Tetrapodomorphs Amphibians Newly named temnospondylians Newly named amphibians Ichthyosaurs Lepidosauromorphs Newly named basal lepidosauromorphs Newly named plesiosaurs Newly named squamates Turtles Archosauromorphs Newly named crurotarsans Newly named dinosaurs * Vickaryous, M K., 2006, New information on the cranial anatomy of Edmontonia rugosidens Gilmore, a Late Cretaceous nodosaurid dinosaur from Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta: JVP, v. 26, n. 4: 1011–1013. Data are courtesy of George Olshevky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs Synapsids Non-mammalian Mammals Trace fossils * The trace fossil genera ''Nihilichnus'' (''Nihilichnus nihilicus'' and ''Nihilichnus mortalis''), ''Machichnus'' (''Machichnus regularis,'' ''Machichnus multilineatus'', and ''Machichnus bohemicus'') and ''Brutalichnus'' (''Brutalichnus'' ''brutalis'') are described fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapeytoia
''Parapeytoia'' was a prehistoric arthropod that lived over 530 million years ago (Cambrian Stage 3) in the Maotianshan shales of prehistoric China. It was interpreted as an anomalocaridid (radiodont) with legs, but later studies reveal it was a megacheiran, a group of arthropods which are no longer thought to be closely related to the radiodonts. ''Parapeytoia'' is known from a few incomplete fossil materials with part of its ventral structures preserved. The frontmost appendages were a pair of great appendages that had a peduncle and 4 spines on each of them, a characteristic feature shared by other megacheirans such as ''Yohoia'' and '' Fortiforceps''. Behind the great appendages were 2 or 3 pairs of short appendages, and numerous pairs of well-developed biramous appendages, each formed by a basipod with spiny gnathobase, lobe-like exopod and leg-like endopod with 8 segments. A narrow sternite associated between each of those appendages. Some features originally interpret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peytoia
''Peytoia'' is a genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived in the Cambrian period, containing two species, ''Peytoia nathorsti'' from the Miaolingian of Canada and ''Peytoia infercambriensis'' from Poland, dating to Cambrian Stage 3. Its two frontal appendages had long bristle-like spines, it had no fan tail, and its short stalked eyes were behind its large head. 108 specimens of ''Peytoia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.21% of the community. ''Peytoia nathorsti'' and its junior synonym ''Laggania cambria'' played a major role in the discovery of the radiodont body plan. Initially interpreted as a jellyfish and a sea cucumber respectively, they were eventually shown to be the mouthparts and body of a single animal, which bore ''Anomalocaris''-like appendages. ''Peytoia infercambriensis'' is the geologically oldest known radiodont species. Classification ''Peytoia'' belongs to the clade Hurdiidae, and is closely related to the contemporary genus ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 In Paleontology
Plants Conifers Angiosperms Arthropods Insects Molluscs Bivalves Fishes Newly named bony fishes Archosauromorphs * Aff. Rebbachisaurus gastroliths documented.Calvo (1994). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. * The "Talkeetna Mountains Hadrosaur" specimen was discovered in a quarry being excavated for road material. The quarry is near the Glenn Highway, approximately 150 miles northeast of Anchorage. That fall, excavation began, and was resumed in the summer of 1996. Newly named pseudosuchians Newly named basal dinosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Birds Plesiosaurs * Plesiosaur gastroliths documented.Martin (1994). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. New taxa Pterosaurs New taxa Other diapsids New taxa Footnotes {{Reflist, , refs= "Introduction," in Pasche and May (2001); page 220. "Location and Geologic Setting," in Pasche and May (2001) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirius Passet
Sirius Passet is a Cambrian Lagerstätte in Peary Land, Greenland. The Sirius Passet Lagerstätte was named after the Sirius sledge patrol that operates in North Greenland. It comprises six places in Nansen Land, on the east shore of J.P. Koch Fjord in the far north of Greenland. It was discovered in 1984 by A. Higgins of the Geological Survey of Greenland. A preliminary account was published by Simon Conway Morris and others in 1987 and expeditions led by J. S. Peel and Conway Morris have returned to the site several times between 1989 and the present. A field collection of perhaps 10,000 fossil specimens has been amassed. It is a part of the Buen Formation. Age The fauna is inevitably compared to that of the Burgess Shale, although it is probably ten to fifteen million years older – vs. ) – and more closely contemporaneous with the fauna of the Maotianshan shales from Chengjiang, which are dated to . Preservation The preservation of the Sirius Passet is traditionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Stage 3
Cambrian Stage 3 is the still unnamed third stage of the Cambrian. It succeeds Cambrian Stage 2 and precedes Cambrian Stage 4, although neither its base nor top have been formally defined. The plan is for its lower boundary to correspond approximately to the first appearance of trilobites, about million years ago, though the globally asynchronous appearance of trilobites warrants the use of a separate, globally synchronous marker to define the base. The upper boundary and beginning of Cambrian Stage 4 is informally defined as the first appearance of the trilobite genera ''Olenellus'' or '' Redlichia'' around million years ago. Naming The International Commission on Stratigraphy has not officially named the 3rd stage of the Cambrian. The stage approximately corresponds to the "Atdabanian", which is used by geologists working in Siberia. Biostratigraphy The oldest trilobite known is ''Lemdadella'' which appears at the beginning of the '' Fallotaspis'' zone. The Cambrian radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euarthropoda
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |