|
Oilill Olum
Ailill Ollamh (or Oilill Olum) in Irish traditional history was the son of Mug Nuadat and was a king of the southern half of Ireland, placed in the 3rd century by early modern Irish genealogy. Sadb ingen Chuinn, daughter of Conn of the Hundred Battles, in her second marriage, married Ailill. He divided the kingdom between his sons Éogan Mór, Cormac Cas, and Cían. Éogan founded the dynasty of the Eóganachta. Sadb's son Lugaid Mac Con, who was Ailill's foster-son, became High King of Ireland. The Book of Leinster contains poems ascribed to him. The O'Sullivans are one of the number of surnames listed below as descendants of Ailill Ollamh. The An Leabhar Muimhneach (Book of Munster) has an extensive genealogy of the Eóganacht septs. Legend Ailill, King of Munster, discovered that the grass in his fields would not grow. Without the grass, there were no herds; without the cattle, his people would starve. Ferchess the Druid told him to go to Knockainey at Samhain Eve. When he arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mug Nuadat
In Irish mythological history Mug Nuadat (servant of NuadaDictionary of the Irish Language entry for ''mug'') son of Mug Neit, son of Derg, son of Dergthene, son of Enna Munchain, son of Loch Mor, son of Muiredach Mucna, son of Eochaid Garb, son of Dui Dalta Dedad was a legendary, supposed in the 2nd century AD. He was, according to later medieval tradition, a rival of the High King, |
Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year was into two parts, the summer half beginning at Bealtaine (May 1st) and the winter half at Samhain (November 1st) ... The festivals properly began at sunset on the day before the actual date, evincing the Celtic tendency to regard the night as preceding the day". marking the end of the harvest season and beginning of winter or "darker half" of the year. Celebrations begin on the evening of 31 October, since the Celtic day began and ended at sunset. This is about halfway between the autumnal equinox and winter solstice. It is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals along with Imbolc, Beltaine and Lughnasa. Historically it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland, Galicia and the Isle of Man (where it is spelled Sauin). A simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legendary Irish Kings
Legendary may refer to: * Legend, a folklore genre * Legendary (hagiography) ** Anjou Legendarium * J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium Film and television * ''Legendary'' (film), a 2010 American sports drama film * ''Legendary'', a 2013 film featuring Dolph Lundgren * ''Legendary'' (TV series), a 2020 American reality competition series * "Legendary" (''Legends of Tomorrow''), a television episode Music Albums * ''Legendary'' (AZ album), 2009 * ''Legendary'' (The Summer Set album) or the title song, 2013 * ''Legendary'' (TQ album) or the title song, 2013 * ''Legendary'' (Tyga album) or the title song, 2019 * ''Legendary'' (Z-Ro album), 2016 * ''Legendary'' (Zao album), 2003 * ''Legendary'', by Kaysha, 2006 * ''The Legendary'', an EP by the Roots, 1999 Songs * "Legendary" (Deadmau5 and Shotty Horroh song), 2017 * "Legendary" (Welshly Arms song), 2016 * "Legendary", by Alaska Thunderfuck from ''Anus'', 2015 * "Legendary", by Daya from '' Daya'', 2015 * "Legendary", by Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
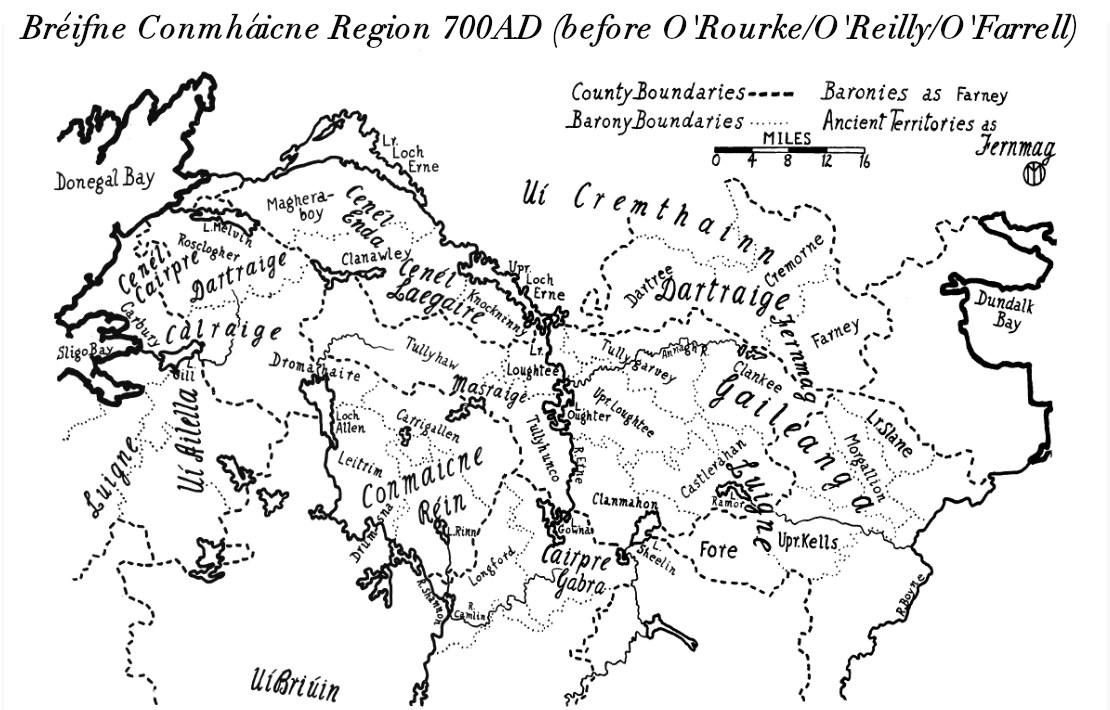
Luighne Connacht
Luighne Connacht was a territory located in north-central Connacht, on the borders of what is now County Mayo and County Sligo, Ireland. Origin The Luighne were a people, originally found in Brega, south of Kells in what is now County Meath. The baronies of Lune in Meath, and Leyney in Sligo, were called after them. According to Lambert McKenna (pp.xvi-xvii): ''"heyprobably acquired their land in Connacht as a reward for military service rendered to the tribes which had victoriously invaded that part of the country. Their migration ... and their settlement in Connacht are constantly referred to in the poems of this book" (see The Book of O'Hara) "and are the chief subject of the story of the Battle of Crionna; it evidently remained a very lively tradition among them even down to late times."'' According to this story, the Luighne accompanied Tadhg mac Cian, who ''"The genealogists brought Tadc and his descendants from Éli in northern Munster, but since we find the Luign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gailenga
Gailenga was the name of two related peoples and kingdoms found in medieval Ireland in Brega and Connacht. Origins Along with the Luighne, Delbhna, Saitne and Ciannachta, the Gailenga claimed descent from Tadc mac Cein mac Ailill Aulom. Francis John Byrne, in agreement with Eoin MacNeill, believes that ''"they were vassal tribes of fighting men whom the Connachta and Ui Neill ... planted on the lands they conquered."'' (IKHK, p. 69) While Byrne and MacNeill believed they originated in Connacht, recent research on the derivation of the term Connachta would indicate that they originated within Brega, and were transplanted west across the Shannon by the Connachta. A genealogy, cited by Geoffrey Keating, states: "Tadhg son of Cian, son of Oilill Olom, had two sons, namely, Connla and Cormac Gaileang. From Iomchaidh son of Connla comes O Cearbhaill, and from Fionnachta son of Connla comes O Meachair. From Cormac Gaileang son of Tadhg, son of Cian, comes O Eadhra and O Gadhra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nia Segamain
Nia Segamain, son of Adamair, was, according to medieval Irish legend and historical tradition, a High King of Ireland. He took power after killing his predecessor, Conall Collamrach. Geoffrey Keating says his mother was the presumed woodland goddess Flidais of the Tuatha Dé Danann, whose magic made wild does give milk as freely as domesticated cattle during his reign. He ruled for seven years, until he was killed by Énna Aignech. The ''Lebor Gabála'' synchronises his reign with that of Ptolemy VIII Physcon in Egypt (145–116 BC). The chronology of Keating's ''Foras Feasa ar Éirinn'' dates his reign to 226–219 BC, that of the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' to 320–313 BC. His name means "sister's son or champion of Segamon", and is perhaps related to Segomo, an ancient Gaulish deity equated in Roman times with Mars and Hercules. A slightly more historical Nia Segamain occurs in early Eóganachta pedigrees, and this is sometimes interpreted as evidence for the Gaulish origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. The earliest known references to the druids date to the 4th century BCE. The oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (50s BCE). They were described by other Roman writers such as Cicero, Cicero (44) I.XVI.90. Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st-century CE emperors Tiberius and Claudius, and had disappeare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deirgtine
The Deirgtine (Deirgthine, Dergtine, Dergthine), Clanna Dergthened or "Descendants of Dego Dergthened" were the proto-historical ancestors of the historical Eóganachta dynasties of Munster. Their origins are unclear but they may have been of fairly recent Gaulish derivation. Some evidence exists for their having been active in Roman Britain. History Legendary figures belonging to the Deirgtine include Mug Nuadat, Ailill Aulom, Éogan Mór, and Fiachu Muillethan. Though literary claims were later made that these early figures were rulers of Munster, their descendants did not in fact gain political supremacy over the established Dáirine or Corcu Loígde until the 7th century AD.Ó Corráin 2001 Among the famous tales from which the Deirgtine are known is the Cath Maige Mucrama. While kinship is not asserted, the Deirgtine are known to have had a close political relationship with the Déisi of Munster, who may have been their most important early facilitators. The names of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brehon Law
Early Irish law, historically referred to as (English: Freeman-ism) or (English: Law of Freemen), also called Brehon law, comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norman invasion of 1169, but underwent a resurgence from the 13th until the 17th century, over the majority of the island, and survived into Early Modern Ireland in parallel with English law. Early Irish law was often mixed with Christian influence and juristic innovation. These secular laws existed in parallel, and occasionally in conflict, with canon law throughout the early Christian period. The laws were a civil rather than a criminal code, concerned with the payment of compensation for harm done and the regulation of property, inheritance and contracts; the concept of state-administered punishment for crime was foreign to Ireland's early jurists. They show Ireland in the early medieval period to have been a hierarchical society, taking g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Áine
Áine () is an Irish goddess of summer, wealth and sovereignty. She is associated with midsummer and the sun,MacKillop, James (1998) ''Dictionary of Celtic Mythology'' Oxford: Oxford University Press pp.10, 16, 128 and is sometimes represented by a red mare. She is the daughter of Egobail,Cotterell, Arthur: ''The Encyclopedia of Mythology'', page 96. Hermes House, 2007. the sister of Aillen and/or Fennen, and is claimed as an ancestor by multiple Irish families. As the goddess of love and fertility, she has command over crops and animals and is also associated with agriculture. Áine is strongly associated with County Limerick. The hill of Knockainey ( ga, Cnoc Áine) is named after her, and was site of rites in her honour, involving fire and the blessing of the land, recorded as recently as 1879.Meehan, CarySacred Ireland/ref> She is also associated with sites such as Toberanna ( ga, Tobar Áine), County Tyrone; Dunany ( ga, Dun Áine), County Louth; Lissan ( ga, Lios Ái ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Leabhar Muimhneach
''An Leabhar Muimhneach'', also known as ''The Book of Munster'', is an Irish genealogical manuscript. ''An Leabhar Muimhneach'' is preserved in a number of 18th century manuscripts, the best being the work of the scribe Richard Tipper of Dublin, 1716-1717. Based on works compiled by Domhnall Ó Duinnín and Tadhg mac Dáire Mheic Bhruaideadha, in the early 17th century. A translation was made by Rev. Eugene O'Keeffe in 1703, and a complete scholarly edition by Tadhg Ó Donnchadha in 1940. Sources * ''The Celebrated Antiquary'', p. 156, Nollaig Ó Muraíle, Maynooth, 1996. References External links * Ó Donnchadha, Tadhg (ed.)''An Leabhar Muimhneach maraon le suim aguisíní''(''The Book of Munster''). Produced for the Irish Manuscripts Commission The Irish Manuscripts Commission was established in 1928 by the newly founded Irish Free State with the intention of furthering the study of Ireland's manuscript collections and archives. Its foundation was primarily motiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |