|
Ohawe
Ohawe or Ōhawe is a rural community in South Taranaki, New Zealand. It is located about 9 kilometres west of Hāwera, and south of State Highway 45. Ohawe is at the mouth of the Waingongoro River, where it reaches the South Taranaki Bight. The name means "place of a river bend", referring to the winding Waingongoro River. A coastal walk at low tide goes to Waihi Beach. History Māori settled in the area around 1300 CE. They hunted moa and other birds. Richard Taylor described it as "a regular necropolis" in 1843. In 1847, Walter Mantell realised that Māori and moa had lived in the area at the same time. In 1865, during the Second Taranaki War, General Duncan Cameron built redoubts on both sides of the Waingongoro river mouth. About 45 troops killed during the war are buried at Ohawe Soldiers' Cemetery. Demographics Ohawe is defined by Statistics New Zealand as a rural settlement that covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waingongoro River
The Waingongoro River is a river of the Taranaki Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows initially southeast from the slopes of Taranaki/Mount Egmont and passes through the town of Eltham before veering southwest to meet the Tasman Sea five kilometres west of Hawera, at Ohawe Ohawe or Ōhawe is a rural community in South Taranaki, New Zealand. It is located about 9 kilometres west of Hāwera, and south of State Highway 45. Ohawe is at the mouth of the Waingongoro River, where it reaches the South Taranaki Bight. ... Beach. The Normanby Power Station is located on the Waingongoro River at Normanby Road. See also * List of rivers of New Zealand References South Taranaki District Rivers of Taranaki Rivers of New Zealand {{Taranaki-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Mantell
Walter Baldock Durrant Mantell (11 March 1820 – 7 September 1895) was a 19th-century New Zealand naturalist, politician, and land purchase commissioner. He was a founder and first secretary of the New Zealand Institute, and a collector of moa remains. Early life Mantell was born in Lewes, Sussex, England, the son of geologists Gideon Mantell and Mary Ann Mantell (née Woodhouse). He arrived in Wellington on the ''Oriental'' in 1840. In 1848, Mantell was appointed to the office of commissioner for extinguishing native titles in the South Island. After his father committed suicide in 1852, much of his collection of fossils was inherited by Walter and consequently transported to New Zealand. Mantell left New Zealand as he did not feel right about trying to convince the indigenous Māori people to undersell their land and returned to England in 1856, where he met Geraldine Jewsbury, a woman eight years his senior. When in New Zealand, the Maori people called Mantell "Matara". Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Religion
Māori religion encompasses the various religious beliefs and practices of the Māori, the Polynesian indigenous people of New Zealand. Traditional Māori religion Traditional Māori religion, that is, the pre-European belief-system of the Māori, differed little from that of their tropical Eastern Polynesian homeland ( Hawaiki Nui), conceiving of everything - including natural elements and all living things - as connected by common descent through whakapapa or genealogy. Accordingly, Māori regarded all things as possessing a life force or mauri. Illustrating this concept of connectedness through genealogy are the major personifications dating from before the period of European contact: * Tangaroa was the personification of the ocean and the ancestor or origin of all fish. * Tāne was the personification of the forest and the origin of all birds. * Rongo was the personification of peaceful activities and agriculture and the ancestor of cultivated plants. (Some sources ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people with an estimated 60% of Māori pledging allegiance to the Christian message within the first 35 years. It remains New Zealand's largest religious group despite there being no official state church. Today, slightly less than half the population identify as Christian. The largest Christian groups are Catholic, Anglican and Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian services conducted in New Zealand were carried out by Father Paul-Antoine Léonard de Villefeix, the Dominican chaplain on the ship ''Saint Jean Baptiste'' commanded by the French navigator and explorer Jean-François-Marie de Surville. Villefeix was the first Christian minister to set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
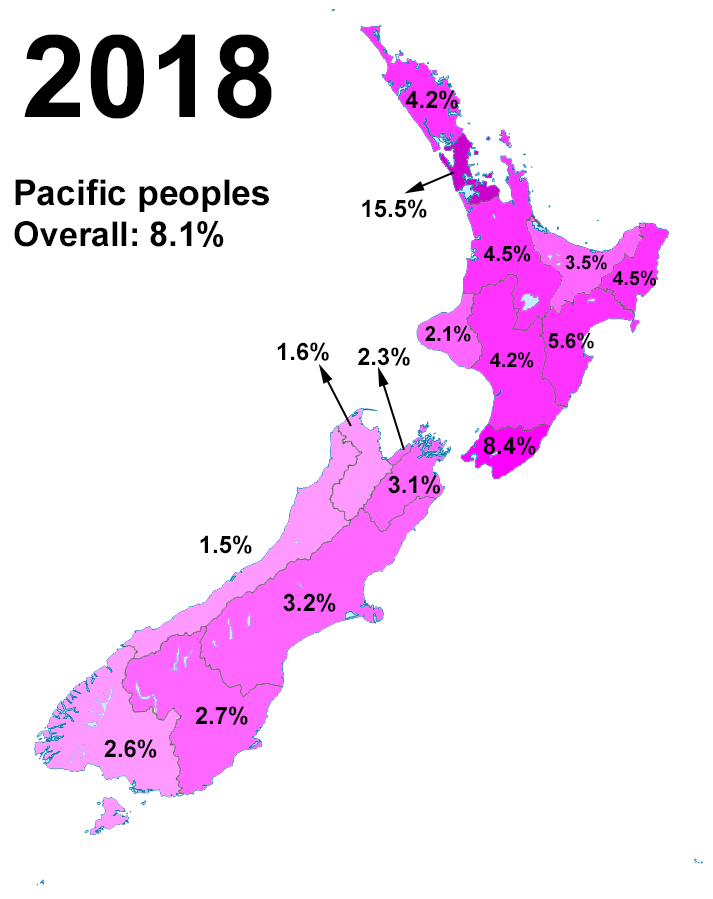
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands outside of New Zealand itself (also known as Pacific Islanders). They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European-descended Pākehā, indigenous Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. There are over 380,000 Pasifika people in New Zealand, with the majority living in Auckland. 8% of the population of New Zealand identifies as being of Pacific origin. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both Labour and National), migration officials, and special police squads targeted Pasifika illegal overstayers. Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Initial contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising tensions over disputed land sales led to conflict in the 1860s, and massive land confiscations, to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
Pākehā (or Pakeha; ; ) is a Māori term for New Zealanders primarily of European descent. Pākehā is not a legal concept and has no definition under New Zealand law. The term can apply to fair-skinned persons, or to any non-Māori New Zealander. Papa'a has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Historically before the arrival of other ethnic groups the word Māori meant 'ordinary' or 'normal'. The arrival of Europeans led to the formation of a new term to distinguish the self-regarded 'ordinary' or 'normal' Māori from the new arrivals. The etymology of the word ''Pākehā'' remains unclear, but the term was in use by the late-18th century. In December 1814 the Māori children at Rangihoua in the Bay of Islands were "no less eager to see the ''packaha'' than the grown folks". In Māori, plural noun-phrases of the term include (the definite article) and (the indefinite article). When the word was first adopted into English, the usual plural was 'Pakehas'. However, spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 New Zealand Census
The New Zealand Census of Population and Dwellings ( mi, Te Tatauranga o ngā Tāngata Huri Noa i Aotearoa me ō rātou Whare Noho) is a national population and housing census conducted by government department Statistics New Zealand every five years. There have been 34 censuses since 1851. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to local service providers. The 2018 census took place on Tuesday 6 March 2018. The next census is expected in March 2023. Census date Since 1926, the census has always been held on a Tuesday and since 1966, the census always occurs in March. These are statistically the month and weekday on which New Zealanders are least likely to be travelling. The census forms have to be returned by midnight on census day for them to be valid. Conducting the census Until 2018, census forms were hand-delivered by census workers during the lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 New Zealand Census
The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048, – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 2006 census. The 2013 census forms were the same as the forms developed for the 2011 census which was cancelled due to the February 2011 major earthquake in Christchurch. There were no new topics or questions. New Zealand's next census was conducted in March 2018. Collection methods The results from the post-enumeration survey showed that the 2013 census recorded 97.6 percent of the residents in New Zealand on census night. However, the overall response rate was 92.9 percent, with a non-response rate of 7.1 percent made up of the net undercount and people who were counted in the census but had not received a form. Results Population and dwellings Population counts for New Zealand regions. Note: All figures are for the census usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 New Zealand Census
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okaiawa
Okaiawa or Ōkaiawa is a rural community in South Taranaki, New Zealand. It is located about 14 kilometres north-west of Hāwera, north of State Highway 45 and State Highway 3. The settlement is located south-east of Mount Taranaki, close to Inaka River. According to the New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage, Okaiawa translates as place of food. ''Ō'' means "place of"; ''kai'' means "food"; and ''awa'' means "river or valley". History 19th century Okaiawa Public School was established in 1884. The original school house was built of wood and iron, with two classrooms, two porches, and a teachers' residence on site. The school could accommodate a roll of 120 children. Frank Bremer, a Taranaki farmer originally from Adelaide, purchased a property in Okaiawa in 1890. His farm covered 284 acres of freehold land and 316 of leasehold land. He became a breeder of high-class draught horses which won several races, was president of the local racing club, and milked about 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |