|
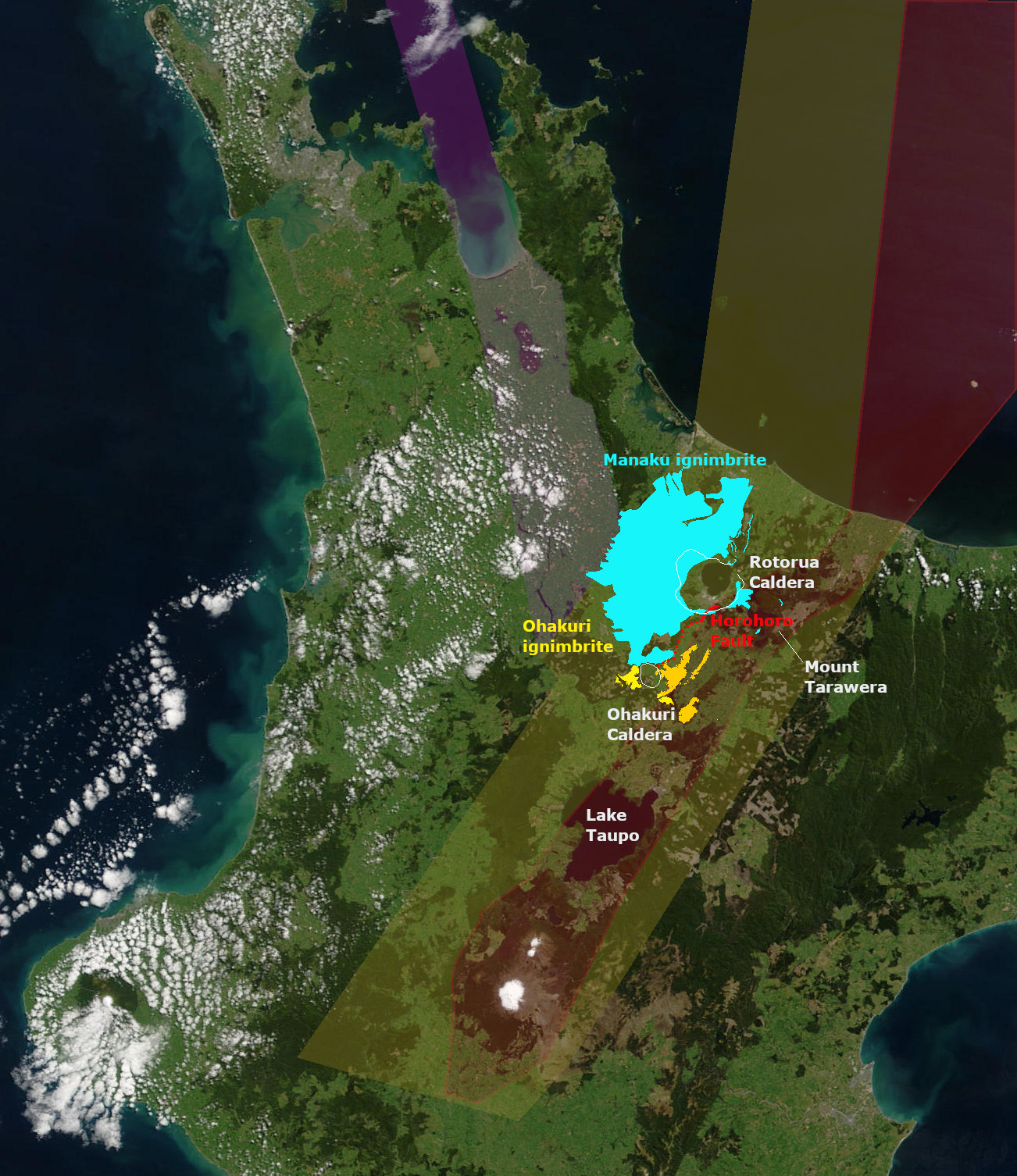
Ohakuri Caldera
The Ohakuri Caldera was formed in a paired single event eruption of Ohakuri ignimbrite and is located in the Taupo Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand. Its significance was first recognised in 2004, as the geology of the area had been misunderstood until then. The paired eruption resulted in a very large eruption sequence in the Taupō Volcanic Zone about 240,000 years ago that included the formation of Lake Rotorua. Geography The Ohakuri Caldera lies mainly to the east and north of the Atiamuri Dam and extends almost to the Ohakuri Dam. Its borders are ill-defined, particularly the northern and eastern borders, possibly because later volcanotectonic activity has completely replaced landforms that could have at one stage included a lake extending almost from Lake Rotorua to this caldera. Its western border is believed to be defined by the valley of the Mangaharakeke stream that the main highway uses and towards the north west of Atiamuri the caldera floor extends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horohoro Fault
The Horohoro Fault is in the old Taupō Rift of the central North Island of New Zealand and is associated with the spectacular Horohoro cliffs. Geology Just south of Lake Rotorua, Horohoro mountain, a rhyolite dome, has very high cliffs in an apparent fault scarp that defines the western edge of the lower lying Paeroa Garben and its northern Kapenga Caldera. The Paeroa Garben's eastern edge is defined by the Paeroa Fault. The cliffs are composed of Mamaku ignimbrite from the Rotorua Caldera eruption and older ignimbrites and Rotorua rhyolite. This fault area of the Taupō Rift is controversial as the components of historic tectonic and volcanic contribution have led to debate. Some authors have also extended and widened the definition of the Ngakuru Graben, which is to the south, during this debate. The northern portion of the fault for the last 20,000 years is displacing at a low rate of up to 0.2 mm/yr but it is unknown if the southern portion is active. The far north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In New Zealand
This is a partial list of active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes in New Zealand. Kermadec Arc and Havre Trough North Island Taupō Volcanic Zone Elsewhere Mangakino Culdera South Island Other Ross Dependency New Zealand also has ''de facto'' administration over Ross Dependency in Antarctica, which contains the following volcanoes: References External links {{GeoGroupTemplateNew Zealand's Volcanoesat GNS Science New Zealand Volcanoes Volcanoes Geography of the Kermadec Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompassing Rotorua and several other nearby towns. Rotorua has an estimated resident population of , making it the country's 12th largest urban area, and the Bay of Plenty's second largest urban area behind Tauranga. Rotorua is a major destination for both domestic and international tourists; the tourism industry is by far the largest industry in the district. It is known for its geothermal activity, and features geysers – notably the Pōhutu Geyser at Whakarewarewa – and hot mud pools. This thermal activity is sourced to the Rotorua Caldera, in which the town lies. Rotorua is home to the Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology. History The name Rotorua comes from the Māori language, where the full name for the city and lake is . ''Roto'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a Planetary core, core and above by a Crust (geology), crust. Mantles are made of Rock (geology), rock or Volatiles, ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone planetary differentiation, differentiation by density. All Terrestrial planet, terrestrial planets (including Earth), a number of Asteroid, asteroids, and some planetary Natural satellite, moons have mantles. Earth's mantle The Earth's mantle is a layer of Silicate minerals, silicate rock between the Crust (geology), crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in Geologic time scale, geological time it behaves as a Viscosity, viscous fluid. Partial melting of the mantle at mid-ocean ridges produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surrounding atmosphere. New Zealand geologist Patrick Marshall (1869-1950) coined the term ''ignimbrite'' from the Latin ''igni-'' [fire] and ''imbri-'' [rain]. Ignimbrites are made of a very poorly sorted mixture of volcanic ash (or tuff when Lithification, lithified) and pumice lapilli, commonly with scattered lithic fragments. The ash is composed of glass shards and crystal fragments. Ignimbrites may be loose and unconsolidated, or lithified (solidified) rock called lapilli-tuff. Near the volcanic source, ignimbrites often contain thick accumulations of lithic blocks, and distally, many show meter-thick accumulations of rounded cobbles of pumice. Ignimbrites may be white, grey, pink, beige, brown, or black depending on their composition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua Caldera
The Rotorua Caldera, now in filled with Lake Rotorua, is a large rhyolitic caldera. It is one of several large volcanoes located in the Taupō Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand. Geography The major regional settlement of Rotorua is located in the caldera. There is geothermal activity in the city of Rotorua and the geothermal areas of Tikitere and Whakarewarewa are associated with the caldera. These areas are still associated with small hydrothermal eruptions. Geology Eruption history The caldera was formed in a single event paired List of large volcanic eruptions, major eruption, that lasted only weeks, is now dated about 240,000 years ago, and which ejected more than of rhyolitic Mamaku ignimbrite giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7. The eruption has been reinterpreted as a paired eruption with a very slightly later, slightly smaller southerly eruption from the same mush body feeding the Ohakuri Caldera. Ignimbrite, up to thick covering about , was depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohakuri
Ohakuri is a rural community in the Taupō District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It features the Orakei Korako Geothermal Area, the artificial Lake Ohakuri and the Ohakuri Dam. The area also includes Maroanui Marae, a meeting place of the local Ngāti Tūwharetoa hapū of Ngāti Hinerau. It features a meeting house of the same name. The marae was renovated between 2008 and 2010, with a grant from the nearby Wairakei Power Station. The renovations included wheelchair ramps and accessible toilets for disabled members of the hapū. Demographics Ohakuri statistical area, which also includes Ātiamuri and Oruanui, covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Ohakuri statistical area had a population of 1,842 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 171 people (10.2%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 408 people (28.5%) since the 2006 census. There were 654 households, comprising 963 males an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paeroa Fault
The Paeroa Fault is a seismically active area in the Taupō District, Waikato, Waikato Region of the central North Island of New Zealand. Geology North of Lake Taupō, volcanic ignimbrite at least thick, and called the Paeroa Ignimbrite (dated to 339 ± 5 ) is exposed along the very steep fault scarp of the Paeroa Fault that defines the western flank of the high Paeroa Range. The Paeroa Ignimbrite appears to have been erupted from a linear vent alignment parallel to the current Paeroa Range and fault. This fault area of the Taupo Rift is displacing at a rate of /year. At the north eastern end of the fault is the geothermally active Maungaongaonga volcano that with the fault defines the far south western border of the :Okataina Volcanic Centre, Ōkataina Volcanic Centre. The Ngapouri-Rotomahana Fault too extends to the Ōkataina Caldera and is a splay from the Paeroa Fault. The southern portion of the fault is associated with the raised Paeroa Fault block immediately to its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |