|
Olduvai Hominid 8
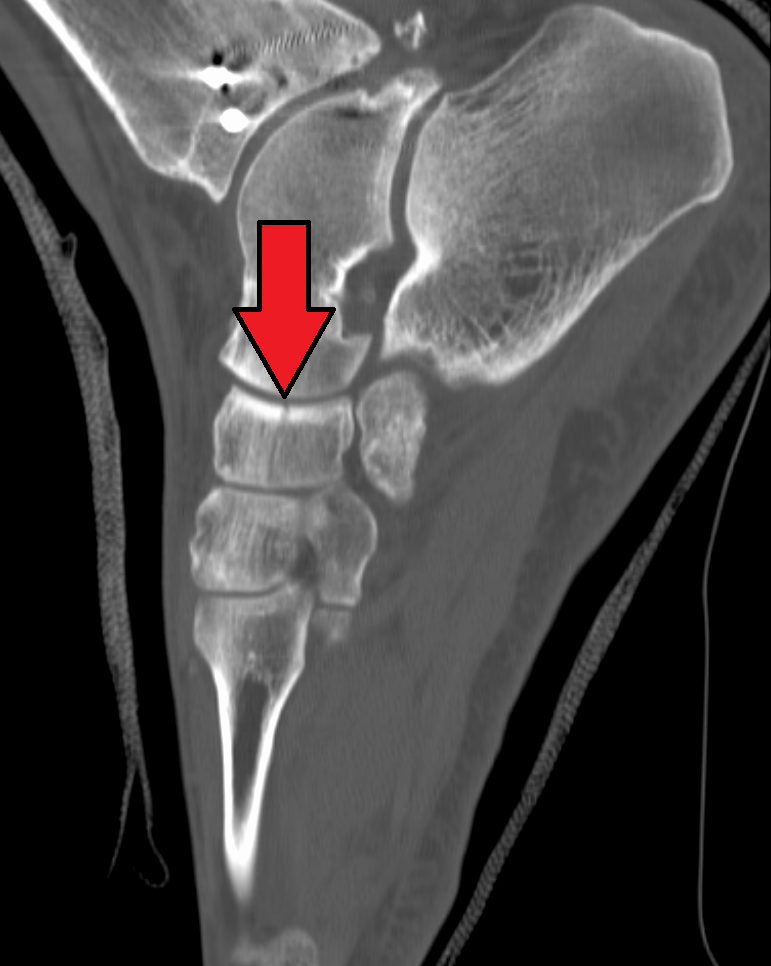
Olduvai Hominid number 8 (OH 8) is a fossilized foot of an early hominin found in Olduvai Gorge by Louis Leakey in the early 1960s. Kidd et al. (1996) argued that the fossil assemblage exhibits both ape and human characteristics. The lateral side (i.e. the outside of the foot) contains human-like characteristics while the medial side (i.e. the side towards the midline) contains ape-like features proximally, and human-like features distally. Specifically, the cuboid (laterally) is human-like, the talus and navicular (medially) are ape-like, and the medial cuneiform (medially), is human-like. This may be looked upon as a missing link in terms of mid-tarsal joint function. Later fossil finds, as exemplified by the so-called "Little Foot" (Stw573 complement this finding (Kidd & Oxnard 2004). Stw573 is a medial column assemblage, consisting of a talus, navicular, medial cuneiform and a first metatarsal stub. The three hindfood bones present a pattern consistent with those of the OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly contested, with many researchers recommending it be synonymised with '' Australopithecus africanus'', the only other early hominin known at the time, but ''H. habilis'' received more recognition as time went on and more relevant discoveries were made. By the 1980s, ''H. habilis'' was proposed to have been a human ancestor, directly evolving into '' Homo erectus'' which directly led to modern humans. This viewpoint is now debated. Several specimens with insecure species identification were assigned to ''H. habilis'', leading to arguments for splitting, namely into "''H. rudolfensis''" and "'' H. gautengensis''" of which only the former has received wide support. Like contemporary ''Homo'', ''H. habilis'' brain size generally varied from . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the cuneiform lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Sediba
''Australopithecus sediba'' is an extinct species of australopithecine recovered from Malapa Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa. It is known from a partial juvenile skeleton, the holotype MH1, and a partial adult female skeleton, the paratype MH2. They date to about 1.98 million years ago in the Early Pleistocene, and coexisted with ''Paranthropus robustus'' and ''Homo ergaster'' / ''Homo erectus''. Malapa is interpreted as having been a natural death trap, the base of a long vertical shaft which creatures could accidentally fall into. ''A. sediba'' was initially described as being a potential human ancestor, and perhaps the progenitor of ''Homo'', but this is contested and it could also represent a late-surviving population or sister species of '' A. africanus'' which had earlier inhabited the area. MH1 has a brain volume of about 420–440 cc, similar to other australopithecines. The face of MH1 is strikingly similar to ''Homo'' instead of other australopithecines, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal Bones
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head (distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedge-shaped, articulating proximally with the tarsal bones, and by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Foot
"Little Foot" (Stw 573) is the nickname given to a nearly complete Australopithecus fossil skeleton found in 1994–1998 in the cave system of Sterkfontein, South Africa. Originally nicknamed "little foot" in 1995 when four ankle bones in a museum collection were sufficient to ascertain that the individual had been able to walk upright, the remainder of the skeleton was, subsequently, located in the cave from which the ankle bones had been collected. Because the bones were completely embedded in concrete-like rock, their extremely difficult and tedious extraction took around 15 years. The bones proved to be the most complete skeleton of the early hominin lineage leading to humans, with 90% of the body being recovered. Dating of the specimen has proved controversial, with estimates ranging from 2.2 to 3.5 million years old, and its taxonomic placement is likewise disputed. Discovery Four ankle bones of this specimen were collected in 1980 but were unidentified among numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals. Human anatomy The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the strongly concave proximal articular surface. The term ''navicular bone'' or ''hand navicular bone'' was formerly used for the scaphoid bone, one of the carpal bones of the wrist. The navicular bone in humans is located on the medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the talus, distally with the three cuneiform bones, and laterally with the cuboid. It is the last of the foot bones to start ossification and does not tend to do so until the end of the third year in girls and the beginning of the fourth year in boys, although a large range of variation has been reported. The tibialis posterior is the only muscle that attaches to the navicular bone. The main portion of the muscle inserts into the tuberosity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olduvai Gorge
The Olduvai Gorge or Oldupai Gorge in Tanzania is one of the most important paleoanthropology, paleoanthropological localities in the world; the many sites exposed by the gorge have proven invaluable in furthering understanding of early human evolution. A steep-sided ravine in the Gregory Rift, Great Rift Valley that stretches across East Africa, it is about long, and is located in the eastern Serengeti Plains within the Ngorongoro Conservation Area in the Olbalbal ward located in Ngorongoro District of Arusha Region, about from Laetoli, another important archaeological locality of early human occupation. The British/Kenyan paleoanthropologist-archeologist team of Mary Leakey, Mary and Louis Leakey established excavation and research programs at Olduvai Gorge that achieved great advances in human knowledge and are world-renowned. The site is registered as one of the National Historic Sites of Tanzania. The gorge takes its name from the Maasai language, Maasai word ''oldupai'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the lateral and medial malleoli) that articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of its surface area covered by articular cartilage. It is also unusual in that it has a retrograde blood supply, i.e. arterial blood enters the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
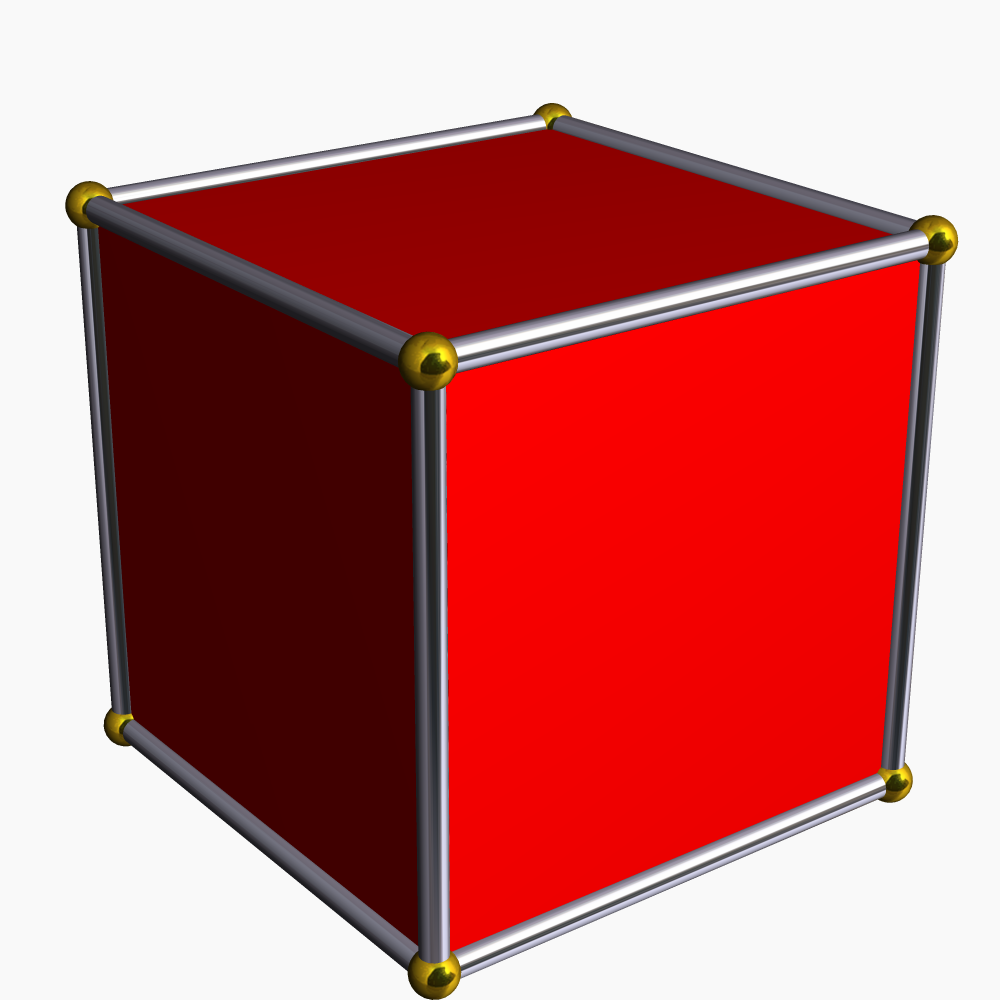
Cuboid
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. Cuboid means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a cube. In mathematical language a cuboid is a convex polyhedron, whose polyhedral graph is the same as that of a cube. Special cases are a cube, with 6 squares as faces, a rectangular prism, rectangular cuboid or rectangular box, with 6 rectangles as faces, for both, cube and rectangular prism, adjacent faces meet in a right angle. General cuboids By Euler's formula the numbers of faces ''F'', of vertices ''V'', and of edges ''E'' of any convex polyhedron are related by the formula ''F'' + ''V'' = ''E'' + 2. In the case of a cuboid this gives 6 + 8 = 12 + 2; that is, like a cube, a cuboid has 6 faces, 8 vertices, and 12 edges. Along with the rectangular cuboids, any parallelepiped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)