|
Omega Process
The OMEGA process ("Only MEG Advantage") is a chemical process discovered by the Shell Global Solutions company that is used to produce ethylene glycol from ethylene. This process comprises two steps, the controlled oxidation of ethylene to ethylene oxide, and the net hydrolysis of ethylene oxide to monoethylene glycol (MEG). The first chemical plant using the OMEGA process was started in South Korea. Subsequent OMEGA plants have been started in Saudi Arabia and Singapore. Shell claims that this process, compared to conventional ones, does not produce higher glycols, uses less steam and water, and generates less waste. Ethylene oxidation To produce ethylene oxide, ethylene is oxidized with dioxygen in the presence of a silver catalyst. Some ethylene is over-oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, which is wasteful; early processes only gave ~ 65% selectivity for ethylene oxide as a result. In the OMEGA process, over-oxidation is reduced by including ethyl chloride as a moderator. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Global Solutions
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New York Stock Exchange. It is one of the oil and gas "supermajors" and by revenue and profits is consistently one of the largest companies in the world. Measured by both its own emissions, and the emissions of all the fossil fuels it sells, Shell was the ninth-largest corporate producer of greenhouse gas emissions in the period 1988–2015. Shell was formed in 1907 through the merger of Royal Dutch Petroleum Company of the Netherlands and The "Shell" Transport and Trading Company of the United Kingdom. The combined company rapidly became the leading competitor of the American Standard Oil and by 1920 Shell was the largest producer of oil in the world. Shell first entered the chemicals industry in 1929. Shell was one of the " Seven Sisters" whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, but it is toxic in high concentrations. Production Industrial routes Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation: This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the oligomers diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, and tetraethylene glycol. The separation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
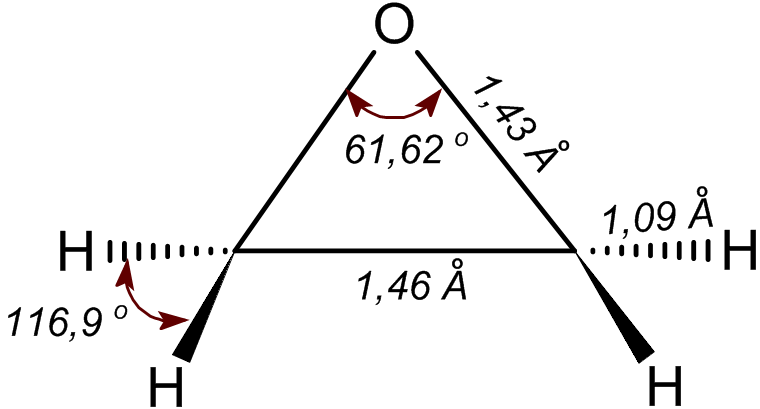
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward polyethylene, a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are connected by a double bond. All six atoms that comprise ethylene are coplanar. The H-C-H angle is 117.4°, close to the 120° for ideal sp² hybridized carbon. The molecule is also relatively weak: rota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered Ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, but it is toxic in high concentrations. Production Industrial routes Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation: This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the oligomers diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, and tetraethylene glycol. The separation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Chloride
Chloroethane, commonly known as ethyl chloride, is a chemical compound with chemical formula CH3CH2Cl, once widely used in producing tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive. It is a colorless, flammable gas or refrigerated liquid with a faintly sweet odor. Production Chloroethane is produced by hydrochlorination of ethylene: :C2H4 + HCl → C2H5Cl At various times in the past, chloroethane has also been produced from ethanol and hydrochloric acid, from ethane and chlorine, or from ethanol and phosphorus trichloride, but these routes are no longer economical. Some chloroethane is generated as a byproduct of polyvinyl chloride production. Uses Chloroethane is an inexpensive ethylating agent. It reacts with aluminium metal to give ethylaluminium sesquichloride, a precursor to polymers and other useful organoaluminium compounds. Chloroethane is used to convert cellulose to ethylcellulose, a thickening agent and binder in paints, cosmetics, and similar products. Like other chlorinated h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylene Glycol
Diethylene glycol (DEG) is an organic compound with the formula (HOCH2CH2)2O. It is a colorless, practically odorless, and hygroscopic liquid with a sweetish taste. It is a four carbon dimer of ethylene glycol. It is miscible in water, alcohol, ether, acetone, and ethylene glycol. DEG is a widely used solvent.Siegfried Rebsdat and Dieter Mayer "Ethylene Glycol" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.. It can be a contaminant in consumer products; this has resulted in numerous epidemics of poisoning since the early 20th century. Preparation DEG is produced by the partial hydrolysis of ethylene oxide. Depending on the conditions, varying amounts of DEG and related glycols are produced. The resulting product is two ethylene glycol molecules joined by an ether bond. "Diethylene glycol is derived as a co-product with ethylene glycol (MEG) and triethylene glycol. The industry generally operates to maximize MEG production. Ethylene glycol is by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(ethylene Glycol)
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH. Uses Medical uses * Pharmaceutical-grade PEG is used as an excipient in many pharmaceutical products, in oral, topical, and parenteral dosage forms. * PEG is the basis of a number of laxatives (as ''MiraLax''). Whole bowel irrigation with polyethylene glycol and added electrolytes is used for bowel preparation before surgery or colonoscopy. * PEG is used in medicines for treating disimpaction and maintenance therapy for children with constipation. * When attached to various protein medications or drug carriers, polyethylene glycol of suitable length slows down their clearance from the blood. * The possibility that PEG could be used to fuse axons is being exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Carbonate
Ethylene carbonate (sometimes abbreviated EC) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2O)2CO. It is classified as the Cyclic compound, cyclic carbonate ester of ethylene glycol and carbonic acid. At room temperature (25 °C) ethylene carbonate is a transparent crystalline solid, practically odorless and colorless, and somewhat soluble in water. In the liquid state (m.p. 34-37 °C) it is a colorless odorless liquid. JEFFSOL ETHYLENE CARBONATE catalog entry at www.huntsman.com. Accessed on 2010-02-18. Production and reactions Ethylene carbonate is produced by the reaction between ethylene oxide and carbon dioxide. The reaction is catalyzed by a variety of cations and complexes: :(CH2)2O + CO2[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi Chemicals
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries. Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 1870 to 1946. The company was disbanded during the occupation of Japan following World War II. The former constituents of the company continue to share the Mitsubishi brand and trademark. Although the group of companies participate in limited business cooperation, most famously through monthly "Friday Conference" executive meetings, they are formally independent and are not under common control. The four main companies in the group are MUFG Bank (the largest bank in Japan), Mitsubishi Corporation (a general trading company), Mitsubishi Electric and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (both diversified manufacturing companies). History The Mitsubishi company was established as a shipping firm by Iwasaki Yatarō (1834–1885) in 1870 under the name . I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Ester
In organic chemistry, a carbonate ester (organic carbonate or organocarbonate) is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is and they are related to esters (), ethers () and also to the inorganic carbonates. Monomers of polycarbonate (e.g. Makrolon or Lexan) are linked by carbonate groups. These polycarbonates are used in eyeglass lenses, compact discs, and bulletproof glass. Small carbonate esters like dimethyl carbonate, ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate are used as solvents, dimethyl carbonate is also a mild methylating agent. Structures Carbonate esters have planar OC(OC)2 cores, which confers rigidity. The unique O=C bond is short (1.173 Å in the depicted example), while the C-O bonds are more ether-like (the bond distances of 1.326 Å for the example depicted). Carbonate esters can be divided into three structural classes: acyclic, cyclic, and polymeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |