|
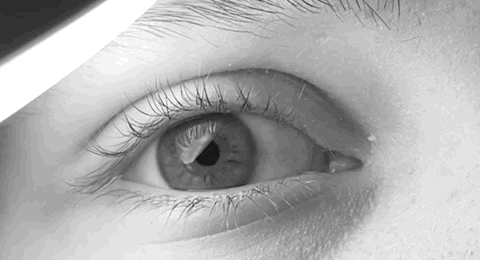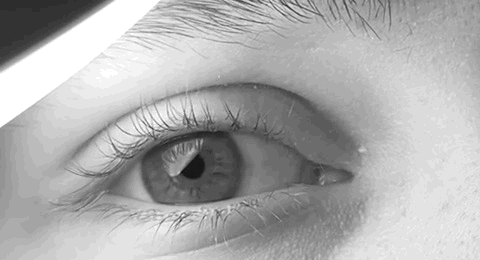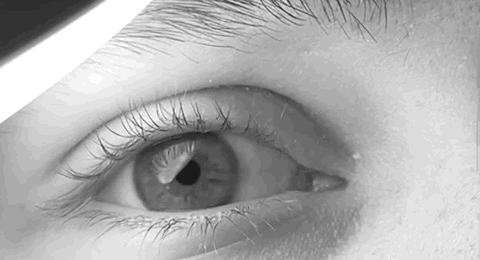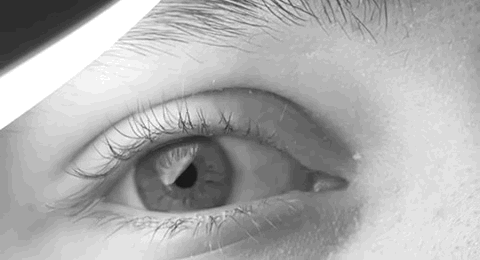
Ocular Flutter
Ocular flutter is an opsoclonic disorder that results in horizontal saccades. It is caused by damage to the brainstem paramedian pontine reticular formation cells or the cerebellar neurons controlling those cells. See also * Nystagmus * Opsoclonus Opsoclonus refers to uncontrolled, irregular, and nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements without inter-saccadic intervals. It is a ... References Vision {{Eye-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsoclonus
Opsoclonus refers to uncontrolled, irregular, and nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements without inter- saccadic intervals. It is also referred to as saccadomania or reflexive saccade. The movements of opsoclonus may have a very small amplitude, appearing as tiny deviations from primary position. Possible causes of opsoclonus include neuroblastoma and encephalitis in children, and breast, lung, or ovarian cancer in adults. Other considerations include multiple sclerosis, toxins, medication effects (e.g. Serotonin Syndrome), celiac disease, certain infections (West Nile virus, Lyme disease), non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and renal adenocarcinoma. It can also be caused by a lesion in the omnipause neurons which tonically inhibit initiation of saccadic eye movement (until signaled by the superior colliculus) by blocking paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) burst neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccades
A saccade ( , French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. In contrast, in smooth pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. The phenomenon can be associated with a shift in frequency of an emitted signal or a movement of a body part or device. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for fixation, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many animals do not look at a scene in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation
The paramedian pontine reticular formation, also known as PPRF or paraabducens nucleus, is part of the pontine reticular formation, a brain region without clearly defined borders in the center of the pons. It is involved in the coordination of eye movements, particularly horizontal gaze and saccades. Input, output, and function The PPRF is located anterior and lateral to the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). It receives input from the superior colliculus via the predorsal bundle and from the frontal eye fields via frontopontine fibers. The rostral PPRF probably coordinates vertical saccades; the caudal PPRF may be the generator of horizontal saccades. In particular, activity of the excitatory burst neurons (EBNs) in the PPRF generates the "pulse" movement that initiates a saccade. In the case of horizontal saccades the "pulse" information is conveyed via axonal fibres to the abducens nucleus, initiating lateral eye movements. The angular velocity of the eye during horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opsoclonus
Opsoclonus refers to uncontrolled, irregular, and nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements without inter- saccadic intervals. It is also referred to as saccadomania or reflexive saccade. The movements of opsoclonus may have a very small amplitude, appearing as tiny deviations from primary position. Possible causes of opsoclonus include neuroblastoma and encephalitis in children, and breast, lung, or ovarian cancer in adults. Other considerations include multiple sclerosis, toxins, medication effects (e.g. Serotonin Syndrome), celiac disease, certain infections (West Nile virus, Lyme disease), non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and renal adenocarcinoma. It can also be caused by a lesion in the omnipause neurons which tonically inhibit initiation of saccadic eye movement (until signaled by the superior colliculus) by blocking paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) burst neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |