|
Old Kannada Script
The Kannada–Telugu script (or Telugu–kannada script) was a writing system used in Southern India. Despite some differences, the scripts used for the Kannada and Telugu languages remain quite similar and highly mutually intelligible. History The Dravidian family comprises about 73 languages including Tamil, Kannada, Telugu and Malayalam. Satavahanas introduced the Brahmi to present-day Telugu and Kannada speaking regions. Bhattiprolu script introduced by the Satavahanas gave rise to the Kadamba script. During the 5th to 7th centuries the early Bādāmi Chālukyās and Early Banavasi Kadambās used an early form of the Kannada script in inscriptions, called the Kadamba script. The Kadamba script evolved into the Kannada script. When Chalukya empire extended towards Telugu speaking regions they establihed another branch in Vengi, namely the Eastern Chalukyas or the Chalukyas of Vengi who later introduced Kannada script to Telugu language which devloped Kannada-Telugu script ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez language, Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional (although in less formal contexts, all three types of script may be termed alphabets). The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which the symbols cannot be split into separate consonants and vowels. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain Février (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic languages, Ethiopic term "abugi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
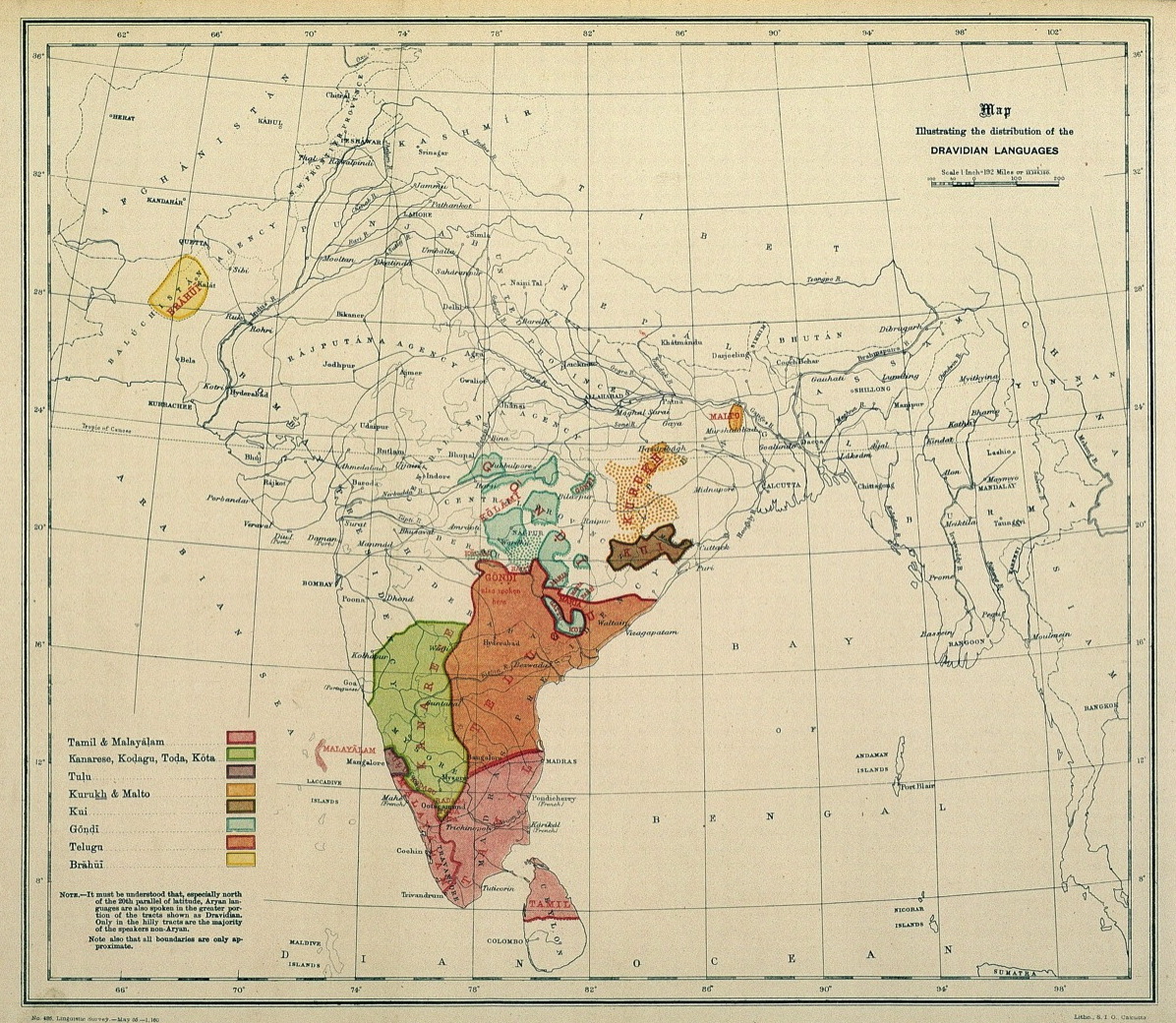
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallava Script
The Pallava script or Pallava Grantha, is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script, named after the Pallava dynasty of South India, attested since the 4th century AD. As epigrapher Arlo Griffiths makes clear, however, the term is misleading as not all of the relevant scripts referred to have a connection with the Pallava dynasty. He instead advocates that these scripts be called 'late Southern Brāhmī' scripts. In India, Pallava script evolved into the Tamil script, Tamil and Grantha script. Pallava Indianization of Southeast Asia, spread to Southeast Asia and evolved into local scripts such as Balinese script, Balinese, Baybayin, Javanese script, Javanese, Kawi alphabet, Kawi, Khmer alphabet, Khmer, Tai Tham alphabet, Lanna, Lao alphabet, Lao, Mon–Burmese script, Mon–Burmese, New Tai Lue alphabet, Sundanese script, Sundanese, and the Thai alphabet, Thai A proposal to encode the script in Unicode was submitted in 2018. History During the rule of Pallavas, the script accompanied pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic History Of The Indian Subcontinent
Since the Iron Age in India, the native languages of the Indian subcontinent are divided into various language families, of which the Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian are the most widely spoken. There are also many languages belonging to unrelated language families such as Austroasiatic and Sino-Tibetan, spoken by smaller groups. Indo-Aryan languages Proto-Indo-Aryan Proto-Indo-Aryan is a proto-language hypothesized to have been the direct ancestor of all Indo-Aryan languages. It would have had similarities to Proto-Indo-Iranian, but would ultimately have used Sanskritized phonemes and morphemes. Old Indo-Aryan Vedic Sanskrit Vedic Sanskrit is the language of the Vedas, a large collection of hymns, incantations, and religio-philosophical discussions which form the earliest religious texts in India and the basis for much of the Hindu religion. Modern linguists consider the metrical hymns of the Rigveda to be the earliest. The hymns preserved in the Rigveda were preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada Inscriptions
About 25,000 inscriptions found in Karnataka and states near by belongs to Kannada rulers like Kadambas, Western Ganga Dynasty, Rashtrakuta, Chalukya, Hoysala and Vijayanagara Empire. Many inscriptions related to Jainism are unearthed. The inscriptions generally found are on stone (''Shilashasana'') or copper plates (''Tamarashasana''). The Kannada inscriptions (Old Kannada, Kadamba script) found on historical Hero Stone, coin and temple wall, piller, tablet and rock edict. These Inscription have contributed towards Kannada literature and helped to classify as ''Proto Kannada, Pre Old Kannada, Old Kannada, Middle Kannada and New Kannada. ''Inscriptions'' depicts culture, tradition and prosperity of those era. The world wide recognized literature '' Ramayana '' and '' Mahabharata '' are transferred through generation by these Inscription Hazara Rama Temple and Aranmula Parthasarathy Temple are the best example. Earliest Kannada inscriptions The first written record in Kan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic script (Unicode), scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.International Phonetic Association (IPA), ''Handbook''. The IPA is used by lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguistics, linguists, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of wiktionary:lexical, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, phonemes, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth wiktionary:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 15919
ISO 15919 (Transliteration of Devanagari and related Indic scripts into Latin characters) is one of a series of international standards for romanization by the International Organization for Standardization. It was published in 2001 and uses diacritics to map the much larger set of consonants and vowels in Brahmic and Nastaliq scripts to the Latin script. Overview Relation to other systems ISO 15919 is an international standard on the romanization of many Brahmic scripts, which was agreed upon in 2001 by a network of the national standards institutes of 157 countries. However, the Hunterian transliteration system is the "national system of romanization in India" and a United Nations expert group noted about ISO 15919 that "there is no evidence of the use of the system either in India or in international cartographic products." Another standard, United Nations Romanization Systems for Geographical Names (UNRSGN), was developed by the United Nations Group of Experts on Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu-Kannada
The Kannada–Telugu script (or Telugu–kannada script) was a writing system used in Southern India. Despite some differences, the scripts used for the Kannada and Telugu languages remain quite similar and highly mutually intelligible. History The Dravidian family comprises about 73 languages including Tamil, Kannada, Telugu and Malayalam. Satavahanas introduced the Brahmi to present-day Telugu and Kannada speaking regions. Bhattiprolu script introduced by the Satavahanas gave rise to the Kadamba script. During the 5th to 7th centuries the early Bādāmi Chālukyās and Early Banavasi Kadambās used an early form of the Kannada script in inscriptions, called the Kadamba script. The Kadamba script evolved into the Kannada script. When Chalukya empire extended towards Telugu speaking regions they establihed another branch in Vengi, namely the Eastern Chalukyas or the Chalukyas of Vengi who later introduced Kannada script to Telugu language which devloped Kannada-Telugu script ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalukya Dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani (modern Basavakalyan) until the end of the 12t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Chalukyas
Eastern Chalukyas, also known as the Chalukyas of Vengi, were a dynasty that ruled parts of South India between the 7th and 12th centuries. They started out as governors of the Chalukyas of Badami in the Deccan region. Subsequently, they became a sovereign power, and ruled the Vengi region of present-day Andhra Pradesh until . They continued ruling the region as feudatories of the Cholas until 1189 CE. Originally, the capital of the Eastern Chalukyas was located at the Vengi city (present-day Pedavegi, near Eluru). It was subsequently moved to Rajamahendravaram (now Rajahmundry). Throughout their history the Eastern Chalukyas were the cause of many wars between the more powerful Cholas and Western Chalukyas over the control of the strategic Vengi country. The five centuries of the Eastern Chalukya rule of Vengi saw not only the consolidation of this region into a unified whole, but also saw the efflorescence of Telugu and Kannada culture, literature, poetry and art during the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)