|
Obedience Training
Dog training is the application of behavior analysis which uses the environmental events of antecedents (trigger for a behavior) and consequences to modify the dog behavior, either for it to assist in specific activities or undertake particular tasks, or for it to participate effectively in contemporary domestic life. While training dogs for specific roles dates back to Roman times at least, the training of dogs to be compatible household pets developed with suburbanization in the 1950s. A dog learns from interactions it has with its environment. This can be through classical conditioning, where it forms an association between two stimuli; non-associative learning, where its behavior is modified through habituation or sensitisation; and operant conditioning, where it forms an association between an antecedent and its consequence. There are a variety of established methods of animal training, each with its adherents and critics. Some of the better known dog training procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Training Exercises 130129-F-HX529-104
Control may refer to: Basic meanings Economics and business * Control (management), an element of management * Control, an element of management accounting * Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization * Controlling interest, a percentage of voting stock shares sufficient to prevent opposition * Foreign exchange controls, regulations on trade * Internal control, a process to help achieve specific goals typically related to managing risk Mathematics and science * Control (optimal control theory), a variable for steering a controllable system of state variables toward a desired goal * Controlling for a variable in statistics * Scientific control, an experiment in which "confounding variables" are minimised to reduce error * Control variables, variables which are kept constant during an experiment * Biological pest control, a natural method of controlling pests * Control network in geodesy and surveying, a set of reference points of known geospatial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest And Stream
''Forest and Stream'' was a magazine featuring hunting, fishing, and other outdoor activities in the United States. The journal was founded in August 1873 by Charles Hallock. At the time of its 1930 cancellation it was the ninth oldest magazine still being issued in the US. Published in New York City by Hallock in newspaper format measuring 16" x 11", it published many articles by "Nessmuk" (George W. Sears) in the 1880s that helped to popularize canoeing, the Adirondack lakes, self-guided canoe camping tours and ultralight camping. An early vehicle for conservationism, ''Forest and Stream'' was dedicated to wildlife conservation, helped to launch the National Audubon Society, was an early sponsor the national park movement, and supported the U.S.-Canadian Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918. Naturalist George Bird Grinnell was editor for 35 years, and contributors included Theodore Roosevelt. Another notable contributor was Theodore Gordon, long considered "the father of Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicki Hearne
Vicky, Vicko, Vick, Vickie or Vicki is a feminine given name, often a hypocorism of Victoria. The feminine name Vicky in Greece comes from the name Vasiliki. Women * Family nickname of Victoria, Princess Royal (1840–1901), wife of German Emperor Frederick III, mother of Emperor Wilhelm II and daughter of Queen Victoria of Great Britain * Vicki Adams (born 1989), Scottish curler * Vicki Adams (born 1951) Rodeo performer * Victoria Vicki Barr (athlete) (born 1982), British sprinter * Victoria Vicky Beeching (born 1979), British musician and religious commentator * Vicki Berner (1945–2017), Canadian tennis player * Victoria Vicky Binns (born 1981), English actress * Vicky Botwright (born 1977), English squash coach and former player * Vicki Brown (1940–1991), English singer born Victoria Haseman * Victoria Vicky Bullett (born 1967), American college head basketball coach and retired Women's National Basketball Association player * Vicki Butler-Henderson (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Koehler
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Kennel Club
The American Kennel Club (AKC) is a registry of purebred dog pedigrees in the United States. In addition to maintaining its pedigree registry, this kennel club also promotes and sanctions events for purebred dogs, including the Westminster Kennel Club Dog Show, an annual event which predates the official forming of the AKC, the National Dog Show and the AKC National Championship. The AKC is a non-member partner with the Fédération Cynologique Internationale. The AKC recognizes 200 dog breeds, as of 2022. History In the early 1800s, the English became concerned with the beauty of dogs as well as their function. This fad spread to North America, and in 1877, the Westminster Kennel Club Dog Show began. Soon after, the need for a regulating body became obvious. The National American Kennel Club, which had been founded in 1876, began to publish and make publicly available its studbook in 1879. This organization, however, had a more vested interest in field trials than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Solomon's Ring (nonfiction)
