|
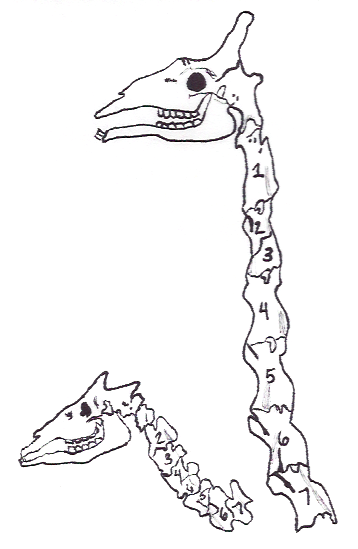
Okapia
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe and zebra giraffe, is an artiodactyl mammal that is endemic to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo in central Africa. However, non-invasive genetic identification has suggested that a population has occurred south-west of the Congo River as well. It is the only species in the genus ''Okapia''. Although the okapi has striped markings reminiscent of zebras, it is most closely related to the giraffe. The okapi and the giraffe are the only living members of the family Giraffidae. The okapi stands about tall at the shoulder and has a typical body length around . Its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large, flexible ears. Its coat is a chocolate to reddish brown, much in contrast with the white horizontal stripes and rings on the legs, and white ankles. Male okapis have short, distinct horn-like protuberances on their heads called ossicones, less than in length. Females p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family (biology), family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a recent common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (between one and eight, usually four, species of ''Giraffa'', depending on taxonomic interpretation) and the okapi (the only known species of ''Okapia''). Both are confined to sub-Saharan Africa: the giraffe to the open savannas, and the okapi to the dense rainforest of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Congo. The two genera look very different on first sight, but share a number of common features, including a long, dark-coloured tongue, lobed canine teeth, and horns covered in skin, called ossicones. Taxonomy Evolutionary background The giraffids are ruminants of the clade Pecora. Other extant pecorans are the families Antilocapridae (pronghorns), Cervidae (deer), Moschidae (musk deer), and Bovidae (Bovini, cattl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okapi Conservation Project
The Okapi Conservation Project (OCP) was founded in 1987 for the protection of the okapis (''Okapia johnstoni'') and their habitat. Okapis are found only in the Democratic Republic of Congo and are seen as the major flagship species of the Ituri Forest. The OCP has about one hundred staff members and one hundred and ten government rangers under the direction of the Institute in Congo for the Conservation of Nature. The Okapi Conservation Project is partnered with the Wildlife Conservation Network. OCP's founder John Lukas is also a founding member of the Wildlife Conservation Network. In 1992 the project helped create the Okapi Wildlife Reserve, encompassing 13,700 square kilometers of the Ituri Forest, which was designated as a United Nations World Heritage Site in 1996. 2012 attack In June 2012 the headquarters for the Okapi Wildlife Reserve was taken over by poachers, intent on retaliating against the staff who had been stopping their elephant poaching and mining operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers by their unique development and a permanent covering of skin and fur. Structure Giraffe ossicones consist of a highly vascularized and innervated bone core covered with similarly vascularized and innervated skin. They are attached to the skull with vascularized, innervated connective tissue. Ossicones are formed at late gestation, but in early development they are not bony and not fused to the skull yet. Ossicones usually fuse to the skull at sexual maturity. All male and female giraffes have a pair of parietal ossicones on the parietal bones of the skull. Males also usually have a single median ossicone on the frontal bone that is larger in northern animals and smaller in southern giraffes. Giraffes can also have small additional paire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZooParc De Beauval
The ZooParc de Beauval (), more commonly called Beauval Zoo or, more simply, Beauval, is a French zoological park located in Saint-Aignan-sur-Cher, Centre-Val de Loire Centre-Val de Loire (; ,In isolation, ''Centre'' is pronounced . ) or Centre Region (, ), as it was known until 2015, is one of the eighteen Regions of France, administrative regions of France. It straddles the middle Loire Valley in the interior .... It features more than 35,000 animals on 40 hectares, which is one of the largest animal collections in France and in Europe. Created in 1980 by Françoise Delord, it is now run by her son, Rodolphe Delord, and managed by his family, which owns most of the capital. Beauval was often the first zoo to house certain animals in France, which contributed to its reputation and to its development. It was the first zoo in France to present leucistic big cats, such as white tigers and white lions, in the 1990s. Other rare, unique or endangered species housed at the zoo incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canopy (biology)
In biology, the canopy is the aboveground portion of a plant community, plant cropping or crop, formed by the collection of individual Crown (botany), plant crowns. In forest ecology, the canopy is the upper layer or habitat zone, formed by mature tree crowns and including other biological organisms (epiphytes, lianas, Arboreal, arboreal animals, etc.). The communities that inhabit the canopy layer are thought to be involved in maintaining forest diversity, Ecological resilience, resilience, and functioning. Shade trees normally have a dense canopy that blocks light from lower growing plants. Early observations of canopies were made from the ground using binoculars or by examining fallen material. Researchers would sometimes erroneously rely on extrapolation by using more reachable samples taken from the understory. In some cases, they would use unconventional methods such as chairs suspended on vines or hot-air dirigibles, among others. Modern technology, including adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Morton Stanley
Sir Henry Morton Stanley (born John Rowlands; 28 January 1841 – 10 May 1904) was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author, and politician famous for his exploration of Central Africa and search for missionary and explorer David Livingstone. Besides his discovery of Livingstone, he is mainly known for his search for the sources of the Nile and Congo River, Congo rivers, the work he undertook as an agent of King Leopold II of the Belgians that enabled the occupation of the Congo Basin region, and his command of the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition. He was knighted in 1897, and served in Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament as a Liberal Unionist member for Lambeth North (UK Parliament constituency), Lambeth North from 1895 to 1900. More than a century after his death, Stanley's legacy remains the subject of enduring controversy. Although he personally had high regard for many of the native African people who accompanied him on his expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicorn
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since Classical antiquity, antiquity as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn (anatomy), horn projecting from its forehead. In European literature and art, the unicorn has for the last thousand years or so been depicted as a white horse- or goat-like animal with a long straight horn with spiraling grooves, cloven hooves, and sometimes a goat's beard. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance, it was commonly described as an extremely wild forest, woodland creature, a symbol of purity and grace, which could be captured only by a virgin. In encyclopedias, its horn was described as having the power to render poisoned water potable and to heal sickness. In medieval and Renaissance times, the tusk of the narwhal was sometimes sold as a unicorn horn. A bovine type of unicorn is thought by some scholars to have been depicted in Indus seal, seals of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation, Indus Valley civilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex infrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
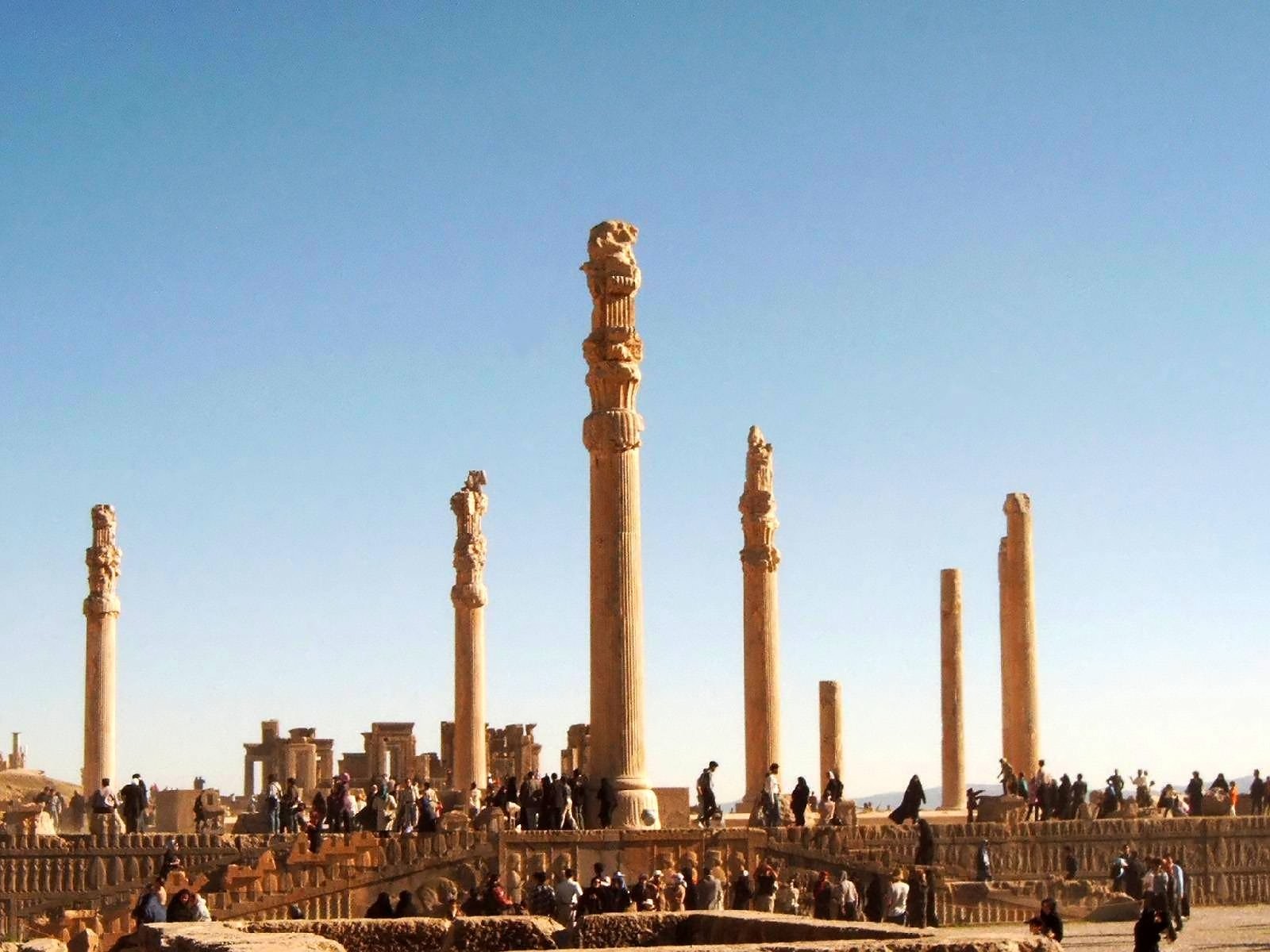
Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The earliest remains of Persepolis date back to 515 BC. The city, acting as a major center for the empire, housed a palace complex and citadel designed to serve as the focal point for governance and ceremonial activities. It exemplifies the Achaemenid style of architecture. The complex was taken by the army of Alexander the Great in 330 BC, and soon after, its wooden parts were completely destroyed by fire, likely deliberately. The function of Persepolis remains unclear. It was not one of the largest cities in ancient Iran, let alone the rest of the empire, but appears to have been a grand ceremonial complex that was only occupied seasonally; the complex was raised high on a walled platform, with five "palac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apadana
Apadana (, or ) is a large hypostyle hall in Persepolis, Iran. It belongs to the oldest building phase of the city of Persepolis, in the first half of the 5th century BC, as part of the original design by Darius I, Darius the Great. Its construction was completed by Xerxes I. Modern scholarship "demonstrates the metaphorical nature of the Apadana reliefs as idealised social orders".#refmcool, M. Root (1986) p. 1. Etymology As a word, (Old Persian wikt:𐎠𐎱𐎭𐎠𐎴, 𐎠𐎱𐎭𐎠𐎴, masc.) is used to designate a hypostyle hall, i.e., a palace or audience hall of stone construction with columns. The word is rendered in Elamite as ''ha-ha-da-na'' and in Akkadian language, Babylonian ''ap-pa-da-an'' is etymologically ambiguous. It has been compared to the Sanskrit (आपादन) which means 'to arrive at', and also to the Sanskrit ''apa-dhā'' (अपधा) which means "a hide-out or concealment", and the Greek language, Greek (), meaning "storehouse". The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Façade
A façade or facade (; ) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a loanword from the French language, French (), which means "frontage" or "face". In architecture, the façade of a building is often the most important aspect from a design standpoint, as it sets the tone for the rest of the building. From the engineering perspective, the façade is also of great importance due to its impact on Efficient energy use, energy efficiency. For historical façades, many local zoning regulations or other laws greatly restrict or even forbid their alteration. Etymology The word is a loanword from the French , which in turn comes from the Italian language, Italian , from meaning 'face', ultimately from post-classical Latin . The earliest usage recorded by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' is 1656. Façades added to earlier buildings It was quite common in the Georgian architecture, Georgian period for existing houses in English towns to be given a fashionable new f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieces From Okapi Leather, Obtained By Sir Harry Johnston (crop)
Piece or Pieces (not to be confused with peace) may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Games * Piece (chess), pieces deployed on a chessboard for playing the game of chess * ''Pieces'' (video game), a 1994 puzzle game for the Super NES * Pieces, parts of a jigsaw puzzle or board game Music Albums * ''Piece'' (Lena Park album), 1998 * ''Piece'' (Monsta X album), 2018 * ''Pieces'' (Bobby Womack album), 1978 * ''Pieces'' (Erik Hassle album), 2010 * ''Pieces'' (IU album), 2021 * ''Pieces'' (Manassas album), 2009 * ''Pieces'' (Matt Simons album) or the title song, 2012 * ''Pieces'' (Michele Stodart album), 2016 * ''Pieces, Part One'', by Epik High, 2008 * ''Pieces'', by Daeg Faerch, 2020 * ''Pieces'', by Kokia, 2011 * ''Pieces'', an EP by Dismember, 1992 Songs * "Piece" (song), by Yui Aragaki, 2009 * "Pieces" (Chase & Status song), 2008 * "Pieces" (Gary Allan song), 2013 * "Pieces" (L'Arc-en-Ciel song), 1999 * "Pieces" (Sum 41 song), 2005 * "Hide"/"Pieces", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |