|
Old Uyghur Language
Old Uyghur () was a Turkic language which was spoken in Qocho from the 9th–14th centuries and in Gansu. History The Old Uyghur language evolved from Old Turkic after the Uyghur Khaganate broke up and remnants of it migrated to Turfan, Qomul (later Hami) and Gansu in the 9th century. The Uyghurs in Turfan and Qomul founded Qocho and adopted Manichaeism and Buddhism as their religions, while those in Gansu first founded the Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom and became subjects of the Western Xia; and their descendants are the Yugur. The Kingdom of Qocho survived as a client state of the Mongol Empire but was conquered by the Muslim Chagatai Khanate which conquered Turfan and Qomul and Islamisized the region. The Old Uyghur language then became extinct in Turfan and Qomul. The ''modern'' Uyghur language is not descended from Old Uyghur; rather, it is a descendant of the Karluk languages spoken by the Kara-Khanid Khanate, in particular the ''Xākānī'' language described by Mahm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Khaganate
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, 𐱃𐰆𐰴𐰕:𐰆𐰍𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Toquz Oγuz budun, Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that existed for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. They were a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur () nobility, referred to by the Chinese as the ''Jiu Xing'' ("Nine Clans"), a calque of the name '' Toquz Oghuz'' or ''Toquz Tughluq''. History Rise In 657, the Western Turkic Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty, after which the Uyghurs defected to the Tang. Prior to this the Uyghurs had already shown an inclination towards alliances with the Tang when they fought with them against the Tibetan Empire and Turks in 627. In 742, the Uyghurs, Karluks, and Basmyls rebelled against the Second Turkic Khaganate. In 744, the Basmyls captured the Turk capital of Ötüken and killed the reigning Özmiş Khagan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; "taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele Of Sulaiman
The Stele of Sulaiman is a Yuan Dynasty stele that was erected in 1348 to commemorate the benefactors and donors to a Buddhist temple at the Mogao Caves southeast of Dunhuang in Gansu, China. The principal benefactor is named as Sulaiman (), Prince of Xining (died 1351). The stele, which is now held at the Dunhuang Academy, is renowned for an inscription of the Buddhist ''mantra'' ''Om mani padme hum'' in six different scripts. Another stele, commemorating the restoration of the Huangqing Temple () in 1351 by Sulaiman was found at the same location as the 1348 stele. Discovery The two steles were first recorded by the French explorer, Charles Eudes Bonin (1865–1929), during an expedition to western China from 1898 to 1900. When Aurel Stein visited Dunhuang in 1900–1901 he found both steles outside a shrine next to Cave 96, the home of a colossal Buddha statue, 35.5 m in height. Stein supposed that the steles originally belonged in the cave of the colossal Buddha, and that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Platform At Juyong Pass
The Cloud Platform at Juyongguan () is a mid-14th-century architectural feature situated in the Guangou Valley at the Juyongguan Pass of the Great Wall of China, in the Changping District of Beijing Municipality, about northwest of central Beijing. Although the structure looks like a gateway, it was originally the base for three white dagobas or stupas, with a passage through it, a type of structure known as a "crossing street tower" (). The platform is renowned for its Buddhist carvings and for its Buddhist inscriptions in six languages. The Cloud Platform was the 98th site included in the first batch of 180 Major Historical and Cultural Sites Protected at the National Level as designated by the State Council of China in April 1961. History The platform was built between 1342 and 1345, during the reign of Emperor Huizong of the Yuan Dynasty, by imperial command. It was part of the Buddhist Yongming Baoxiang Temple (), which was situated at the Juyongguan Pass northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunhuang Manuscripts
