|
Obfuscated TCP
Obfuscated TCP (ObsTCP) was a proposal for a transport layer protocol which implements opportunistic encryption over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It was designed to prevent mass wiretapping and malicious corruption of TCP traffic on the Internet, with lower implementation cost and complexity than Transport Layer Security (TLS). In August 2008, IETF rejected the proposal for a TCP option, suggesting it be done on the application layer instead. The project has been inactive since a few months later. In 2010 June, a separate proposal called tcpcrypt has been submitted, which shares many of the goals of ObsTCP: being transparent to applications, opportunistic and low overhead. It requires even less configuration (no DNS entries or HTTP headers). Unlike ObsTCP, tcpcrypt also provides primitives down to the application to implement authentication and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM). Historical origin ObsTCP was created by Adam Langley. The concept of obfuscating TCP com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
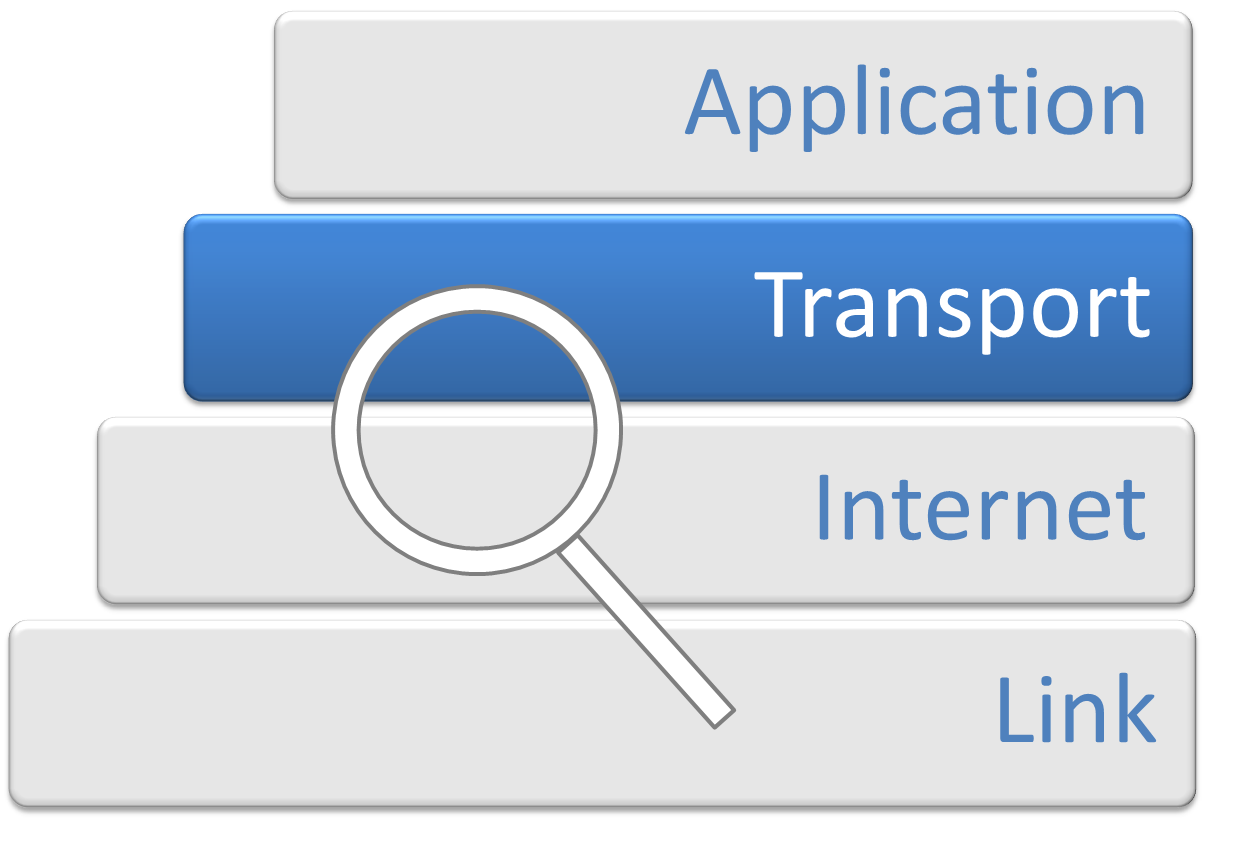
Transport Layer
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing. The details of implementation and semantics of the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite, which is the foundation of the Internet, and the OSI model of general networking are different. The protocols in use today in this layer for the Internet all originated in the development of TCP/IP. In the OSI model the transport layer is often referred to as Layer 4, or L4, while numbered layers are not used in TCP/IP. The best-known transport protocol of the Internet protocol suite is the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It is used for connection-oriented transmissions, whereas the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certificate Authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others (relying parties) to rely upon signatures or on assertions made about the private key that corresponds to the certified public key. A CA acts as a trusted third party—trusted both by the subject (owner) of the certificate and by the party relying upon the certificate. The format of these certificates is specified by the X.509 or EMV standard. One particularly common use for certificate authorities is to sign certificates used in HTTPS, the secure browsing protocol for the World Wide Web. Another common use is in issuing identity cards by national governments for use in electronically signing documents. Overview Trusted certificates can be used to create secure connections to a server via the Internet. A certificate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Encryption
Opportunistic encryption (OE) refers to any system that, when connecting to another system, attempts to encrypt communications channels, otherwise falling back to unencrypted communications. This method requires no pre-arrangement between the two systems. Opportunistic encryption can be used to combat passive wiretapping. (an ''active'' wiretapper, on the other hand, can disrupt encryption negotiation to either force an unencrypted channel or perform a man-in-the-middle attack on the encrypted link.) It does not provide a strong level of security as authentication may be difficult to establish and secure communications are not mandatory. However, it does make the encryption of most Internet traffic easy to implement, which removes a significant impediment to the mass adoption of Internet traffic security. Opportunistic encryption on the Internet is described in "Opportunistic Encryption using the Internet Key Exchange (IKE)", "Opportunistic Security: Some Protection Most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNAME Record
A Canonical Name record (abbreviated as CNAME record) is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS) that maps one domain name (an alias) to another (the canonical name). This can prove convenient when running multiple services (like an FTP server ''and'' a web server, each running on different ports) from a single IP address. One can, for example, use CNAME records to point ''ftp.example.com'' and ''www.example.com'' to the DNS entry for ''example.com'', which in turn has an A record which points to the IP address. Then, if the IP address ever changes, one only has to record the change in one place within the network: in the DNS A record for ''example.com''. CNAME records must always point to another domain name, never directly to an IP address. Details DNS CNAME records are specified in RFC 1034 and clarified in Section 10 of RFC 2181. CNAME records are handled specially in the domain name system, and have several restrictions on their use. When a DNS resolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Record
This list of DNS record types is an overview of resource records (RRs) permissible in zone files of the Domain Name System The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned ... (DNS). It also contains pseudo-RRs. Resource records Other types and pseudo-RRs Other types of records simply provide some types of information (for example, an HINFO record gives a description of the type of computer/OS a host uses), or others return data used in experimental features. The "type" field is also used in the protocol for various operations. Obsolete record types Progress has rendered some of the originally defined record-types obsolete. Of the records listed at IANA, some have limited use, for various reasons. Some are marked obsolete in the list, some are for very obscure services, some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the associated entities. Most prominently, it translates readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985. The Domain Name System delegates the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to Internet resources by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Network administrators may delegate authority over sub-domains of their allocated name space to other name servers. This mechanism provides distributed and fault-tolerant service and was designed to avoid a single large ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighttpd
lighttpd (pronounced "lighty") is an open-source web server optimized for speed-critical environments while remaining standards-compliant, secure and flexible. It was originally written by Jan Kneschke as a proof-of-concept of the c10k problem – how to handle 10,000 connections in parallel on one server, but has gained worldwide popularity. Its name is a portmanteau of "light" and ". Premise The low memory footprint (compared to other web servers), small central processing unit, CPU load and speed optimizations make lighttpd suitable for servers that are suffering load problems, or for serving static media separately from dynamic content. lighttpd is free and open-source software and is distributed under the BSD license. It runs natively on Unix-like operating systems, as well as Microsoft Windows. Application support lighttpd supports the FastCGI, SCGI and CGI interfaces to external programs, allowing web applications written in any programming language to be used with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name " Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox was created in 2002 unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Key Infrastructure
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. It is required for activities where simple passwords are an inadequate authentication method and more rigorous proof is required to confirm the identity of the parties involved in the communication and to validate the information being transferred. In cryptography, a PKI is an arrangement that ''binds'' public keys with respective identities of entities (like people and organizations). The binding is established through a process of registration and issuance of certificates at and by a certificate authority (CA). Depending on the assurance level of the binding, this may be carried out by an aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Key Certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate, also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate, is an electronic document used to prove the validity of a public key. The certificate includes information about the key, information about the identity of its owner (called the subject), and the digital signature of an entity that has verified the certificate's contents (called the issuer). If the signature is valid, and the software examining the certificate trusts the issuer, then it can use that key to communicate securely with the certificate's subject. In email encryption, code signing, and e-signature systems, a certificate's subject is typically a person or organization. However, in Transport Layer Security (TLS) a certificate's subject is typically a computer or other device, though TLS certificates may identify organizations or individuals in addition to their core role in identifying devices. TLS, sometimes called by its older name Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Encryption
Opportunistic encryption (OE) refers to any system that, when connecting to another system, attempts to encrypt communications channels, otherwise falling back to unencrypted communications. This method requires no pre-arrangement between the two systems. Opportunistic encryption can be used to combat passive wiretapping. (an ''active'' wiretapper, on the other hand, can disrupt encryption negotiation to either force an unencrypted channel or perform a man-in-the-middle attack on the encrypted link.) It does not provide a strong level of security as authentication may be difficult to establish and secure communications are not mandatory. However, it does make the encryption of most Internet traffic easy to implement, which removes a significant impediment to the mass adoption of Internet traffic security. Opportunistic encryption on the Internet is described in "Opportunistic Encryption using the Internet Key Exchange (IKE)", "Opportunistic Security: Some Protection Most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Langley
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as "mankind". tells of God's creation of the world and its creatures, including ''adam'', meaning humankind; in God forms "Adam", this time meaning a single male human, out of "the dust of the ground", places him in the Garden of Eden, and forms a woman, Eve, as his helpmate; in Adam and Eve eat the fruit of the tree of knowledge and God condemns Adam to labour on the earth for his food and to return to it on his death; deals with the birth of Adam's sons, and lists his descendants from Seth to Noah. The Genesis creation myth was adopted by both Christianity and Islam, and the name of Adam accordingly appears in the Christian scriptures and in the Quran. He also features in subsequent folkloric and mystical elaborations in later Judaism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |