|
Okobo
, also referred to as , or (all onomatopoeic terms taken from the sound make when walking), are traditional Japanese wooden sandals worn by young girls for , young women during Coming of Age Day and apprentice geisha in some regions of Japan. are typically made from a solid block of paulownia wood, a lightweight hardwood native to East Asia and often cultivated there. range from tall, and can be decorated, lacquered black or left plain; the plain varieties are not waxed. are kept on the foot with a thong strap known as the ; this is tied to the shoe by the use of knots passed through drilled holes – one at the front of the shoe, through the underside of the slope, and two through the central block of the shoe. The centre of the shoe is drilled out, leaving it hollow, and the ends of the are tied in this hollow. The front knot may hold a small bell in place, and the hole is typically covered with a small metal cover known as the (, literally , "front" + , "metal") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okobo Pokkurigeta
, also referred to as , or (all onomatopoeic terms taken from the sound make when walking), are traditional Japanese wooden sandals worn by young girls for , young women during Coming of Age Day and apprentice geisha in some regions of Japan. are typically made from a solid block of paulownia wood, a lightweight hardwood native to East Asia and often cultivated there. range from tall, and can be decorated, lacquered black or left plain; the plain varieties are not waxed. are kept on the foot with a thong strap known as the ; this is tied to the shoe by the use of knots passed through drilled holes – one at the front of the shoe, through the underside of the slope, and two through the central block of the shoe. The centre of the shoe is drilled out, leaving it hollow, and the ends of the are tied in this hollow. The front knot may hold a small bell in place, and the hole is typically covered with a small metal cover known as the (, literally , "front" + , "metal") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
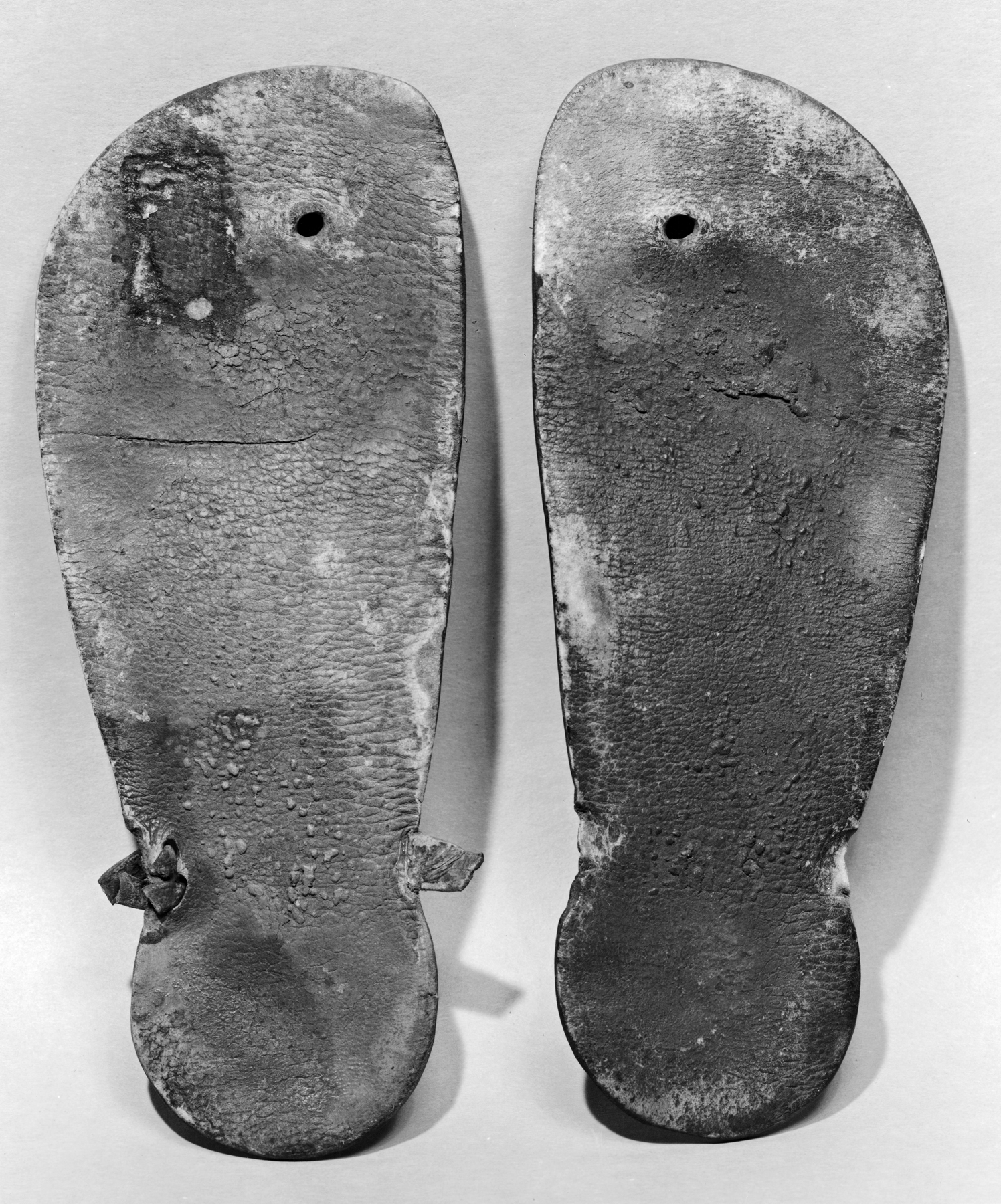
Geta (footwear)
A Geta, ( zh, 木屐, ja, 下駄; geta or getas) is a traditional East Asian footwear that resembles flip-flops. A kind of sandals, geta have a flat wooden base elevated with up to three (though commonly two) "teeth", held on the foot with a fabric thong, which keeps the foot raised above the ground. History The earliest known pair of geta was excavated in a neolithic archaeological site near Ningbo, Zhejing, China, dated to the Liangzhu culture (3400–2250 BCE). These geta differed in construction to modern geta, having five or six holes in place of the modern-day three. The use and popularity of wooden clogs in China has been recorded in other sources dating to between the Spring and Autumn period (771–476 BCE) to the Qin (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasties (202 BCE–220 CE). Geta-style shoes were worn in Southern China likely until sometime between the Ming (1368–1644) and Qing dynasties (1636/1644–1912), when they were replaced by other types of footwear. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geta (footwear)
A Geta, ( zh, 木屐, ja, 下駄; geta or getas) is a traditional East Asian footwear that resembles flip-flops. A kind of sandals, geta have a flat wooden base elevated with up to three (though commonly two) "teeth", held on the foot with a fabric thong, which keeps the foot raised above the ground. History The earliest known pair of geta was excavated in a neolithic archaeological site near Ningbo, Zhejing, China, dated to the Liangzhu culture (3400–2250 BCE). These geta differed in construction to modern geta, having five or six holes in place of the modern-day three. The use and popularity of wooden clogs in China has been recorded in other sources dating to between the Spring and Autumn period (771–476 BCE) to the Qin (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasties (202 BCE–220 CE). Geta-style shoes were worn in Southern China likely until sometime between the Ming (1368–1644) and Qing dynasties (1636/1644–1912), when they were replaced by other types of footwear. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Items Traditionally Worn In Japan
This is a list of items of clothing, as well as clothing accessories, traditionally worn in Japan. These include items worn in both formal and informal situations, such as the kimono and coats, as well as items reserved for auspicious, ceremonial and/or religious occasions. Members of the Imperial family on formal occasions, geisha, , and sumo wrestlers wear variations on common traditional accessories that are not found in everyday dress, such as certain types of kimono. As an extension of this, many practitioners of Japanese traditional dance wear similar kimono and accessories to geisha and . For certain traditional holidays and occasions, some specific types of kimono accessories are worn. For instance, are worn to festivals, and and are worn by girls for and young women on (Coming of Age Day). A slightly taller, plainer variation of are also worn by in some areas of Japan throughout their apprenticeship. C D F G H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waraji
() are light tie-on sandals, made from (usually straw) ropemaking fibers, that were the standard footwear of the common people in Japan. Use resemble other forms of traditional Japanese footwear, such as zori and geta, with a few key differences. They were historically the simplest form of outdoor footwear (sandals of any type were not worn indoors). , due to their cheap and rustic nature, are considered to be a very informal type of footwear, and are not worn with formal kimono. They are typically not worn with socks, and are woven so that the wearer's toes generally protrude slightly over the edge of the shoe. were once common footwear in Japan. There are records of in the Heian period (794–1185 CE), with the possibility of having existed before this time. In the Edo period (1603–1867 CE), geta were worn in cities, but anyone making a long journey wore . (sponsored article) They were also worn for energetic or prolonged labour. Their light weight and grip were val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zōri
Zori (), also rendered as zōri ( ja, , ), are thonged Japanese sandals made of rice straw, cloth, lacquered wood, leather, rubber, or—most commonly and informally—synthetic materials. They are a slip-on descendant of the tied-on sandal. Similar in form, modern flip-flops became popular in the United States, Australia and New Zealand when soldiers returning from World War II brought Japanese zori with them. Use Like many Japanese sandals, zori are easily slipped on and off, which is important in Japan, where shoes are removed and put back on when entering and leaving a house, and where tying shoelaces would be impractical when wearing traditional clothing. The traditional forms of zori are seen when worn with other traditional clothing. Modern forms are fairly common, however, with casual Western wear, especially in summer. While geta are now mostly worn with the informal , traditional zori are often worn with the more formal kimono. In rain, zori may be worn with toe c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandals
Sandals are an open type of footwear, consisting of a sole held to the wearer's foot by straps going over the instep and around the ankle. Sandals can also have a heel. While the distinction between sandals and other types of footwear can sometimes be blurry (as in the case of '' huaraches''—the woven leather footwear seen in Mexico, and peep-toe pumps), the common understanding is that a sandal leaves all or most of the foot exposed. People may choose to wear sandals for several reasons, among them comfort in warm weather, economy (sandals tend to require less material than shoes and are usually easier to construct), and as a fashion choice. Usually, people wear sandals in warmer climates or during warmer parts of the year in order to keep their feet cool and dry. The risk of developing athlete's foot is lower than with enclosed shoes, and the wearing of sandals may be part of the treatment regimen for such an infection. History The oldest known sandals (and the olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabi
are traditional Japanese socks worn with thonged footwear such as zori, dating back to the 15th century. History Japanese are usually understood today to be a kind of split-toed sock that is not meant to be worn alone outdoors, much like regular socks. However, were originally a kind of leather shoe made from a single animal hide, as evidenced by historical usage and the earlier form of the word, , written , with the kanji literally signifying "single hide".''Nihon Kokugo Daijiten'', entry for tabi available onlinhere(in Japanese)'' Dajirin'', second edition, 1995''Shin Meikai Kokugo Jiten'', fifth edition, 1997 As Japanese footwear evolved, also changed, with the split-toe design emerging towards the late Heian period (794–1185 CE) to allow the wearer to accommodate the thong of straw sandals to reinforce the sole.'' Sekai Dai Hyakka Jiten'', second edition, entry available onlinhere(in Japanese) Outdoor versions of involved some kind of reinforcement, with soles trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jandal
Flip-flops are a type of light sandal, typically worn as a form of casual footwear. They consist of a flat sole held loosely on the foot by a Y-shaped strap known as a toe thong that passes between the first and second toes and around both sides of the foot or can be a rigid base with a strap across all the toes. This style of footwear has been worn by the people of many cultures throughout the world, originating as early as the ancient Egyptians in 1,500 B.C. In the United States the flip-flop has been popularized from the Japanese ''zōri'', after World War II as soldiers brought them back from Japan. They became a prominent unisex summer footwear starting in the 1960s. Etymology Although the Beach Boys 1964 song All Summer Long mentions "T-shirts, cut-offs, and a pair of thongs", the term ''flip-flop'' has been used in American and British English since the 1960s to describe the thong or no-heel-strap sandal. This type of footwear is also known as " slides" or "sliders". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllostachys Bambusoides
''Phyllostachys bambusoides'', commonly called , giant timber bamboo, or Japanese timber bamboo, is a species of flowering plant in the bamboo subfamily of the grass family Poaceae, native to China, and possibly also to Japan. Description ''Phyllostachys bambusoides'' is a "running" (monopodial type) evergreen bamboo which can reach a height of roughly and a diameter of . The culms are dark green, with a thin wall that thickens with maturity, and very straight, with long internodes and two distinctive rings at the node. The species is thin-skinned, easily split lengthwise, has long fibres, and is strong and highly flexible, even when split finely. Leaves are dark green, and the sheaths are strong and hairless. New stalks emerge in late spring and grow at a rate of up to a day; one specimen produced culms growing a remarkable in 24 hours. The flowering interval of this species is very long, lasting roughly 120 years. Uses In Asia, ''Phyllostachys bambusoides'', known in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brocade
Brocade is a class of richly decorative shuttle-woven fabrics, often made in colored silks and sometimes with gold and silver threads. The name, related to the same root as the word "broccoli", comes from Italian ''broccato'' meaning "embossed cloth", originally past participle of the verb ''broccare'' "to stud, set with nails", from ''brocco'', "small nail", from Latin ''broccus'', "projecting, pointed". Brocade is typically woven on a draw loom. It is a supplementary weft technique; that is, the ornamental brocading is produced by a supplementary, non-structural, weft in addition to the standard weft that holds the warp threads together. The purpose of this is to give the appearance that the weave was actually embroidered on. In Guatemala, brocade is the most popular technique used to decorate fabric woven by Maya weavers on backstrap looms. Ornamental features in brocade are emphasized and wrought as additions to the main fabric, sometimes stiffening it, though more fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Finishing
Wood finishing refers to the process of refining or protecting a wooden surface, especially in the production of furniture where typically it represents between 5 and 30% of manufacturing costs. Finishing is the final step of the manufacturing process that gives wood surfaces desirable characteristics, including enhanced appearance and increased resistance to moisture and other environmental agents. Finishing can also make wood easier to clean and keep it sanitized, sealing pores that can be breeding grounds for bacteria. Finishing can also influence other wood properties, for example tonal qualities of musical instruments and hardness of flooring. In addition, finishing provides a way of giving low-value woods the appearance of ones that are expensive and difficult to obtain. Planning the finish Finishing of wood requires careful planning to ensure that the finished piece looks attractive, performs well in service and meets safety and environmental requirements. Planning fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)