Dunhuang manuscripts refer to a wide variety of religious and secular documents (mostly manuscripts, but also including some woodblock-printed texts) in Chinese and other languages that were discovered at the Mogao Caves of Dunhuang, China, during the 20th century. The majority of the surviving texts come from a large cache of documents produced between the late 4th and early 11th centuries which had been sealed in the so-called ' Library Cave' (Cave 17) at some point in the early 11th century. The Library Cave was discovered by a Daoist monk called Wang Yuanlu in 1900, and much of the contents of the cave were subsequently sold to European explorers such as Aurel Stein and Paul Pelliot. In addition to the Library Cave, manuscripts and printed texts have also been discovered in several other caves at the site. Notably, Pelliot retrieved a large number of documents from Caves 464 and 465 in the northern section of the Mogao Caves. These documents mostly date to the Yuan dynasty (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
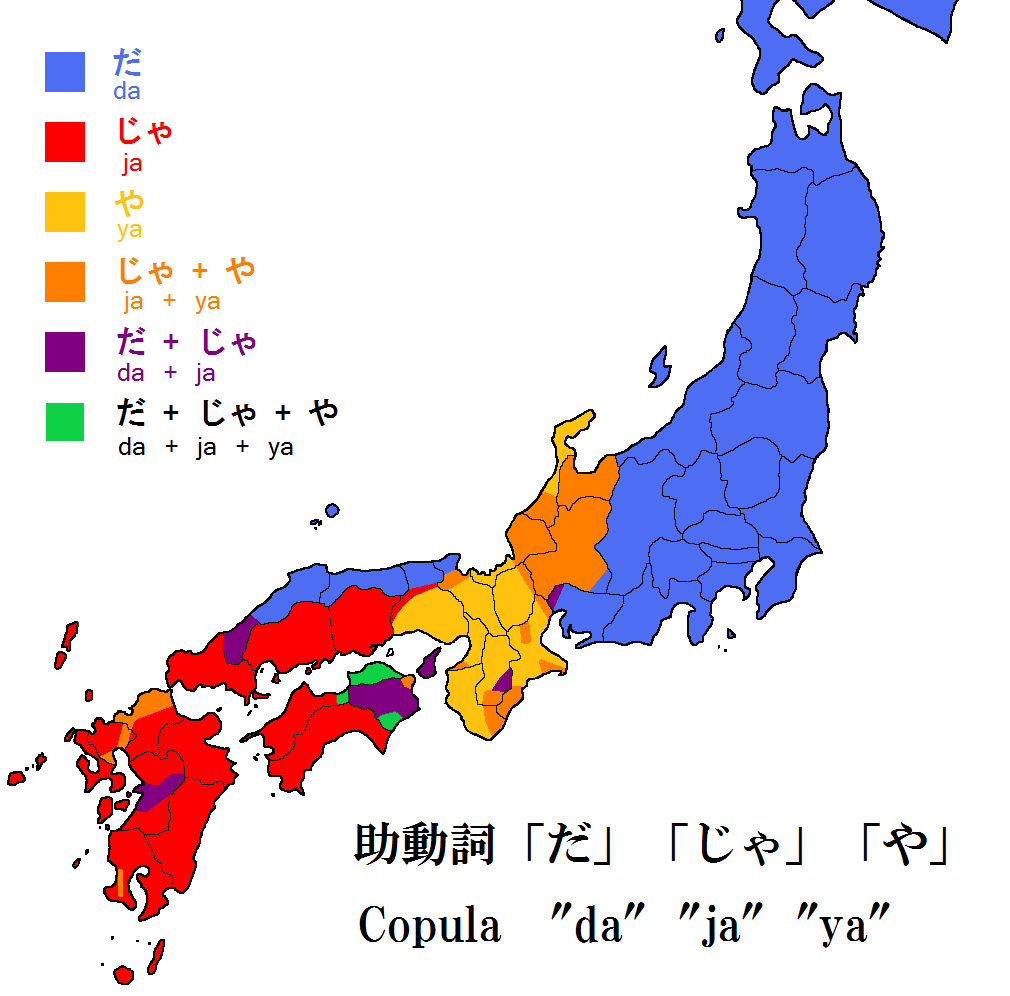
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being co-operative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula, although some (like Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while others have none. In the case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Yugur Language
Western Yugur (Western Yugur: (Yugur speech) or (Yugur word)) also known as Neo-Uygur is the Turkic language spoken by the Yugur people. It is contrasted with Eastern Yugur, a Mongolic language spoken within the same community. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term "Yellow Uygur", from the endonym of the Yugur. There are approximately 4,600 Turkic-speaking Yugurs. Classification Besides similarities with Uyghuric languages, Western Yugur also shares a number of features, mainly archaisms, with several of the Northeastern Turkic languages, but it is not closer to any one of them in particular. Neither Western nor Eastern Yugur are mutually intelligible with Uyghur. Western Yugur also contains archaisms which are attested in neither modern Uyghuric nor Siberian, such as its anticipating counting system coinciding with Old Uyghur, and its copula ''dro'', which originated from Old Uyghur but substitutes the Uyghur copulative personal suffixes. Geographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud Al-Kashgari
Mahmud ibn Husayn ibn Muhammed al-Kashgari, ''Maḥmūd ibnu 'l-Ḥusayn ibn Muḥammad al-Kāšġarī'', , tr, Kaşgarlı Mahmûd, ug, مەھمۇد قەشقىرى, ''Mehmud Qeshqiri'' / Мәһмуд Қәшқири uz, Mahmud Qashg'ariy / Махмуд Қашғарий was an 11th-century Kara-Khanid scholar and lexicographer of the Turkic languages from Kashgar. His father, Husayn, was the mayor of Barsgan, a town in the southeastern part of the lake of Issyk-Kul (nowadays village of Barskoon in Northern Kyrgyzstan's Issyk-Kul Region) and related to the ruling dynasty of Kara-Khanid Khanate. Work Al-Kashgari studied the Turkic languages of his time and in Baghdad he compiled the first comprehensive dictionary of Turkic languages, the ' (English: "Compendium of the languages of the Turks") in 1072–74. It was intended for use by the Abbasid Caliphate, the new Arab allies of the Turks. Mahmud Kashgari's comprehensive dictionary, later edited by the Turkish historian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara-Khanid Khanate
The Kara-Khanid Khanate (; ), also known as the Karakhanids, Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the Afrasiabids (), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of Karakhanids and Ilek Khanids refer to royal titles with Kara Khagan being the most important Turkic title up until the end of the dynasty. The Khanate conquered Transoxiana in Central Asia and ruled it between 999 and 1211. Their arrival in Transoxiana signaled a definitive shift from Iranian to Turkic predominance in Central Asia, yet the Kara-khanids gradually assimilated the Perso-Arab Muslim culture, while retaining some of their native Turkic culture. The capitals of the Kara-Khanid Khanate included Kashgar, Balasagun, Uzgen and Samarkand. In the 1040s, the Khanate split into the Eastern and Western Khanates. In the late 11th century, they came under the suzerainty of the Seljuk Empire, followed by the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) in the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karluk Languages
The Karluk or Qarluq languages are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family that developed from the varieties once spoken by Karluks. Many Middle Turkic works were written in these languages. The language of the Kara-Khanid Khanate was known as Turki, Ferghani, Kashgari or Khaqani. The language of the Chagatai Khanate was the Chagatai language. Karluk Turkic was once spoken in the Kara-Khanid Khanate, Chagatai Khanate, Timurid Empire, Mughal Empire, Yarkent Khanate and the Uzbek-speaking Khanate of Bukhara, Emirate of Bukhara. Classification Languages * Uzbek language, Uzbek – spoken by the Uzbeks; approximately 44 million speakers * Uyghur language, Uyghur – spoken by the Uyghurs; approximately 8-11 million speakers * Ili Turki language, Ili Turki – endangered language, moribund language spoken by Ili Turkis, who are legally recognized as a subgroup of Uzbeks; 120 speakers and decreasing (1980) * Chagatai language, Chagatai – extinct language which was once widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Language
The Uyghur or Uighur language (; , , , or , , , , CTA: Uyğurçä; formerly known as Eastern Turki), is a Turkic language written in a Uyghur Perso-Arabic script with 8-11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur speakers are located in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, and various other countries have Uyghur-speaking expatriate communities. Uyghur is an official language of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region; is widely used in both social and official spheres, as well as in print, television, and radio; and is used as a common language by other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang. Uyghur belongs to the Karluk branch of the Turkic language family, which includes languages such as Uzbek. Like many other Turkic languages, Uyghur displays vowel harmony and agglutination, lacks noun classes or grammatical gender, and is a left-branching language with subject–obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the late 13th century the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the area once ruled by the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty). Initially, the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan,Dai Matsui – A Mongolian Decree from the Chaghataid Khanate Discovered at Dunhuang. Aspects of Research into Central Asian Buddhism, 2008, pp. 159–178 but by the reign of Kublai Khan, Ghiyas-ud-din Baraq no longer obeyed the emperor's orders. During the mid-14th century, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |