|
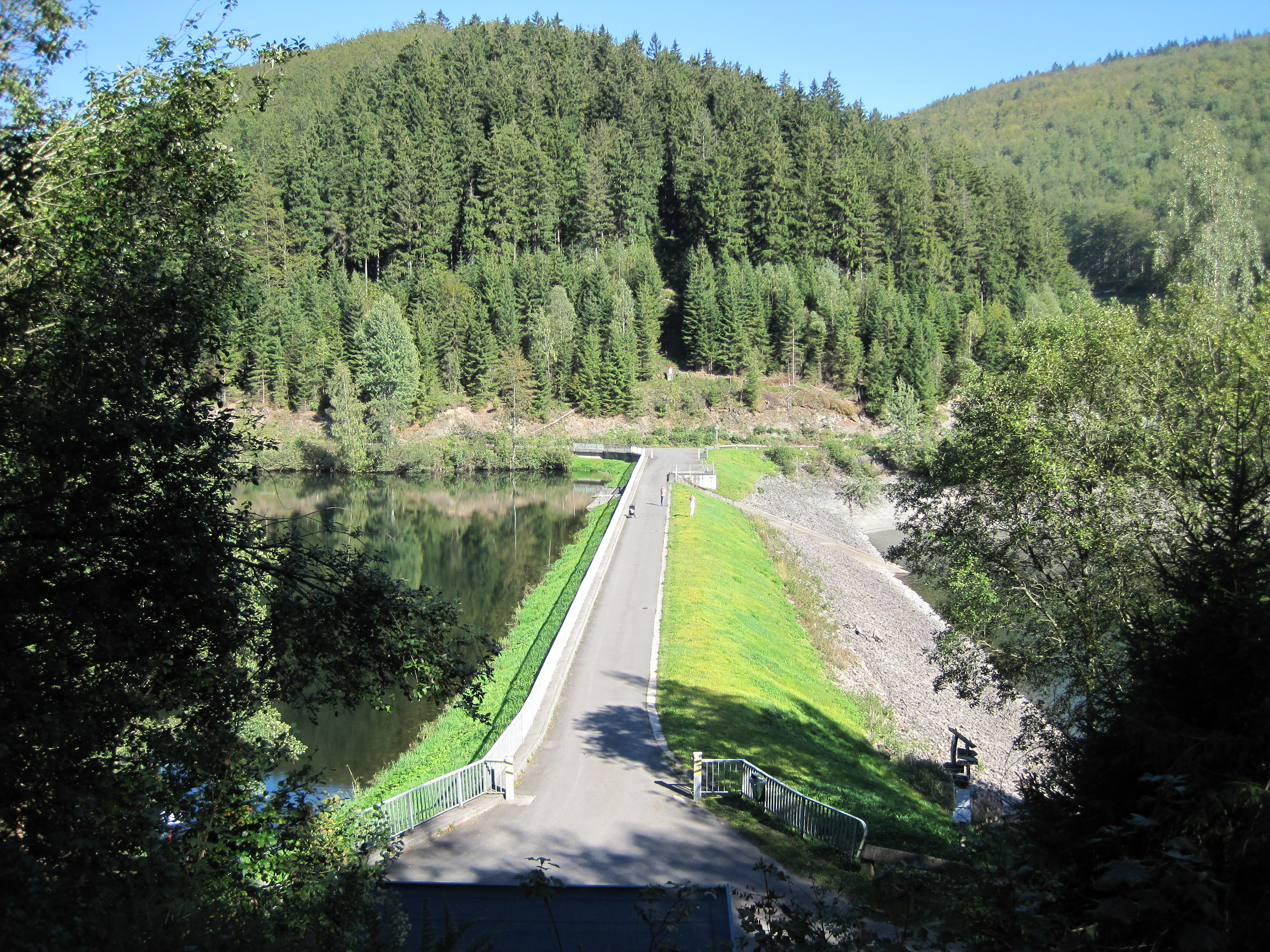
Okertalsperre Staumauer Seeseite
The Oker Dam (german: Okertalsperre) is a dam in the Harz mountains in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is fed by the River Oker. Technology The dam is in the shape of an arch (see arch-gravity dam). It is 75 m high, 260 m long, can impound up to 47 million m³ of water and provides hydropower, flood protection and water regulation at times of low water. It is also used indirectly for the production of drinking water. Its average annual discharge is 75 million m³. The hydro-electric power station at Romkerhalle is fed by the Oker Reservoir. File:Okertalsperre_staumauer_talseite.jpg, Dam, downstream side File:Staumauer okertalsperre.jpg, Downstream face of the dam File:Okertalsperre_Hauptstaumauer_UEberlaeufe.jpg, Spillways on the dam File:Okertalsperre02.jpg, Table with technical data on the Oker Dam History and location The construction of the Oker Dam was begun by Hr. Press in the years 1938 to 1942 and then completed between 1949 and 1956. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigge Reservoir
The Biggesee or Bigge Reservoir (german: Biggetalsperre) is a reservoir in Germany. It lies in the southern part of the Sauerland between Olpe and Attendorn. Purpose The lake serves to regulate the rivers Ruhr and Lenne as well as providing water for the Ruhrgebiet. It is fed from the Bigge, a tributary of the Lenne. The lake serves primarily to store water for the Ruhrgebiet so as to maintain the same level of water in the Ruhr. The lake can deliver, via the rivers Bigge and Lenne, up to 40% of all the water supplied by all the reservoirs in the river system of the Ruhr combined. A hydroelectric power station produces around 24 million kWh electricity annually. The power of the three large and one small Francis turbines amounts to 17.52 MW. The owner of the lake is the Ruhrverband. Along with the Listertalsperre, the Biggestausee forms a large reservoir system. The formerly self-standing Listertalsperre joins immediately on to the Biggesee. In middle of the Biggesee it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
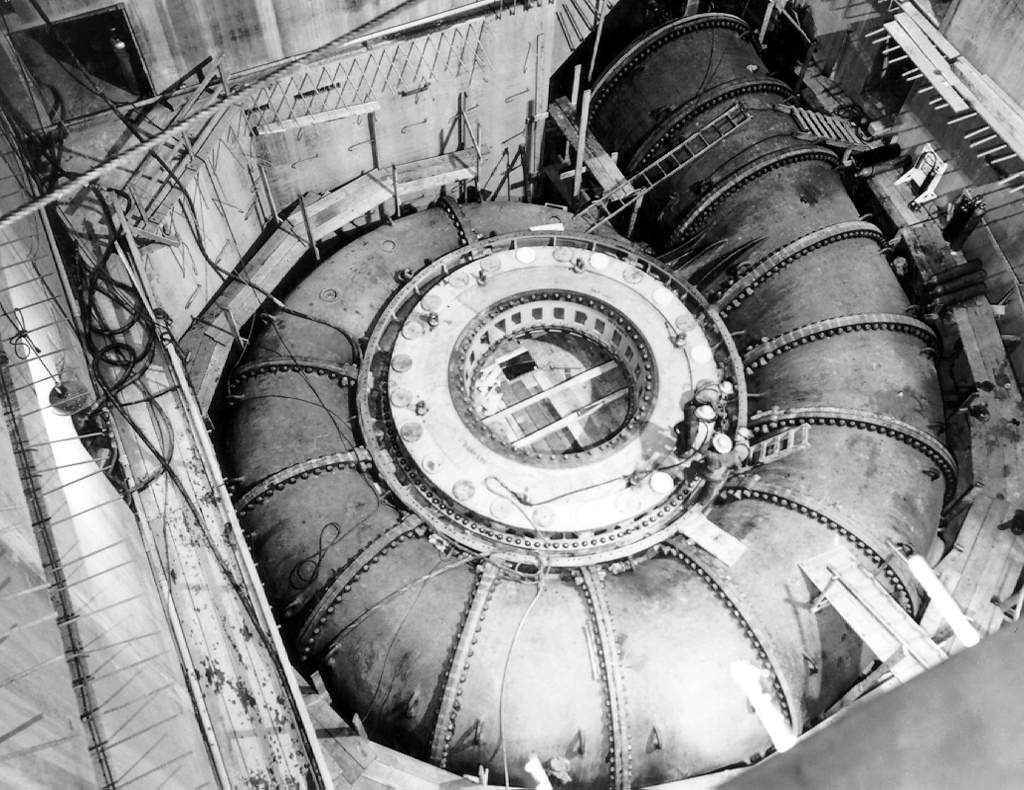
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or Body of water, water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide. Wetlands occur naturally on every continent. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or seawater, saltwater. The main w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retention Basin
A retention basin, sometimes called a wet pond, wet detention basin, or stormwater management pond (SWMP), is an artificial pond with vegetation around the perimeter and a permanent pool of water in its design. It is used to manage stormwater runoff, for protection against flooding, for erosion control, and to serve as an artificial wetland and improve the water quality in adjacent bodies of water. It is distinguished from a detention basin, sometimes called a "dry pond", which temporarily stores water after a storm, but eventually empties out at a controlled rate to a downstream water body. It also differs from an infiltration basin which is designed to direct stormwater to groundwater through permeable soils. Wet ponds are frequently used for water quality improvement, groundwater recharge, flood protection, aesthetic improvement, or any combination of these. Sometimes they act as a replacement for the natural absorption of a forest or other natural process that was lost wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Dam
A gravity dam is a dam constructed from concrete or stone masonry and designed to hold back water by using only the weight of the material and its resistance against the foundation to oppose the horizontal pressure of water pushing against it. Gravity dams are designed so that each section of the dam is stable and independent of any other dam section. Characteristics Gravity dams generally require stiff rock foundations of high bearing strength (slightly weathered to fresh), although in rare cases, they have been built on soil foundations. The bearing strength of the foundation limits the allowable position of the resultant force, influencing the overall stability. Also, the stiff nature of the gravity dam structure is unforgiving to differential foundation settlement, which can induce cracking of the dam structure. Gravity dams provide some advantages over embankment dams, the main advantage being that they can tolerate minor over-topping flows without damage, as the concre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torfhaus
Torfhaus is a village in the borough of the mining town of Altenau in the Harz mountains of Germany and lies at a height of about . It is the highest settlement in Lower Saxony. This small settlement consists mainly of restaurants, youth hostels, ski huts and large car parks. A resort area with hotel and cabins was built in 2012/2013. The B 4 federal road, which is a major traffic route, runs from Brunswick to the north via Torfhaus to Braunlage and on into the South and East Harz. Today Torfhaus is a popular start point for walks along the Goethe Way to the Brocken, but also to the historic Dreieckiger Pfahl boundary stone and on over the mountains of the Wurmberg or Achtermannshöhe to Braunlage. Geography Torfhaus lies about 7 km east of Altenau and roughly 9 km south of Bad Harzburg in the Upper Harz. The river Radau rises east of Torfhaus on the Torfhaus Moor (also called ''Radauborn Moor''). Tourism and sport Torfhaus lies at the heart of the Harz Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roller Skiers
Roller skiing is an off-snow equivalent to cross-country skiing. Roller skis have wheels on their ends and are used on a hard surface, to emulate .Bryhn, Rolf and Knut Are Tvedt (eds.): ''Kunnskapsforlagets idrettsleksikon''. (Norwegian Encyclopedia of Sports). Oslo: Kunnskapsforlaget, 1990. The skiing techniques used are very similar to techniques used in cross-country skiing on snow. First created as a summer training exercise, roller skiing grew into a competitive sport in its own right. Annual championships are held in various locations around the world. Most, if not all, national cross-country ski teams around the world roller ski during the off-season for specific physical training simulating winter skiing. In Norway, separate roller ski facilities have been constructed to allow exercise off public roads. History The first roller skis were built in the mid-1930s in Italy and North Europe. In the early 1950s, when cross-country skiing started to evolve to a serious competit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Skaters
Inline skates are a type of roller skate used for inline skating. Unlike quad skates, which have two front and two rear wheels, inline skates typically have two to five wheels arranged in a single line. Some, especially those for recreation, have a rubber "stop" or "brake" block attached to the rear of one or occasionally both of the skates so that the skater can slow down or stop by leaning back on the foot with the brake skate. During the late 1980s and early 1990s, Rollerblade, Inc., a company founded by Scott and Brennan Olson in Minneapolis, Minnesota, widely promoted inline skating through the registered trademark ''Rollerblade''. This term has since become a generic trademark for inline skates. History John Joseph Merlin experimented with single- to many-rowed devices worn on feet in 1760. Inline skates, skates designed to work like ice skates during periods of warm weather, was patented by Robert John Tyers of London in 1823, his Rolito design featured brass wheels. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclists
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of Bicycle, cycles for transport, recreation, Physical exercise, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from two-wheeled bicycles, "cycling" also includes the riding of unicycles, tricycles, quadricycles, recumbent bicycle, recumbent and similar human-powered transport, human-powered vehicles (HPVs). Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century and now number approximately one billion worldwide. They are the principal means of transportation in many parts of the world, especially in densely populated European cities. Cycling is widely regarded as an effective and efficient mode of transportation optimal for short to moderate distances. Bicycles provide numerous possible benefits in comparison with motor vehicles, including the sustained physical exercise involved in cycling, easier parking, increased maneuverability, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-dam
A forebay is an artificial pool of water in front of a larger body of water. The larger body of water may be natural or man-made. at www.wisegeek.com. Retrieved on 13 Jun 2013 Forebays have a number of functions. They are used in to act as a buffer during or s, impounding water and releasing in a controlled way into the larger waterbody. They may be used upstream of |
Ice Swimming
Winter swimming is the activity of swimming during the winter season, typically in outdoor locations (open water swimming) or in unheated pools or lidos. In colder countries, it may be synonymous with ice swimming, when the water is frozen over. This requires either breaking the ice or entering where a spring prevents the formation of ice. It may also be simulated by a pool of water at , the temperature at which water freezes. In Nordic countries of Europe as well in Eastern Europe (e.g. Ukraine, Russia, Finland, and Baltic countries), winter swimming is a traditional cultural element and part of religious celebrations like the Epiphany in Eastern Orthodoxy. Competitions for winter swimming also exist. Many winter swimmers swim with standard swimsuits rather than with wetsuits or other thermal protection. Famous ice and winter swimmers include Lynne Cox and Lewis Gordon Pugh. Also, many locations in North America and Europe hold polar bear plunges, commonly to celebrate N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





