|
Octopus Kaurna
''Octopus kaurna'', also known as the southern sand octopus, is an octopus native to the waters around the Great Australian Bight and Tasmania. It has an arm span of up to with long, unusually thin tentacles joined at the base by webbing and studded with small suckers. The species was first identified by Timothy Nathaniel Stranks. Kaurna is the name of an Australian Aboriginal clan which lived in the Adelaide region of South Australia. Behaviour Unlike most octopuses, ''O. kaurna'' lacks color-changing Chromatophore, chromatophors. However, it is able to hide from predators by burrowing itself in sand. The process begins with the octopus using its Siphon (mollusc), siphon to inject water into the sand, creating quicksand-like conditions which enable burrowing. Then, it uses its arms to burrow into the sand. Two arms will be extended to the surface, creating a ventilation shaft. At the same time, ''O. kaurna'' will use mucus to stabilize the shape of the burrow. Finally, the oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various regions of the ocean, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Australian Bight
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern coastline of mainland Australia. Extent Two definitions of the extent are in use – one used by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and the other used by the Australian Hydrographic Service (AHS). The IHO defines the Great Australian Bight as having the following limits: ''On the North.'' The south coast of the Australian mainland. ''On the South.'' A line joining West Cape Howe () Australia to South West Cape, Tasmania. ''On the East.'' A line from Cape Otway, Victoria to King Island and thence to Cape Grim, the northwest extreme of Tasmania. The AHS defines the bight with a smaller area, from Cape Pasley, Western Australia, to Cape Carnot, South Australia - a distance of . Much of the bight lies due south of the expansive Nullarbor Plain, which straddles South Australia and Western Australia. The Eyre Highway passes close to the cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
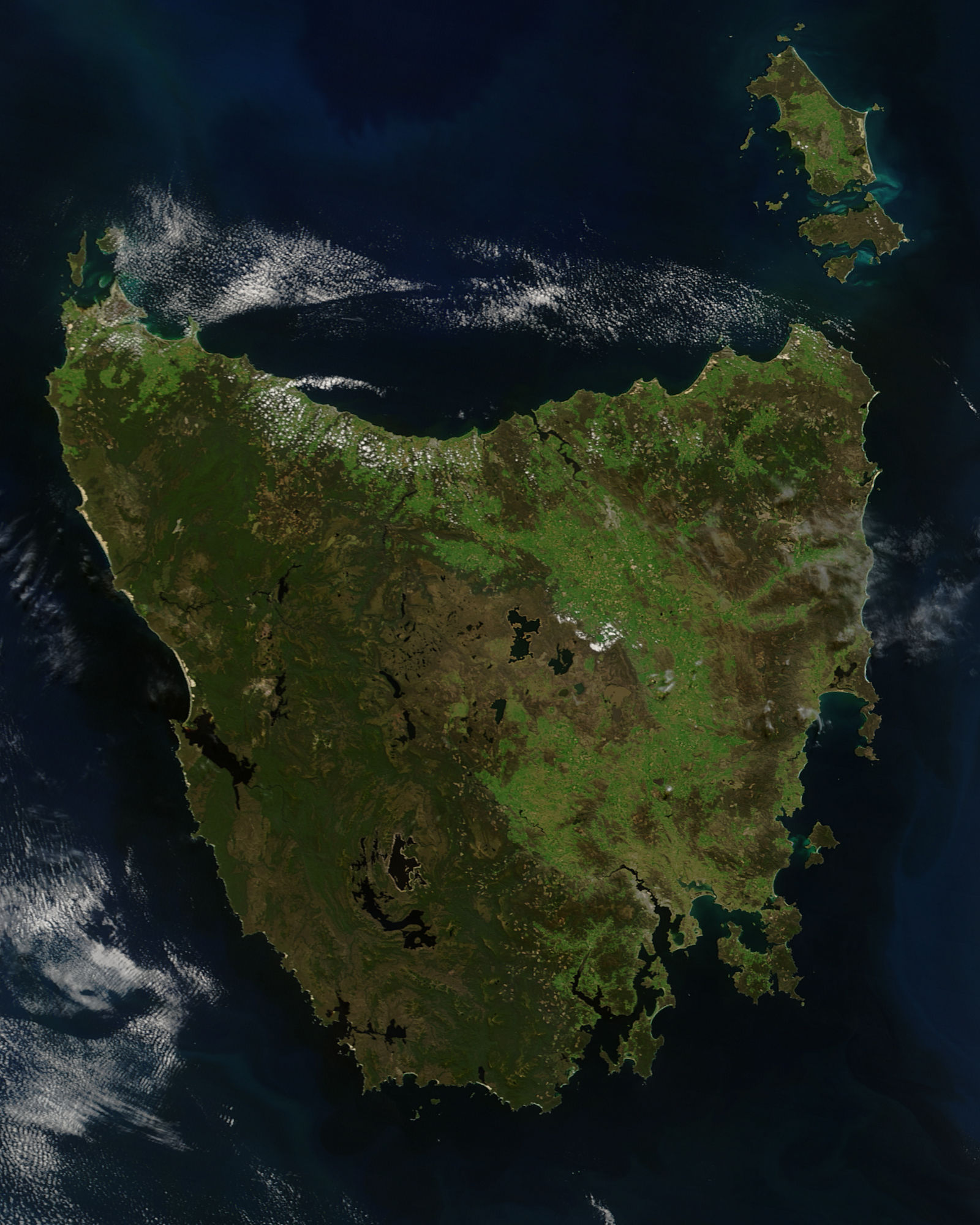
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Faunal Directory
The Australian Faunal Directory (AFD) is an online catalogue of taxonomic and biological information on all animal species known to occur within Australia. It is a program of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water of the Government of Australia. By May 12, 2021, the Australian Faunal Directory has collected information about 126,442 species and subspecies In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species .... It includes the data from the discontinued ''Zoological Catalogue of Australia'' and is regularly updated. Started in the 1980s, it set a goal to compile a "list of all Australian fauna including terrestrial vertebrates, ants and marine fauna" and create an "Australian biotaxonomic information system".''Commonwealth Record'', Volume 5, Issues 26-34, p. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of The Environment, Water, Heritage And The Arts
The Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts was an Australian Government department that existed between December 2007 and September 2010. Scope Information about the department's functions and/or government funding allocation could be found in the Administrative Arrangements Orders, the annual Portfolio Budget Statements and in the department's annual reports. According to the Administrative Arrangements Order (AAO) made at the department's establishment, the department dealt with: *Environment protection and conservation of biodiversity *Air quality *National fuel quality standards *Land contamination *Meteorology *Administration of the Australian Antarctic Territory, and the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands *Natural, built and movable cultural heritage *Environmental research *Water policy and resources *Cultural affairs, including support for the arts **There was a domestic Return of Indigenous Cultural Property (RICP) program run by DEWHA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are Biological pigment, pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for animal coloration, coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye color, eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly "hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescence, iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon (mollusc)
A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda (members of these classes include saltwater and freshwater snails, clams, octopus, squid and relatives). Siphons in molluscs are tube-like structures in which water (or, more rarely, air) flows. The water flow is used for one or more purposes such as locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction. The siphon is part of the mantle of the mollusc, and the water flow is directed to (or from) the mantle cavity. A single siphon occurs in some gastropods. In those bivalves which have siphons, the siphons are paired. In cephalopods, there is a single siphon or funnel which is known as a hyponome. In gastropods In some (but not all) sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon, or inhalant siphon, through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill for respiration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quicksand
Quicksand is a colloid A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ... consisting of fine granular material (such as sand, silt or clay) and water. It forms in saturated loose sand when the sand is suddenly agitated. When water in the sand cannot escape, it creates a Liquefaction, liquefied soil that loses strength and cannot support weight. Quicksand can form in standing water or in upward flowing water (as from an Artesian aquifer, artesian spring). In the case of upward flowing water, effective stress, forces oppose the force of gravity and suspend the soil particles. The saturated sediment may appear quite solid until a sudden change in pressure or shock initiates liquefaction. This causes the sand to form a suspension and lose strength. The cushioning of water gives quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopodidae
The Octopodidae comprise the family containing the majority of known octopus species. Genera The World Register of Marine Species lists these genera: *'' Abdopus'' Norman & Finn, 2001 *'' Ameloctopus'' Norman, 1992 *'' Amphioctopus'' P. Fischer, 1882 *'' Callistoctopus'' Taki, 1964 *'' Cistopus'' Gray, 1849 *'' Euaxoctopus'' Voss, 1971 *'' Galeoctopus'' Norman, Boucher & Hochberg, 2004 *'' Grimpella'' Robson, 1928 *'' Hapalochlaena'' Robson, 1929 *'' Histoctopus'' Norman, Boucher-Rodoni & Hochberg, 2009 *'' Lepidoctopus'' Haimovici & Sales, 2019 *'' Macrochlaena'' Robson, 1929 *''Macroctopus'' Robson, 1928 *'' Macrotritopus'' Grimpe, 1922 *''Octopus'' Cuvier, 1798 *'' Paroctopus'' Naef, 1923 *''Pinnoctopus ''Pinnoctopus'' is a genus of octopuses in the family (biology), family Octopodidae. It is of doubtful validity. Species * ''Pinnoctopus cordiformis'' (Jean René Constant Quoy, Quoy and Joseph Paul Gaimard, Gaimard, 1832. ''nomen dubium'' * '' ...'' d'Orbigny, 1845 *'' Pt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs Of The Pacific Ocean
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopods Of Australia
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been identified. Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)