|
Olsalazine
Olsalazine is an anti-inflammatory medication used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. It is sold under the brand name Dipentum. Olsalazine itself is a pro-drug of mesalazine (5-aminosalicyclic acid or 5-ASA) and is not absorbed in the small intestine. Instead it continues through to the colon where it is cleaved into two molecules of 5-ASA by azoreductases produced by colonic bacteria. Olsalazine thus exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by its colonic breakdown into 5-ASA which inhibits cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase thereby reducing prostaglandin and leukotriene production. History Olsalazine gained Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 1990. Supply The drug is supplied by UCB Pharma. Research In 2006 the Australian biotech company Giaconda received a European patent for a combination therapy for treating constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome that uses olsalazine and the anti-gout drug colchicine Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer. The cause of UC is unknown. Theories involve immune system dysfunction, genetics, changes in the normal gut bacteria, and environmental factors. Rates tend to be higher in the developed world with some proposing this to be the result of less exposure to intestinal infections, or to a Western diet and lifestyle. The removal of the appendix at an early age may be protective. Diagnosis is typically by colonoscopy with tissue biopsies. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UCB (company)
UCB (Union Chimique Belge) is a multinational biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. UCB is an international company with revenue of €4.178 billion in 2016 which focuses primarily on research and development, specifically involving medications centered on epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and Crohn's disease. The company's efforts are focused on treatments for severe diseases treated by specialists, particularly in the fields of central nervous system (CNS) disorders (including epilepsy), inflammatory disorders (including allergy), and oncology. Every three years, the company presents the UCB Award under the patronage of the Queen Elisabeth Medical Foundation to promote neuroscience research. The winner of this award is selected by an independent scientific committee. History UCB was founded on 18 January 1928 by Emmanuel Janssen, a Belgian businessman. Initially focused on industrial chemicals (it was one of the first companies to distill ammonia fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giaconda (pharmaceutical Company)
Giaconda is an Australian biotechnology company headquartered in Sydney. The company was founded in 2004 to commercialise a number of drug combinations developed by Professor Thomas Borody, a Sydney-based gastroenterologist. History Giaconda was named after the Giaconda Vineyard and Winery, which is located nine kilometres southwest of Beechworth in the northeastern part of the Australian state of Victoria. That vineyard in turn derives its name from ''La Gioconda'', which is a nickname for the Mona Lisa of Leonardo da Vinci. Giaconda uses a stylised version of the Mona Lisa in its company logo. Giaconda's CEO is Mr Patrick McLean, a Canadian who was previously Senior Vice-President European Commercial Operations of the Montreal-based Axcan Pharma. Giaconda was a public company whose stock was traded on the Australian Stock Exchange under the stock code GIA. The company completed an initial public offering in September 2005, issuing 12 million shares at 50 Australian cents ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work (absenteeism) or reduced productivity at work (presenteeism). Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.The cited review is based on sources ranging from 1988 to 2001 and is probably biased relative to a more recent research. The causes of IBS may well be multi-factorial. Theories include combinations of "gut–brain axis" problems, alterations in gut motility, visceral hypersensitivity, infections including small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, neurotransmitters, genetic factors, and food sensitivity. Onset may be triggered by an intestinal infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensity in less than 12 hours. The joint at the base of the big toe is affected in about half of cases. It may also result in tophi, kidney stones, or kidney damage. Gout is due to persistently elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. This occurs from a combination of diet, other health problems, and genetic factors. At high levels, uric acid crystallizes and the crystals deposit in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues, resulting in an attack of gout. Gout occurs more commonly in those who: regularly drink beer or sugar-sweetened beverages; eat foods that are high in purines such as liver, shellfish, or anchovies; or are overweight. Diagnosis of gout may be confirmed by the presence of crystals in the joint fluid or in a deposit outsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout and Behçet's disease. In gout, it is less preferred to NSAIDs or steroids. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis and familial Mediterranean fever. Colchicine is taken by mouth. Colchicine has a narrow therapeutic index, so overdosing is a significant risk. Common side effects of colchicine include gastrointestinal upset, particularly at high doses. Severe side effects may include low blood cells and rhabdomyolysis, and the medication can be deadly in overdose. Whether colchicine is safe for use during pregnancy is unclear, but its use during breastfeeding appears to be safe. Colchicine works by decreasing inflammation via multiple mechanisms. Colchicine, in the form of the autumn crocus (''Colchicum autumnale''), has been used as early as 1500 BC to treat joint swelling. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1961. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 241st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bowel dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
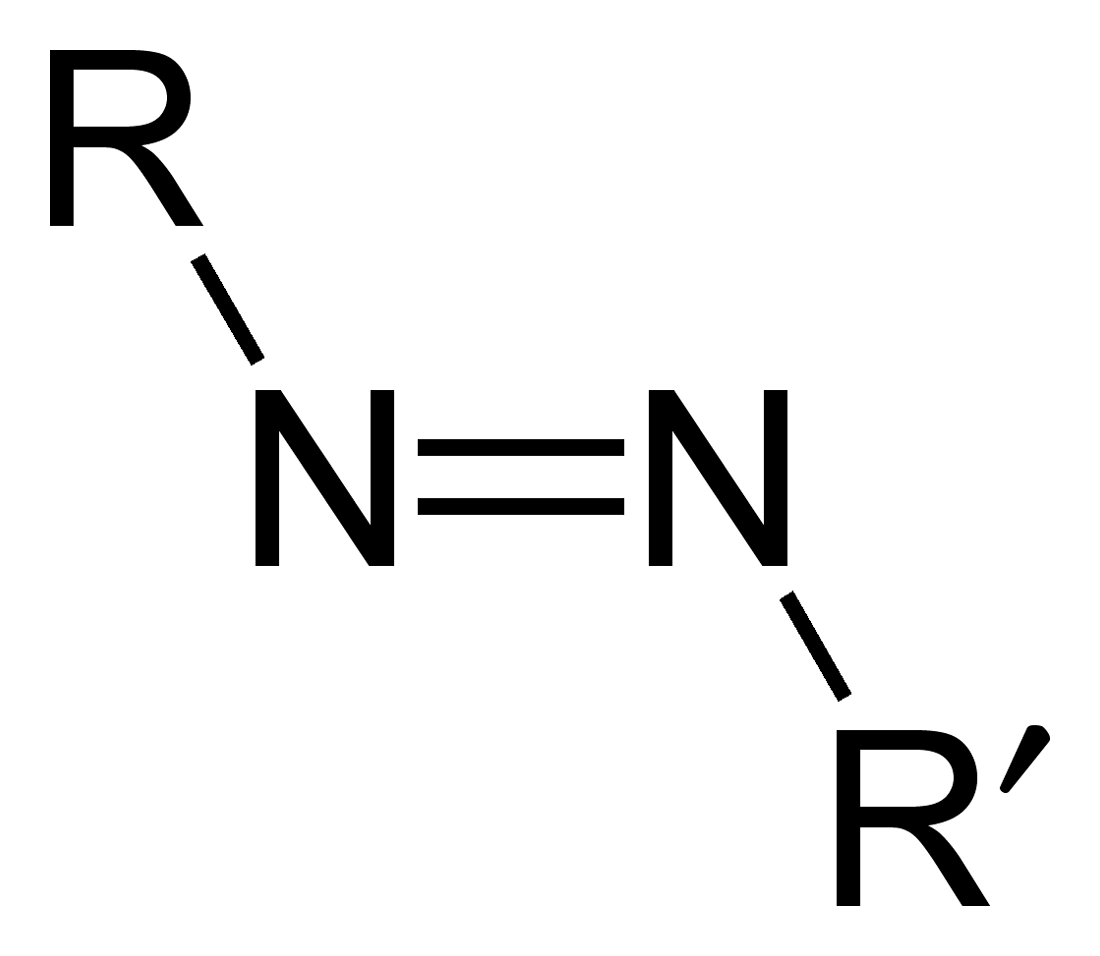
Azo Compounds
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene." The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic substitution reaction where an aryl diazonium cation is attacked by another aryl ring, especially those substituted with electron-donating groups: :ArN2+ + Ar'H -> ArN=NAr' + H+ Since diazoniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.png)