|
Ochrolechia Minuta
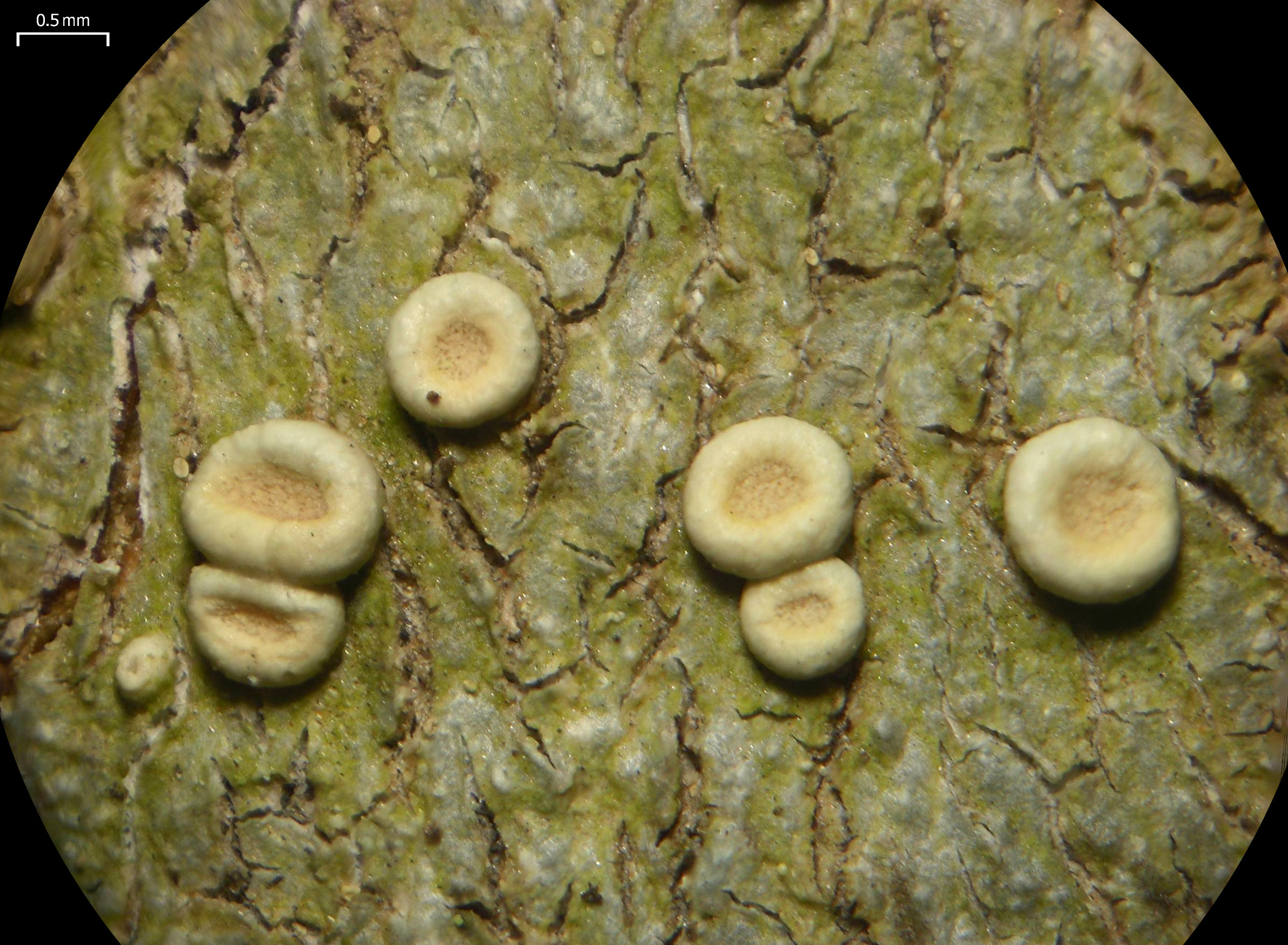
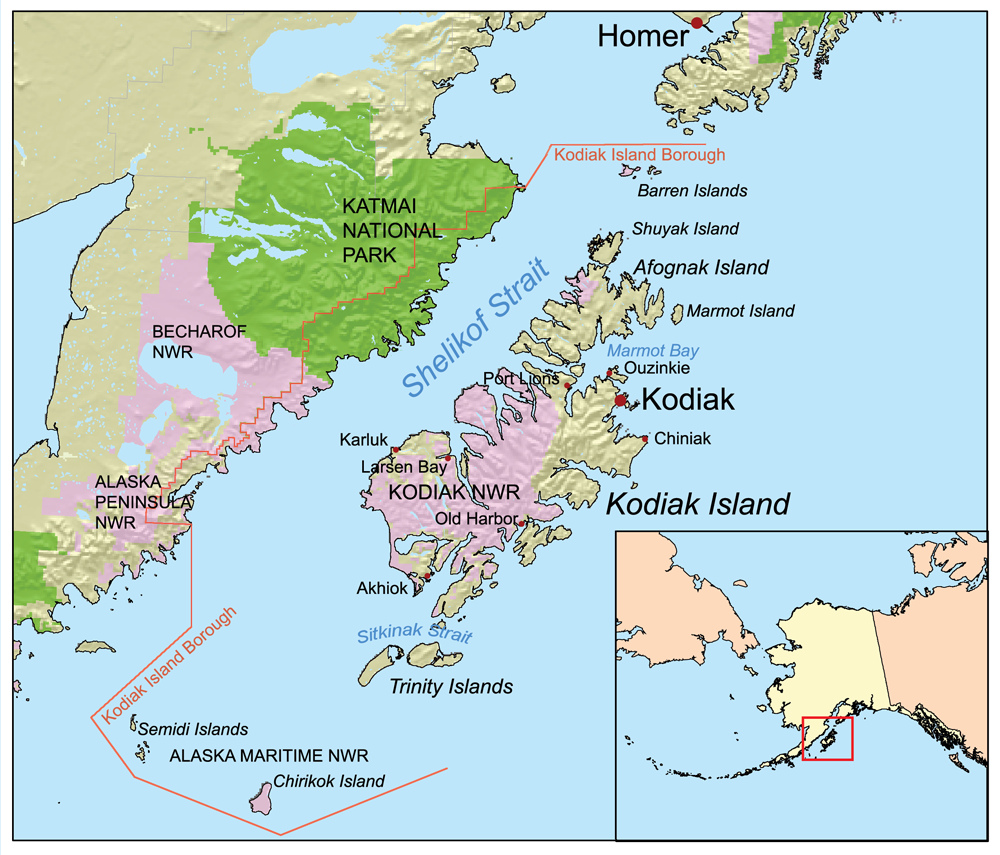
''Ochrolechia minuta'' is a species of crustose lichen in the family Ochrolechiaceae. It was first formally described in 1938 by Swedish lichenologist Gunnar Degelius as ''Perforaria minuta''. The type specimen was collected from the Kodiak Island Borough in Alaska. Toby Spribille transferred it to the genus ''Ochrolechia ''Ochrolechia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Ochrolechiaceae. Species , Species Fungorum accepts 38 species of ''Ochrolechia'': *'' Ochrolechia aegaea'' *'' Ochrolechia africana'' *'' Ochrolechia alaskana'' *'' Ochrolechia a ...'' in 2020, suggesting that the absence of cephalodia, and the presence of alectoronic acid, indicate that it is "related to the alectoronic acid-containing species of poriform ''Ochrolechia''". References Pertusariales Lichen species Lichens described in 1938 Lichens of Subarctic America Fungi without expected TNC conservation status {{Pertusariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degel
Degel is a town in northern Nigeria. Once a part of the Hausa city-state of Gobir, Degel is particularly noted for being the home of Fulani Islamic reformer Usman dan Fodio from 1774 to 1804. Dan Fodio built a large following in the area until, fearing his growing power, Yunfa of Gobir ordered him and his followers into exile, triggering the Fulani War The Fulani War of 1804–1808, also known as the Fulani Jihad or Jihad of Usman dan Fodio, was a military conflict in present-day Nigeria and Cameroon. The war began when Usman Dan Fodiyo, a prominent Islamic scholar and teacher, was exiled .... Populated places in Sokoto State {{Sokoto-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochrolechiaceae
The Ochrolechiaceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Pertusariales The Pertusariales are an order of fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains the following families: Agyriaceae The Agyriaceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Pertusariales. It contains two genera: ''Agyrium ''Agyri .... References Pertusariales Lichen families Lecanoromycetes families {{Pertusariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunnar Degelius
Gunnar Bror Fritiof Degelius (né Nilsson until 1932; 27 January 1903 – 22 July 1993) was a Swedish lichenologist. Between the publications of his first and final scientific papers, Degelius had a 70-year-long research career. While he was best known for his expertise on the lichen genus ''Collema'', he also wrote important papers on lichen biology and ecology, floristic studies of the Nordic countries and various other areas around the world, and lichen succession. Degelius described 124 new taxa (mostly species), and published about 130 scientific papers. In 1992 he was one of the first to be awarded the Acharius Medal for his lifetime contributions to lichenology. Fifteen species and three genera have been named in honour of Degelius. Early life and education Born in Uppsala on 27 January 1903, Degelius spent much of his youth in Mariestad. He was introduced to botany at an early age by his father, Bror Nilsson, who was a pharmacist. By the age of six, Gunnar had a size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska
Kodiak Island Borough (russian: Остров Кадьяк) is a borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. At the 2020 census, the population was 13,101, down from 13,592 in 2010. The borough seat is Kodiak. Geography The borough has a total area of , of which is land and (45.5%) is water. Most of the land area belongs to Kodiak Island, but a thin strip of coastal area on the western part of the Alaska Peninsula and other nearby islands (Afognak Island, Shuyak Island, Marmot Island, Raspberry Island, Little Raspberry Island, Whale Island, Spruce Island, Woody Island, Uganik Island, Sitkalidak Island, Tugidak Island, Sitkinak Island, Chirikof Island, and the Semidi Islands) are also in the borough. The waterway between the island and mainland is known as the Shelikof Strait. South of the island are the open waters of the Pacific Ocean, so the site is considered good for launching certain types of satellites. The Kodiak Launch Complex is ideal for putting satellites i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochrolechia
''Ochrolechia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Ochrolechiaceae. Species , Species Fungorum accepts 38 species of ''Ochrolechia'': *'' Ochrolechia aegaea'' *'' Ochrolechia africana'' *'' Ochrolechia alaskana'' *'' Ochrolechia alticola'' *'' Ochrolechia androgyna'' *'' Ochrolechia arborea'' *'' Ochrolechia brodoi'' *''Ochrolechia cooperi'' *'' Ochrolechia frigida'' *'' Ochrolechia gyrophorica'' *'' Ochrolechia inaequatula'' *''Ochrolechia incarnata'' *''Ochrolechia insularis'' *''Ochrolechia inversa'' *''Ochrolechia kerguelensis'' *''Ochrolechia lijiangensis'' *''Ochrolechia longispora'' *''Ochrolechia macrosperma'' *''Ochrolechia microstictoides'' *''Ochrolechia minuta'' *''Ochrolechia neoisidiata'' *'' Ochrolechia pallenti-isidiata'' *'' Ochrolechia pallescens'' *''Ochrolechia parella'' *'' Ochrolechia pseudotartarea'' *'' Ochrolechia rhodoleuca'' *'' Ochrolechia rugomarginata'' *'' Ochrolechia splendens'' *'' Ochrolechia subathallina'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is somewhat comparable to the International Plant Names Index (IPNI), in which the Royal Botanic Gardens is also involved. A difference is that where IPNI does not indicate correct names, the ''Index Fungorum'' does indicate the status of a name. In the returns from the search page a currently correct name is indicated in green, while others are in blue (a few, aberrant usages of names are indicated in red). All names are linked to pages giving the correct name, with lists of synonyms. ''Index Fungorum'' is one of three nomenclatural repositories recognized by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi; the others are ''MycoBank'' and ''Fungal Names''. Current names in ''Index Fungorum'' (''Specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertusariales
The Pertusariales are an order of fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains the following families: Agyriaceae The Agyriaceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Pertusariales. It contains two genera: ''Agyrium ''Agyrium'' is a genus of saprophytic fungi in the family Agyriaceae. It probably evolved from a lichen ancestor, as it is clos ..., Coccotremataceae, Icmadophilaceae, Megasporaceae, Microcaliciaceae, Ochrolechiaceae, Pertusariaceae, Varicellariaceae, and Variolariaceae. Many of these fungi form lichens. Gallery Image:Pertusaria_paratuberculifera_(EU).jpg, '' Pertusaria paratuberculifera'' (2 verrucae) Image:Pertusaria_paratuberculifera_(EU1).jpg, '' Pertusaria paratuberculifera'' (8 spores per ascus) References Lichen orders Lecanoromycetes orders Taxa named by David Leslie Hawksworth Taxa named by Maurice Choisy Taxa described in 1986 {{Pertusariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
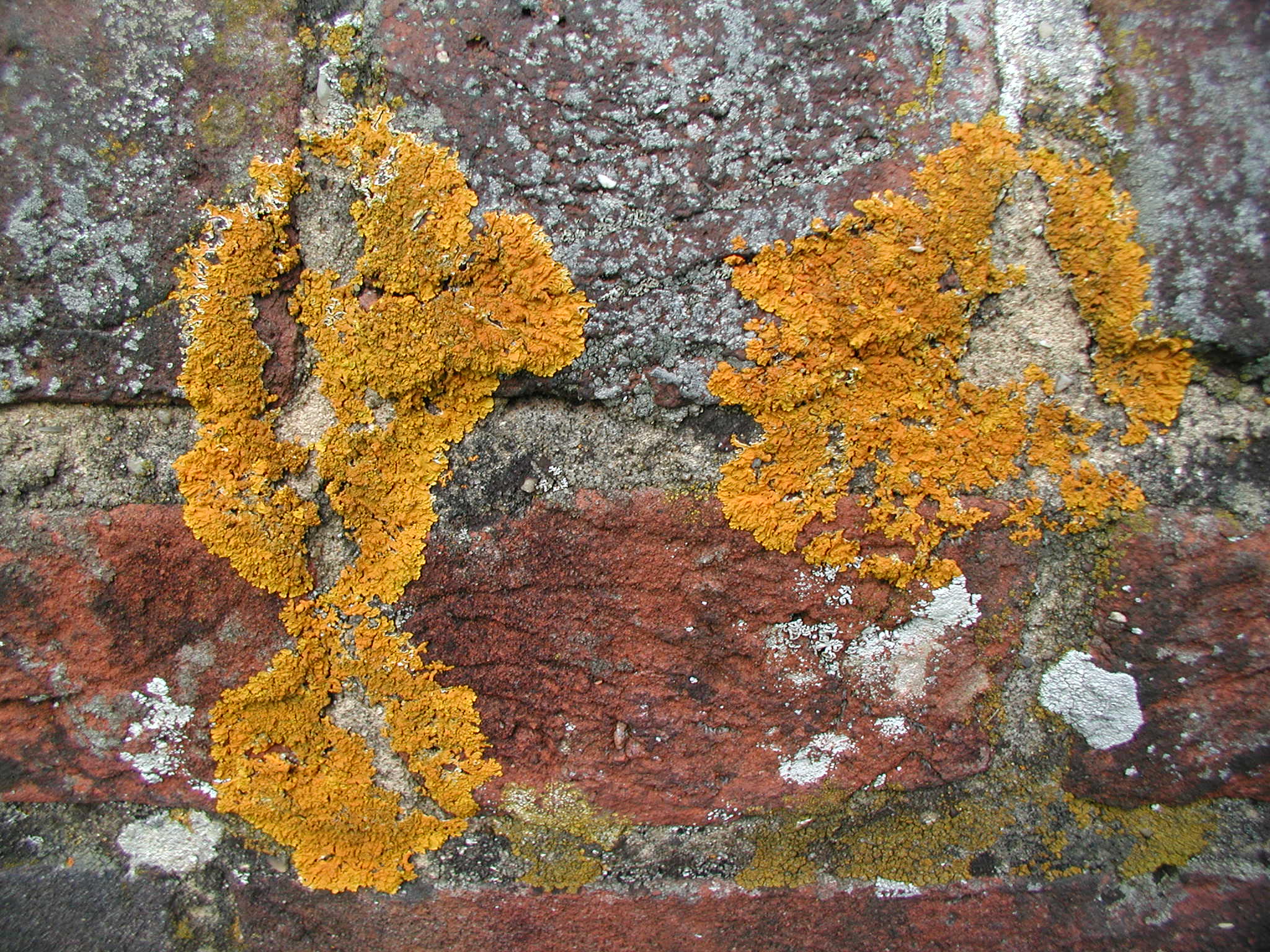


.jpg)