''King Solomon's Ring'' is a general-audience zoological book, written by Austrian scientist Konrad Lorenz in 1949. The first English-language edition was published in 1952. The English title refers to the legendary Seal of Solomon, a ring that supposedly gave King Solomon the power to speak to animals. Lorenz claimed to have achieved this feat of communication with several species, by raising them in and around his home and observing their behavior. ''King Solomon's Ring'' describes the methods of his investigation and his resulting conclusions about animal psychology Comparative psychology refers to the scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of non-human animals, especially as these relate to the phylogenetic history, adaptive significance, and development of behavior. Research in this area addr .... References *Konrad Lorenz (1961) ''King Solomon's Ring'' Translated by Marjorie Kerr Wilson. Methuen, London. 202 pages. {{Konrad Lorenz 1949 non-fiction boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man Meets Dog
''Man Meets Dog'' is a zoological book for the general audience, written by the Austrian scientist Konrad Lorenz in 1949. The first English-language edition appeared in 1954. The original German title is ''So kam der Mensch auf den Hund'', which could be literally translated as "How man ended up with dog". The German title is also a play on the phrase "Auf den Hund kommen", which is a common idiom in German-speaking countries and probably comes from the old days when farmers with economic problems had to sell their livestock animals and ended up with only the dog. Contents The opening chapter "How it may have started" deals with theories concerning the question where and when man first domesticated the predecessor of the modern dog. The book has a lot of interesting anecdotes of the author's experiences with dogs, these stories are often illustrated with simple drawings. Lorenz usually owned several dogs and many other animals and lived with them in his house near Vienna. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethology
Ethology is the scientific study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait. Behaviourism as a term also describes the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, usually referring to measured responses to stimuli or to trained behavioural responses in a laboratory context, without a particular emphasis on evolutionary adaptivity. Throughout history, different naturalists have studied aspects of animal behaviour. Ethology has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Charles O. Whitman, Oskar Heinroth, and Wallace Craig. The modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, the three recipients of the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad Lorenz
Konrad Zacharias Lorenz (; 7 November 1903 – 27 February 1989) was an Austrian zoologist, ethologist, and ornithologist. He shared the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Nikolaas Tinbergen and Karl von Frisch. He is often regarded as one of the founders of modern ethology, the study of animal behavior. He developed an approach that began with an earlier generation, including his teacher Oskar Heinroth. Lorenz studied instinctive behavior in animals, especially in greylag geese and jackdaws. Working with geese, he investigated the principle of imprinting, the process by which some nidifugous birds (i.e. birds that leave their nest early) bond instinctively with the first moving object that they see within the first hours of hatching. Although Lorenz did not discover the topic, he became widely known for his descriptions of imprinting as an instinctive bond. In 1936 he met Tinbergen, and the two collaborated in developing ethology as a separate sub-disciplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
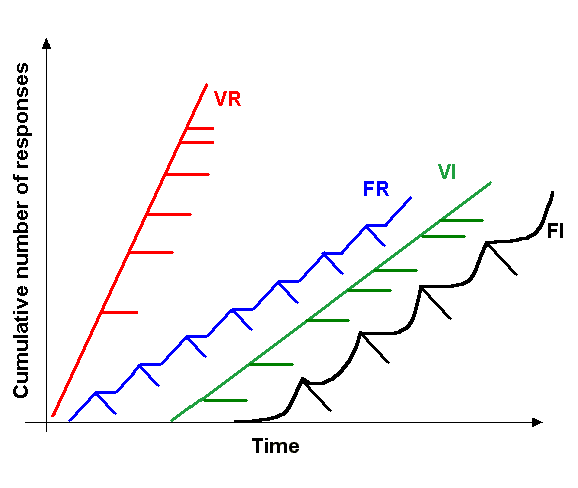
Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clicker Training
Clicker training is a positive reinforcement animal training method based on a bridging stimulus ( the clicker) in operant conditioning. The system uses conditioned reinforcers, which a trainer can deliver more quickly and more precisely than primary reinforcers such as food. The term "clicker" comes from a small metal cricket noisemaker adapted from a child's toy that the trainer uses to precisely mark the desired behavior. When training a new behavior, the clicker helps the animal to quickly identify the precise behavior that results in the treat. The technique is popular with dog trainers, but can be used for all kinds of domestic and wild animals. Sometimes, instead of a click to mark the desired behavior, other distinctive sounds are made (such as a "whistle, a click of the tongue, a snap of the fingers, or even a word") [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marian Breland Bailey
Marian Breland Bailey, born Marian Ruth Kruse (December 2, 1920 – September 25, 2001) and nicknamed "Mouse",Clark, C. (2001). ''The Centre for Applied Canine Behaviour''. Retrieved on February 20, 2007. was an American psychologist, an applied behavior analyst who played a major role in developing empirically validated and humane animal training methods and in promoting their widespread implementation. She and her first husband, Keller Breland (1915–1965), studied at the University of Minnesota under behaviorist B. F. Skinner and became "the first applied animal psychologists." Together they wrote the book Animal Behavior which was first published in 1966, after Keller's death. Childhood and education Born to Christian and Harriet (Prime) Kruse, Marian Ruth Kruse grew up in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Christian, a German immigrant, worked for an automotive supply store, and Harriet was a registered nurse.Bihm, E. M., & J. A. Gillaspy (2006)Marian Breland Bailey (1920–2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)