Midstream on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
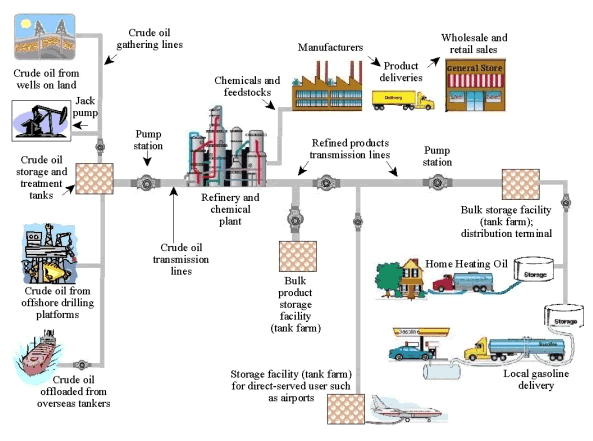
 The
The
3.1.27 midstream
business category involving the processing and
ISO 20815
accessed 6 June 2018 ::''Examples:
"NOV — Midstream Page"
{{petroleum-stub Business terms Petroleum transport Oil storage Natural gas Petroleum industry

 The
The oil and gas industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest ...
is usually divided into three major components: upstream
Upstream may refer to:
* Upstream (bioprocess)
* ''Upstream'' (film), a 1927 film by John Ford
* Upstream (networking)
* ''Upstream'' (newspaper), a newspaper covering the oil and gas industry
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream (software ...
, midstream and downstream. The midstream sector involves the transportation (by pipeline, rail, barge, oil tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk transport of oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined c ...
or truck), storage, and wholesale marketing of crude or refined petroleum products. Pipelines and other transport systems can be used to move crude oil from production sites to refineries
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.
Types of refineries
Different types of refineries ...
and deliver the various refined products to downstream distributors. Natural gas pipeline networks aggregate gas from natural gas purification plants and deliver it to downstream customers, such as local utilities.
The midstream operations are often taken to include some elements of the upstream and downstream sectors. For example, the midstream sector may include natural gas processing
Natural-gas processing is a range of industrial processes designed to purify raw natural gas by removing impurities, contaminants and higher molecular mass hydrocarbons to produce what is known as ''pipeline quality'' dry natural gas. Natural gas ...
plants that purify the raw natural gas as well as removing and producing elemental sulfur and natural gas liquids (NGL) as finished end-products.
Service providers
*Barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. ...
companies
* Railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
companies
* Trucking and hauling companies
* Pipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countr ...
companies
* Logistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
and technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scie ...
companies
* Transloading companies
* Terminal developers and operators
Midstream in ISO standards
ISO 20815 defines "midstream" in its definition section as:3.1.27 midstream
business category involving the processing and
transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipel ...
sectors of petroleum industry.ISOISO 20815
accessed 6 June 2018 ::''Examples:
transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipel ...
pipelines, terminals, gas processing and treatment, LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the vol ...
, LPG, and GTL.''See also
*Coal bed methane
Coalbed methane (CBM or coal-bed methane), coalbed gas, coal seam gas (CSG), or coal-mine methane (CMM) is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds. In recent decades it has become an important source of energy in United States, Canada, Au ...
* Downstream (petroleum industry)
The oil and gas industry is usually divided into three major sectors: upstream, midstream, and downstream. The downstream sector is the refining of petroleum crude oil and the processing and purifying of raw natural gas, as well as the market ...
* Extraction of petroleum
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil dr ...
* Gas field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presenc ...
* Hydrocarbon exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth using petroleum geology.
Exploration methods
Vi ...
* Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
* Natural gas condensate
Natural-gas condensate, also called natural gas liquids, is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. Some gas species within the raw natur ...
* Natural-gas processing
Natural-gas processing is a range of industrial processes designed to purify raw natural gas by removing impurities, contaminants and higher molecular mass hydrocarbons to produce what is known as ''pipeline quality'' dry natural gas. Natural gas ...
* Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
* Petroleum extraction
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil dr ...
* Oil production plant
An oil production plant is a facility which processes production fluids from oil wells in order to separate out key components and prepare them for export. Typical oil well production fluids are a mixture of oil, gas and produced water. An oil ...
* Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial processes, industrial process Factory, plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refining, refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt, asphalt ...
* Oil well
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas ma ...
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
The oil and gas industry is usually divided into three major sectors: upstream (or exploration and production - E&P), ''midstream'' and '' downstream''. The upstream sector includes searching for potential underground or underwater crude oil an ...
References
External links
"NOV — Midstream Page"
{{petroleum-stub Business terms Petroleum transport Oil storage Natural gas Petroleum industry