|
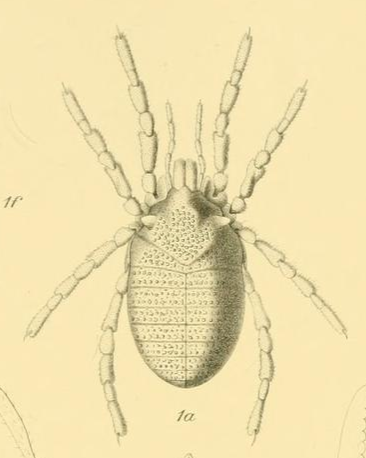
Ogovea Grossa Original Illustration
Ogoveidae is a family of Opiliones, harvestmen with three described species in one genus, ''Ogovea'', which is found in equatorial West Africa. Name The name of the genus giving the family its name refers to the river Ogooué, where the type species was found. The genus was originally named ''Ogovia'' Hansen & William Sørensen, Sørensen, 1904, but later renamed ''Ogovea'' Roewer, 1923,Pinto-da-Rocha, Ricardo; Machado, Glauco; Giribet, Gonzalo (2007)''Harvestmen: The Biology of Opiliones'' Harvard University Press. . as the original name already belonged to a genus of Noctuid moths. Description Ogoveidae are moderately sized Cyphophthalmi, at 3.4 to 5 mm long, and dark reddish-brown in color as adults. Like most members of the Sternophthalmi, they are completely eyeless, exhibit opisthosomal exocrine glands located on the sternum, and possess a complete ''corona analis'' (fusion of sternites 8 & 9, and tergite 9), as well as laterally projecting ozophores. Their body is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Original Illustration Of Ogovea Nasuta
Originality is the aspect of created or invented works that distinguish them from reproductions, clones, forgeries, or substantially derivative works. The modern idea of originality is according to some scholars tied to Romanticism, by a notion that is often called romantic originality.Smith (1924)Waterhouse (1926)Macfarlane (2007) The validity of "originality" as an operational concept has been questioned. For example, there is no clear boundary between "derivative" and "inspired by" or "in the tradition of." The concept of originality is both culturally and historically contingent. For example, unattributed reiteration of a published text in one culture might be considered plagiarism but in another culture might be regarded as a convention of veneration. At the time of Shakespeare, it was more common to appreciate the similarity with an admired classical work, and Shakespeare himself avoided "unnecessary invention".Royal Shakespeare Company (2007) ''The RSC Shakespeare - Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Equatorial Africa
French Equatorial Africa (french: link=no, Afrique-Équatoriale française), or the AEF, was the federation of French colonial possessions in Equatorial Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River into the Sahel, and comprising what are today the countries of Chad, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, and Gabon. History Established in 1910, the Federation contained four (later five) colonial possessions: French Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari and French Chad. The Governor-General was based in Brazzaville with deputies in each territory. In 1911, France ceded parts of the territory to German Kamerun as a result of the Agadir Crisis. The territory was returned after Germany's defeat in World War I, while most of Cameroon proper became a French League of Nations mandate not integrated into the AEF. French Equatorial Africa, especially the region of Ubangi-Shari had a similar concession system as the Congo Free State and similar atrocities were also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogovea Grossa Original Illustration
Ogoveidae is a family of Opiliones, harvestmen with three described species in one genus, ''Ogovea'', which is found in equatorial West Africa. Name The name of the genus giving the family its name refers to the river Ogooué, where the type species was found. The genus was originally named ''Ogovia'' Hansen & William Sørensen, Sørensen, 1904, but later renamed ''Ogovea'' Roewer, 1923,Pinto-da-Rocha, Ricardo; Machado, Glauco; Giribet, Gonzalo (2007)''Harvestmen: The Biology of Opiliones'' Harvard University Press. . as the original name already belonged to a genus of Noctuid moths. Description Ogoveidae are moderately sized Cyphophthalmi, at 3.4 to 5 mm long, and dark reddish-brown in color as adults. Like most members of the Sternophthalmi, they are completely eyeless, exhibit opisthosomal exocrine glands located on the sternum, and possess a complete ''corona analis'' (fusion of sternites 8 & 9, and tergite 9), as well as laterally projecting ozophores. Their body is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaoundé
Yaoundé (; , ) is the capital of Cameroon and, with a population of more than 2.8 million, the second-largest city in the country after the port city Douala. It lies in the Centre Region of the nation at an elevation of about 750 metres (2,500 ft) above sea level. The outpost of Epsumb or Jeundo was founded between the Nyong and Sanaga rivers at the northern edge of the area's forests in 1887 by German explorers as a trading base for rubber and ivory. A military garrison was built in 1895 which enabled further colonization. After Imperial Germany's defeat in World War I, France held eastern Cameroon as a mandate, and Yaoundé was chosen to become the capital of the colony in 1922. Douala remained the more important settlement, but Yaoundé saw rapid growth and continued as the seat of government for the Republic of Cameroon upon its independence in 1960. Most of Yaoundé's economy is still centred on the administrative structure but major industries in Yaoundé inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troglosironidae
Troglosironidae is a family of harvestmen with seventeen described species in a single genus, ''Troglosiro'', which is found on the island of New Caledonia, in the Pacific Ocean. Name The name of the genus giving the family its name is a combination of Ancient Greek ''troglos'' "cave", and the harvestman genus '' Siro,'' a reference to the habitat of the type specimen. Despite this, the genus does not appear to be adapted for a troglobitic lifestyle, and subsequent specimens have been collected from Berlesate (soil samples run through a Berlese Funnel). Description Troglosironidae are 1.7 to 2.5 mm long and eyeless. They have mostly smooth, robust chelicerae, with or without a dorsal crest on the basal segment. They have laterally projecting ozophores, tarsal claws on the second pair of legs with a row of teeth, no opisthosomal median furrow, and a lamelliform adenostyle. The coxae 2 are not fused to the coxae 3, but sternites 8 and 9, and tergite 9, are all fused together, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogoveidae
The Neogoveidae are a family of harvestmen with 27 described species in eight genera. However, eight species of ''Huitaca (harvestman), Huitaca'', 17 species of ''Metagovea'' and 12 species of ''Neogovea'' are currently awaiting description. Name The name is a combination of Ancient Greek ''neo'' "new" and Ogoveidae, a previously described family of Cyphophthalmi that is closely related to Neogoveidae. Description Neogoveidae are 1 to 4.5 mm long and eyeless. They often exhibit a solea (modified area with a high concentration of sensory setae) on the first pair of Arthropod leg, tarsi. Their chelicerae are smooth, with a dorsal crest and ventral process, and can be either short and robust or long and antennuate. They possess laterally projecting ozophores, tarsal claws on the second pair of legs with a row of teeth, tarsal claws on the third and fourth pairs of legs often with small pegs, and an inconspicuous or absent opisthosomal median furrow. The adenostyle is variable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huitaca (harvestman)
''Huitaca'' is a genus of harvestmen belonging to the family Ogoveidae. The species of this genus are found in Southern America. Species: *''Huitaca bitaco'' *''Huitaca boyacaensis'' *'' Huitaca caldas'' *'' Huitaca depressa'' *'' Huitaca sharkeyi'' *'' Huitaca tama'' *''Huitaca ventralis Huitaca may refer to: * Huitaca (goddess) Huitaca or Xubchasgagua was a rebelling goddess in the religion of the Muisca.Ocampo López, 2013, Ch. 6, p.45 The Muisca and their confederation were a civilization who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboya ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q5904775 Harvestmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |