|
Ohrenbrücker Tor
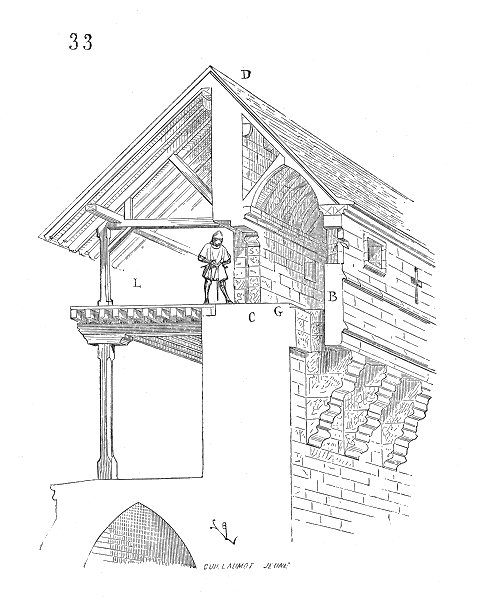
Ohrenbrücker Tor is the southwestern gate in the city wall of Ingelheim am Rhein. Etymology Ohrenbrücke is generally accepted to derive from the Obere Brücke (Upper bridge). During the Middle Ages only two bridges across the Selz existed: the "Lower Bridge" at the ancient Altengässer Tor and the "Upper Bridge" at the Ohrenbrücker Tor. Architecture The gate comprises two towers and a gothic arch. The northern tower had been reconstructed together with the arch in the middle of the 20th century. It is assumed that at the top of two of the towers, slender upright spires at the top of their buttresses existed. The gate was equipped with a machicolation above the arch. Both towers are decorated with Lombard band A Lombard band is a decorative blind arcade, usually located on the exterior of building. It was frequently used during the Romanesque and Gothic periods of Western architecture. It resembles a frieze of arches. Lombard bands are believed to ...s. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or Earthworks (military), earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls with Fortified tower, towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as ''letzis'' were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions representing the status and indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingelheim Am Rhein
Ingelheim (), officially Ingelheim am Rhein (), is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's left bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat since 1996. From the later half of the 8th century, the Ingelheim Imperial Palace, which served emperors and kings as a lodging and a ruling seat until the 11th century, was to be found here. Etymology The typically Rhenish-Hessian placename ending ''—heim'' might well go back to Frankish times, that is to say, likely as far back as the 5th or 6th century. Settlements or estates then took their lords’ names and were given this suffix, which means "home" in German. The name is recorded in later documents as ''Ingilinhaim'', ''Ingilinheim'' (782), ''Ingilenhaim'', ''Engelheim'', ''Hengilonheim'', ''Engilonheim'' (822), ''Engilinheim'' (826), ''Hingilinheim'' (855), ''Ingilunheim'' (874), ''Ingulinheim'' (889), ''Ingelesheim'' (891), ''Ingelenheim'' (940) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selz (river)
The Selz is a river in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, and a left hand tributary of the Rhine. It flows through the largest German wine region, Rheinhessen (Rhenish Hesse). It rises near the village of Orbis in the county of Donnersbergkreis, crosses the border from the Palatinate into Rhenish Hesse and after about the town of Alzey in the Alzey-Worms district. There the river passes a pond, and disappears underground, flowing through ditches under the town. On its way it passes through Gau-Odernheim, Nieder-Olm and Ingelheim, before finally discharging into the Rhine in , a district of Ingelheim. The Selz has a catchment area of characterised by a warm, dry climate with an average annual precipitation of around . Despite its low, and often irregular water flow, the Selz is regarded as the main river in the rather dry rolling countryside of Rhenish Hesse. During periods of low water, its waters consist of a significant amount of clean effluent from sewage farms. Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern Europe, Northern, Southern Europe, Southern and Central Europe, never quite effacing more classical styles in Italy. In the late 14th century, the sophisticated court style of International Gothic developed, which continued to evolve until the late 15th century. In many areas, especially Germany, Late Gothic art continued well into the 16th century, before being subsumed into Renaissance art. Primary media in the Gothic period included sculpture, panel painting, stained glass, fresco and illuminated manuscripts. The easily recognisable shifts in architecture from Romanesque to Gothic, and Gothic to Renaissance styles, are typically used to define the periods in art in all media, although in many ways figurative art developed at a different pace. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but structural load-bearing arches became popular only after their adoption by the Ancient Romans in the 4th century BC. Arch-like structures can be horizontal, like an arch dam that withstands the horizontal hydrostatic pressure load. Arches are usually used as supports for many types of vaults, with the barrel vault in particular being a continuous arch. Extensive use of arches and vaults characterizes an arcuated construction, as opposed to the trabeated system, where, like in the architectures of ancient Greece, China, and Japan (as well as the modern steel-framed technique), posts and beams dominate. Arches had several advantages over the lintel, especially in the masonry construction: with the same amount of material it can have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machicolation
In architecture, a machicolation () is an opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement through which defenders could target attackers who had reached the base of the defensive wall. A smaller related structure that only protects key points of a fortification are referred to as Bretèche. Machicolation, hoarding, bretèche, and murder holes are all similar defensive features serving the same purpose, that is to enable defenders atop a defensive structure to target attackers below. The primary benefit of the design allowed defenders to remain behind cover rather than being exposed when leaning over the parapet. They were common in defensive fortifications until the widespread adoption of gunpowder weapons made them obsolete. Etymology The word machicolation derives from Old French , mentioned in Medieval Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , mentioned in Medieval Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombard Band
A Lombard band is a decorative blind arcade, usually located on the exterior of building. It was frequently used during the Romanesque and Gothic periods of Western architecture. It resembles a frieze of arches. Lombard bands are believed to have been first used during the First Romanesque period, in the early 11th century. At that time, they were the most common architectural decorative motif for facades in regions such as Lombardy, Aragon and Catalonia. Arches of early Christian buildings of Ravenna, such as the Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, have been suggested as the origin of Lombard bands. See also * Lombard architecture * Lesene (low-relief pillars), another Lombardic element Similar-looking structures: * Corbel In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal keyed into and projecting from a wall to carry a wikt:superincumbent, bearing weight, a type of bracket (architecture), bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in t ...s * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gates In Germany
Gates is the plural of gate, a point of entry to a space which is enclosed by walls. It may also refer to: People * Gates (surname), various people with the last name * Gates Brown (1939-2013), American Major League Baseball player * Gates McFadden (born 1949), American actress and choreographer * Gates P. Thruston (1835-1912), American Civil War veteran, lawyer and businessman Places Canada * Gates, British Columbia, Canada, a rural community ** Gates River, a river in British Columbia ** Gates Valley, a valley in British Columbia ** Gates Lake, at the head of the Gates River United States * Gates, Nebraska, an unincorporated community * Gates, New York, a town ** Gates (CDP), New York, census-designated place * Gates, Oregon, a city * Gates, Tennessee, a town * Gates County, North Carolina, United States ** Gates, North Carolina, an unincorporated community in the county * Gates Pass, Arizona, a mountain pass Arts and entertainment * Gates (band), a post rock band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |