|
Oil City (Alberta)
Oil City is an epithet in the province of Alberta, Canada, derived from the province's first major oil well and subsequently used to refer to Northern Albertan cities such as Edmonton and Fort McMurray. The epithet has been employed in the branding of businesses throughout the province, and as of 2021, yellow pages in Alberta show that at least twenty businesses continue to use the epithet in their business names. Waterton In 1892, the site of western Canada's first producing oil well in Waterton Lakes National Park was named Oil City. Oil was struck just over 300 meters below the surface. Although the site was named in 1892, it was not until 1901 that extensive extraction took place under the leadership of Allan P. Patrick and John Leeson with the Rocky Mountain Development Company. By 1906 the oil well had stopped producing. In 2010, Ernest George Mardon wrote that "Oil City in Waterton National Park was a thriving community in 1902, but has totally disappeared." In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, divinities, objects, and binomial nomenclature. It can also be a descriptive title: for example, Pallas Athena, Phoebus Apollo, Alfred the Great, Suleiman the Magnificent, and Władysław I the Elbow-high. Many English monarchs have traditional epithets: some of the best known are Edward the Confessor, William the Conqueror, Richard the Lionheart, Æthelred the Unready, John Lackland and Bloody Mary. The word ''epithet'' can also refer to an abusive, defamatory, or derogatory phrase. This use as a euphemism is criticized by Martin Manser and other proponents of linguistic prescription. H. W. Fowler complained that "epithet is suffering a vulgarization that is giving it an abusive imputation." Linguistics Epithets are sometimes at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Hunter (ice Hockey)
William Dickenson "Wild Bill" Hunter, (May 5, 1920 – December 16, 2002) was a Canadian ice hockey player, general manager and coach. Hunter was involved in hockey, Canadian football, baseball, softball and curling, but he is best known for founding the Western Hockey League (WHL), being a key player in the upstart World Hockey Association (WHA) and for his efforts to bring professional hockey to previously overlooked Western Canadian cities, especially in Edmonton and (unsuccessfully) in Saskatoon. Early years Hunter was born in Saskatoon, the first of ten children and founded his first competitive sports team when he was 18. Hunter's Saskatoon Dukes football club eventually became the Saskatoon Hilltops. Hunter then attended Notre Dame College in Wilcox, Saskatchewan, from 1938 to 1940, where he managed the college baseball team. Following the outbreak of the Second World War Hunter left school to join the Royal Canadian Air Force and served for about four years as a pilot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
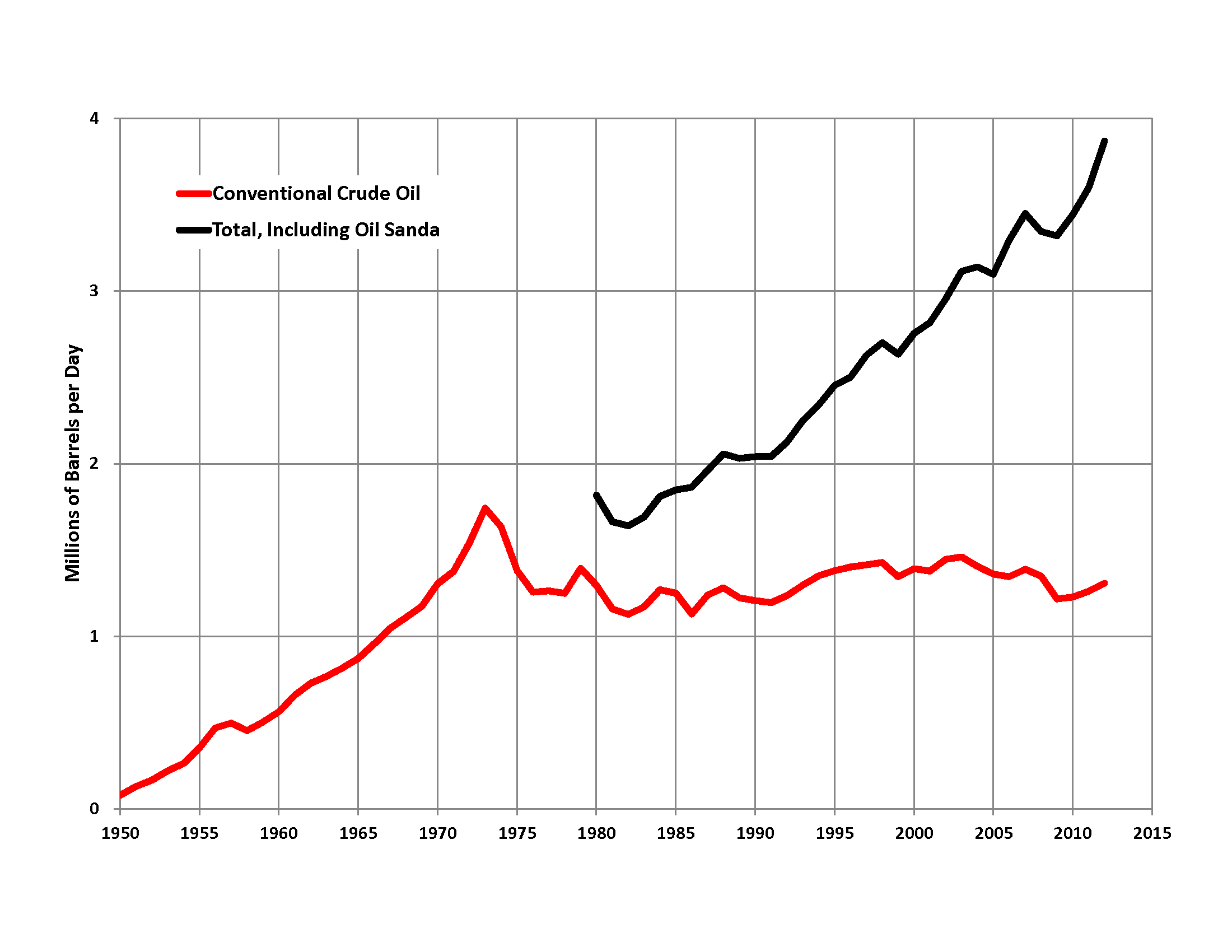
Petroleum Industry In Canada
Petroleum production in Canada is a major industry which is important to the economy of North America. Canada has the third largest oil reserves in the world and is the world's fourth largest oil producer and fourth largest oil exporter. In 2019 it produced an average of of crude oil and equivalent. Of that amount, 64% was upgraded from unconventional oil sands, and the remainder light crude oil, heavy crude oil and natural-gas condensate. Most of Canadian petroleum production is exported, approximately in 2019, with 98% of the exports going to the United States. Canada is by far the largest single source of oil imports to the United States, providing 43% of US crude oil imports in 2015. The petroleum industry in Canada is also referred to as the "Canadian Oil Patch"; the term refers especially to upstream operations (exploration and production of oil and gas), and to a lesser degree to downstream operations (refining, distribution, and selling of oil and gas products). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of City Nicknames And Slogans In Canada
This is a list of nicknames and slogans of cities in Canada. Many List of cities in Canada, Canadian cities and communities are known by various pseudonym, aliases, slogans, sobriquets, and other nicknames to the general population at either the local, regional, national, or international scales, often due to marketing campaigns and widespread usage in the media. Some nicknames are officially adopted by Municipal corporation, municipal governments, Destination marketing organization, tourism boards, or Chamber of commerce, chambers of commerce, while others are unofficial, and some are current while others are Obsolescence, antiquated. Some nicknames are positive, while others are Pejorative, derisive, disparaging or derogatory. City nicknames can help establish a civic identity, promote civic pride, build civic unity, market the community, and attract residents and businesses. They are also believed to have economic value, though their economic value is difficult to measure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Alberta
The economy of Alberta is the sum of all economic activity in Alberta, Canada's fourth largest province by population. Alberta's GDP in 2018 was CDN$338.2 billion. Although Alberta has a presence in many industries such as agriculture, forestry, education, tourism, finance, and manufacturing, the politics and culture of the province have been closely tied to the production of fossil energy since the 1940s. Alberta—with an estimated 1.4 billion cubic metres of unconventional oil resource in the bituminous oil sands—leads Canada as an oil producer. In 2018, Alberta's energy sector contributed over $71.5 billion to Canada's nominal gross domestic product. According to Statistics Canada, in May 2018, the oil and gas extraction industry reached its highest proportion of Canada's national GDP since 1985, exceeding 7% and "surpass ngbanking and insurance" with extraction of non-conventional oil from the oilsands reaching an "impressive", all-time high in May 2018. With conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Alberta Press
University of Alberta Press (UAlberta Press) is a publishing house and a division of the University of Alberta that engages in academic publishing. Overview UAlberta Press is situated in the Rutherford Library on the University of Alberta campus, located in Edmonton, Alberta, and publishes an average of between 15 and 25 books each year. The active title listing has approximately 450 titles, 440 of which are available digitally, as of 2017. History UAlberta Press was originally established as a department of the University of Alberta in 1969 and was one of several academic presses to be established in that decade. In 1974 it had grown to an annual budget of $5,000 and was run by three volunteers under the leadership of Leslie E.S. Gutteridge (1913–2000) who was appointed the first Press Director in 1977. In 1978 in response to the report of the Symons Royal Commission on Canadian Studies, the Alberta Provincial Government provided enough funding for the press to hire its firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Nikiforuk
Andrew Nikiforuk (born 1955) is a Canadian journalist and author. His writing has appeared in many outlets, including '' Saturday Night'', ''Maclean's'', ''Alberta Views'', ''Alternatives Journal'', and national newspapers. He has won multiple National Magazine Awards for his work. In 1990, the ''Toronto Star'' awarded him an Atkinson Fellowship in Public Policy to study AIDS and the failure of public health policy. He has also published numerous books, including ''Saboteurs: Wiebo Ludwig's War Against Oil,'' which won the Governor General's Award in 2002 and ''Tar Sands: Dirty Oil and the Future of a Continent'', which won the Rachel Carson Environment Book Award for 2008-09 from the Society of Environmental Journalists. In 2010, Nikiforuk became ''The Tyee'''s first writer in residence. Awards * 1989: Centre for Investigative Journalism Award in the ''magazine'' category for a 1988 article in ''Report on Business'' about the decline of the prairie wheat economy. * 1990: Centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Identity
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct culture. In this way, cultural identity is both characteristic of the individual but also of the culturally identical group of members sharing the same cultural identity or upbringing. Cultural identity is a fluid process that is changed by different social, cultural, and historical experiences. Some people undergo more cultural identity changes as opposed to others, those who change less often have a clear cultural identity. This means that they have a dynamic yet stable integration of their culture. There are three pieces that make up a persons cultural identity, these are cultural knowledge, category label, and social connections. Cultural knowledge is when a person connects to their identity through understanding their culture's core charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Ethics (journal)
''Environmental Ethics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the study of philosophical aspects of environmental problems. It was established in 1979 by Eugene Hargrove"How, When, Where, and Why", ''Environmental Ethics'', Volume 1, Issue 1 (Spring 1979), https://doi.org/10.5840/enviroethics1979111 and is published by the Center for Environmental Philosophy (University of North Texas). Production of the journal, subscriptions, and online access are managed by the Philosophy Documentation Center. Abstracting and indexing ''Environmental Ethics'' is abstracted and indexed in: * Abstracts in Environmental Management * Academic Search Premier * AgrIndex * ATLA Religion Database * Bibliography of Agriculture * BIOSIS Previews * Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences * Current Philosophy * Dow Jones Insight * Ecology Abstracts * Energy Abstracts * Environment Abstracts * Environment Index * Environmental Engineering Abstracts * Environmental Periodicals Bibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Identity
Place identity or place-based identity refers to a cluster of ideas about place and identity in the fields of geography, urban planning, urban design, landscape architecture, environmental psychology, ecocriticism and urban sociology/ecological sociology. Place identity is sometimes called urban character, neighbourhood character or local character. Place identity has become a significant issue in the last 25 years in urban planning and design. Place identity concerns the meaning and significance of places for their inhabitants and users, and how these meanings contribute to individuals' conceptualizations of self. Place identity also relates to the context of modernity, history and the politics of representation. In other words, historical determinism, which intersects historical events, social spaces and groups by gender, class, ethnicity. In this way, it explores how spaces have evolved over time by exploring the social constructs through time and the development of space, plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Alberta
The economy of Alberta is the sum of all economic activity in Alberta, Canada's fourth largest province by population. Alberta's GDP in 2018 was CDN$338.2 billion. Although Alberta has a presence in many industries such as agriculture, forestry, education, tourism, finance, and manufacturing, the politics and culture of the province have been closely tied to the production of fossil energy since the 1940s. Alberta—with an estimated 1.4 billion cubic metres of unconventional oil resource in the bituminous oil sands—leads Canada as an oil producer. In 2018, Alberta's energy sector contributed over $71.5 billion to Canada's nominal gross domestic product. According to Statistics Canada, in May 2018, the oil and gas extraction industry reached its highest proportion of Canada's national GDP since 1985, exceeding 7% and "surpass ngbanking and insurance" with extraction of non-conventional oil from the oilsands reaching an "impressive", all-time high in May 2018. With conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |