|
Oceanihabitans
''Oceanihabitans'' is a genus of marine bacterium in the family ''Flavobacteriaceae''. It contains a single species, ''O. sediminis''. It is aerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and motile by gliding. ''O. sediminis'' produces flexirubin pigments. It is positive for cytochrome c oxidase and catalase. ''O. sediminis'' can use glucose, mannose, maltose and adipic acid as sole carbon sources for chemoheterotrophic growth. It is a chemoorganotroph and is chemotaxonomically characterized by the presence of menaquinone 6 (MK-6). The type strain is S9-10T. Physiology ''O. sediminis'' is an aerobic microbe and is unable to grow under anaerobic or microaerophilic conditions. The major respiratory quinone is MK-6. It is cytochrome c oxidase and catalase positive. ''Oceanihabitans sediminis'' is capable of synthesizing a variety of hydrolytic enzymes including alkaline phosphatase, acid phosphatase, esterase lipase (C8), cysteine arylamidase, leucine arylamidase, valine aryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavobacteriaceae
The family Flavobacteriaceae is composed of environmental bacteria. Most species are aerobic, while some are microaerobic to anaerobic; for example '' Capnocytophaga'' and ''Coenonia''. Genera The family ''Flavobacteriaceae'' comprises the following genera: * '' Actibacter'' Kim ''et al''. 2008 * ''Aequorivita'' Bowman and Nichols 2002 * ''Aestuariibaculum'' Jeong ''et al''. 2013 * '' Aestuariimonas'' Park ''et al''. 2018 * '' Aestuariivivens'' Park ''et al''. 2015 * ''Algibacter'' Nedashkovskaya ''et al''. 2004 * '' Algitalea'' Yoon ''et al''. 2015 * "''Algorimicrobium''" García-López ''et al''. 2019 * "''Altibacter''" Chen ''et al''. 2014 * "''Altuibacter''" Chen ''et al''. 2013 * ''Amniculibacterium'' Chen ''et al''. 2020 * "''Candidatus'' Amoebinatus" Greub ''et al''. 2004 * '' Antarcticibacterium'' Li ''et al''. 2018 * '' Antarcticimonas'' Yang ''et al''. 2014 * ''Aquaticitalea'' Xamxidin ''et al''. 2016 * ''Aquibacter'' Hameed ''et al''. 2014 * ''Aquimarina'' Nedashk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Bacterium
Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain. Prokaryotes play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers recycling nutrients. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic, causing disease and even death in plants and animals. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
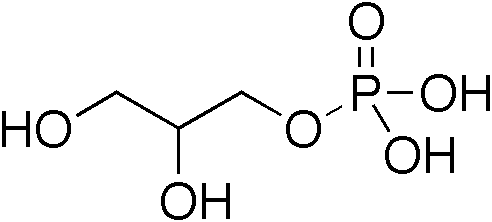
Triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride''). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have ''no'' C=C groups; unsaturated fats feature one or more C=C groups. Unsaturated fats tend to have a lower melting point than saturated analogues; as a result, they are often liquid at room temperature. Chemical structure Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
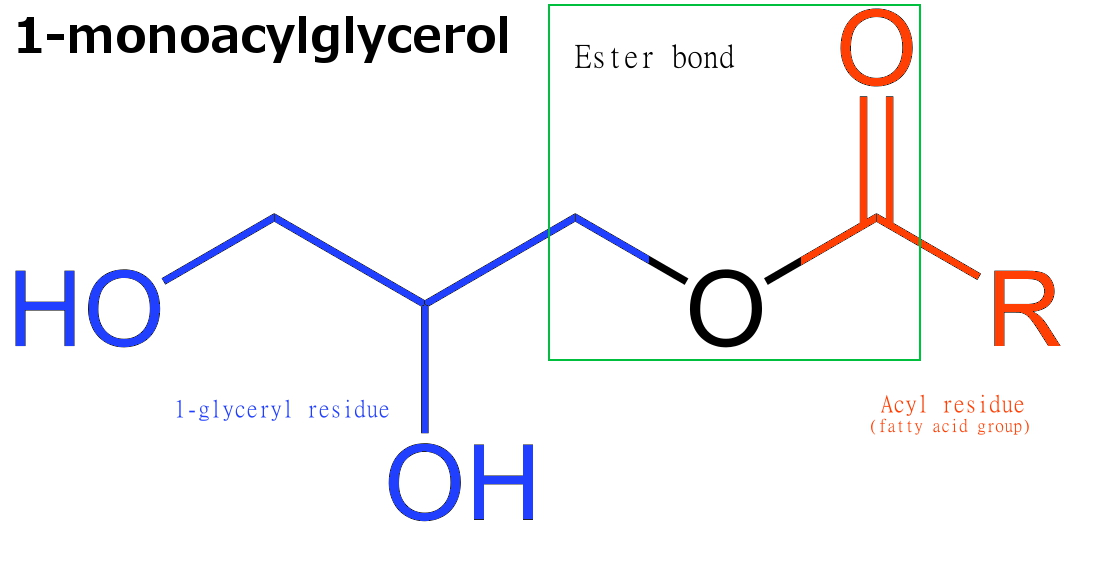
Monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industrial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |