|
Oil Deposits
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as ''conventional'' and '' unconventional'' reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods. Oil field An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Map Software Screen Snapshot Of Isopach Map For 8500ft Deep OIL Reservoir With A Fault Line
Contour may refer to: * Contour (linguistics), a phonetic sound * Pitch contour * Contour (camera system), a 3D digital camera system * Contour, the KDE Plasma 4 interface for tablet devices * Contour line, a curve along which the function has a constant value * Contour drawing, an artistic technique * A closed path in the mathematical method of contour integration * Boundary (topology) of a set Contours may refer to: * Contours (album), ''Contours'' (album), by Sam Rivers * The Contours, a soul music group Contouring may refer to: * The makeup technique contouring Other uses * Ford Contour, a motor car * CONTOUR, a failed NASA space probe * Contour, a North Wing Apache ultralight aircraft variant See also * Contour fort, a type of British Iron Age hillfort * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraction Of Petroleum
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil drilling. Seismic surveys and other methods are used to locate oil reservoirs. Oil rigs and oil platforms are used to drill long holes into the earth to create an oil well and extract petroleum. After extraction, oil is refined to make gasoline and other products such as tires and refrigerators. Extraction of petroleum can be dangerous and have led to oil spills. Locating the oil field Geologists and geophysicists use seismic surveys to search for geological structures that may form oil reservoirs. The "classic" method includes making an underground explosion nearby and observing the seismic response, which provides information about the geological structures underground. However, "passive" methods that extract information from naturally occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
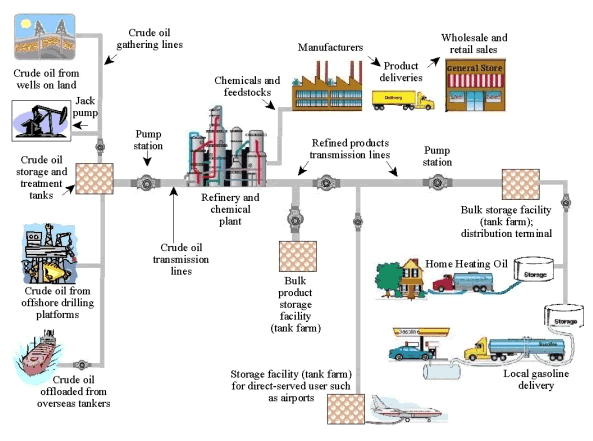
Midstream
The oil and gas industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream and downstream. The midstream sector involves the transportation (by pipeline, rail, barge, oil tanker or truck), storage, and wholesale marketing of crude or refined petroleum products. Pipelines and other transport systems can be used to move crude oil from production sites to refineries and deliver the various refined products to downstream distributors. Natural gas pipeline networks aggregate gas from natural gas purification plants and deliver it to downstream customers, such as local utilities. The midstream operations are often taken to include some elements of the upstream and downstream sectors. For example, the midstream sector may include natural gas processing plants that purify the raw natural gas as well as removing and producing elemental sulfur and natural gas liquids (NGL) as finished end-products. Service providers * Barge companies * Railroad companies * Trucki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil–water Separator
An oil water separator (OWS) is a piece of equipment used to separate oil and water mixtures into their separate components. There are many different types of oil-water separator. Each has different oil separation capability and are used in different industries. Oil water separators are designed and selected after consideration of oil separation performance parameters and life cycle cost considerations. "Oil" can be taken to mean mineral, vegetable and animal oils, and the many different hydrocarbons. Introduction Oil water separators can be designed to treat a variety of contaminants in water including free floating oil, emulsified oil, dissolved oil and suspended solids. Not all oil separator types are capable of separating all contaminants. The most common performance parameters considered are: * Oil droplet size (in the feed to the separator) * Oil density * Water viscosity (temperature) * Discharge water quality desired * Feed oil concentration and the range of oil concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Production
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil drilling. Seismic surveys and other methods are used to locate oil reservoirs. Oil rigs and oil platforms are used to drill long holes into the earth to create an oil well and extract petroleum. After extraction, oil is refined to make gasoline and other products such as tires and refrigerators. Extraction of petroleum can be dangerous and have led to oil spills. Locating the oil field Geologists and geophysicists use seismic surveys to search for geological structures that may form oil reservoirs. The "classic" method includes making an underground explosion nearby and observing the seismic response, which provides information about the geological structures underground. However, "passive" methods that extract information from naturally occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline (petrol). Petroleum is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic fragrances, and plastics. The industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream, and downstream. Upstream regards exploration and extraction of crude oil, midstream encompasses transportation and storage of crude, and downstream concerns refining crude oil into various end products. Petroleum is vital to many industries, and is necessary for the maintenance of industrial civilization in its current configuration, making it a critical concern for many nations. Oil accounts for a large percentage of the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, tunnels, water supply, sewerage, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications (including Internet access, Internet connectivity and Broadband, broadband access). In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing Commodity, commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal quality of life, living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment. Especially in light of the massive societal transformations needed to Climate change mitigation, mitigate and Climate change adaptation, adapt to climate change, contemporary infrastructure conversations frequently focus on sustainable development and gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halliburton
Halliburton Company is an American multinational corporation responsible for most of the world's hydraulic fracturing operations. In 2009, it was the world's second largest oil field service company. It has operations in more than 70 countries. It owns hundreds of subsidiaries, affiliates, branches, brands, and divisions worldwide and employs approximately 55,000 people. The company has dual headquarters located in Houston and in Dubai, and remains incorporated in the United States.''"Halliburton to Move Headquarters to Dubai"'' – '''' – |
Baker Hughes
Baker Hughes Company, organized in Delaware and headquartered in Houston, is one of the world's largest oil field services companies. The company provides products and services for oil well drilling, formation evaluation, completion, production, and reservoir consulting. It operates in over 120 countries, with research and manufacturing facilities in Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, India, Dubai, Saudi Arabia, Italy, Germany, Norway, Oklahoma, Louisiana and Missouri. From 2017 to 2020, the company was majority owned by General Electric (GE); however, GE no longer owns a material stake in the company. Divisions The company divides its organization into the following segments: * Oilfield Services - provides drilling, evaluation, completion, production, and intervention. * Oilfield Equipment - provides deepwater drilling equipment, subsea production systems, onshore wellheads, and related services. * Turbomachinery & Process Solutions - provides equipment and related services for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlumberger Limited
Schlumberger Limited (), doing business as SLB, is an oilfield services company. Schlumberger has four principal executive offices located in Paris, Houston, London, and The Hague. Schlumberger is the world's largest offshore drilling company. It is the biggest offshore drilling contractor (in terms of revenue) in the world. Schlumberger is incorporated in Willemstad, Curaçao as Schlumberger N.V. and trades on the New York Stock Exchange, Euronext Paris, the London Stock Exchange and SIX Swiss Exchange. Schlumberger is a Fortune Global 500 company, ranked 287 in 2016, and also listed in Forbes Global 2000, ranked 349 in 2022. History Schlumberger was founded in 1926 in Paris as the Electric Prospecting Company (french: Société de prospection électrique) by two brothers Conrad and Marcel Schlumberger from Alsace. Schlumberger supplies the petroleum industry with services such as seismic data processing, formation evaluation, well testing and directional drilling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weatherford International
Weatherford International plc, an American Irish public limited company, together with its subsidiaries, is a multinational oilfield service company and one of the largest companies in the world in oil services. Weatherford is a wellbore and production solutions company, providing equipment and services used in the drilling, evaluation, completion, production, and intervention of oil and natural gas wells. Many of the company's businesses, including those of predecessor companies, have been operating for more than 50 years. Weatherford conducts operations in 75 countries and maintains service and sales locations in virtually all the major oil and natural gas producing regions globally. In October 2020, Weatherford International announced Girish K. Saligram as the president and chief executive officer. Before joining Weatherford, Girish served Exterran Corporation as Chief Operating Officer. Girish previously served as President, Global Services, after joining the company in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esso
Esso () is a trading name for ExxonMobil. Originally, the name was primarily used by its predecessor Standard Oil of New Jersey after the breakup of the original Standard Oil company in 1911. The company adopted the name "Esso" (the phonetic pronunciation of Standard Oil's initials, 'S' and 'O'),Don't ignore history by Robert Sobel on Barro's, 7 Dec 1998 to which the other Standard Oil companies would later object. Standard Oil of New Jersey started marketing its products under the Esso brand in 1926. In 1972, the name Esso was largely replaced in the U.S. by the Exxon brand after the Standard Oil of New Jersey bought , while the Esso name remained widely used elsewhere. In most of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |