|
Obdulio Varela
Obdulio Jacinto Muiños Varela (; September 20, 1917 — August 2, 1996) was a Uruguayan football player. He was the captain of the Uruguay national team that won the 1950 World Cup after beating Brazil in the decisive final round match popularly known as the '' Maracanazo''. He was nicknamed "El Negro Jefe" (The Black Chief) because of his dark skin and the influence he had on the pitch, especially during the unlikely victory over Brazil. He was of African, Spanish and Greek ancestry. Commonly regarded as one of the greatest classic holding midfielders, Varela was adept in defence and was renowned for his tenacity and leadership. He is regarded as one of the greatest captains in football history, and "he remains one of the biggest sporting heroes in Uruguay". Club career Varela, born in Montevideo, emerged as a centre half and senior player at Deportivo Juventud, club which he joined in 1936. He debuted in first division with Montevideo Wanderers in 1938. In 1943, he join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruguay National Football Team
The Uruguay national football team ( es, Selección de fútbol de Uruguay) represents Uruguay in international football, and is controlled by the Uruguayan Football Association, the governing body for football in Uruguay. The Uruguayan team is commonly referred to as ''La Celeste'' (The Sky Blue). Regarded to be one of the greatest footballing nations of all time, Uruguay has won the Copa América 15 times being tied with Argentina for the most titles in the history of the tournament. Uruguay won their most recent title in 2011. Additionally, Uruguay are the holders of four FIFA World Championships: The team has won the FIFA World Cup twice, including the first World Cup in 1930 as hosts, defeating Argentina 4–2 in the final. Their second title came in 1950, upsetting host Brazil 2–1 in the final match, which had the highest attendance for a football match ever. Uruguay has also won gold medals at the Olympic football tournament twice, in 1924 and 1928. The gold medal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
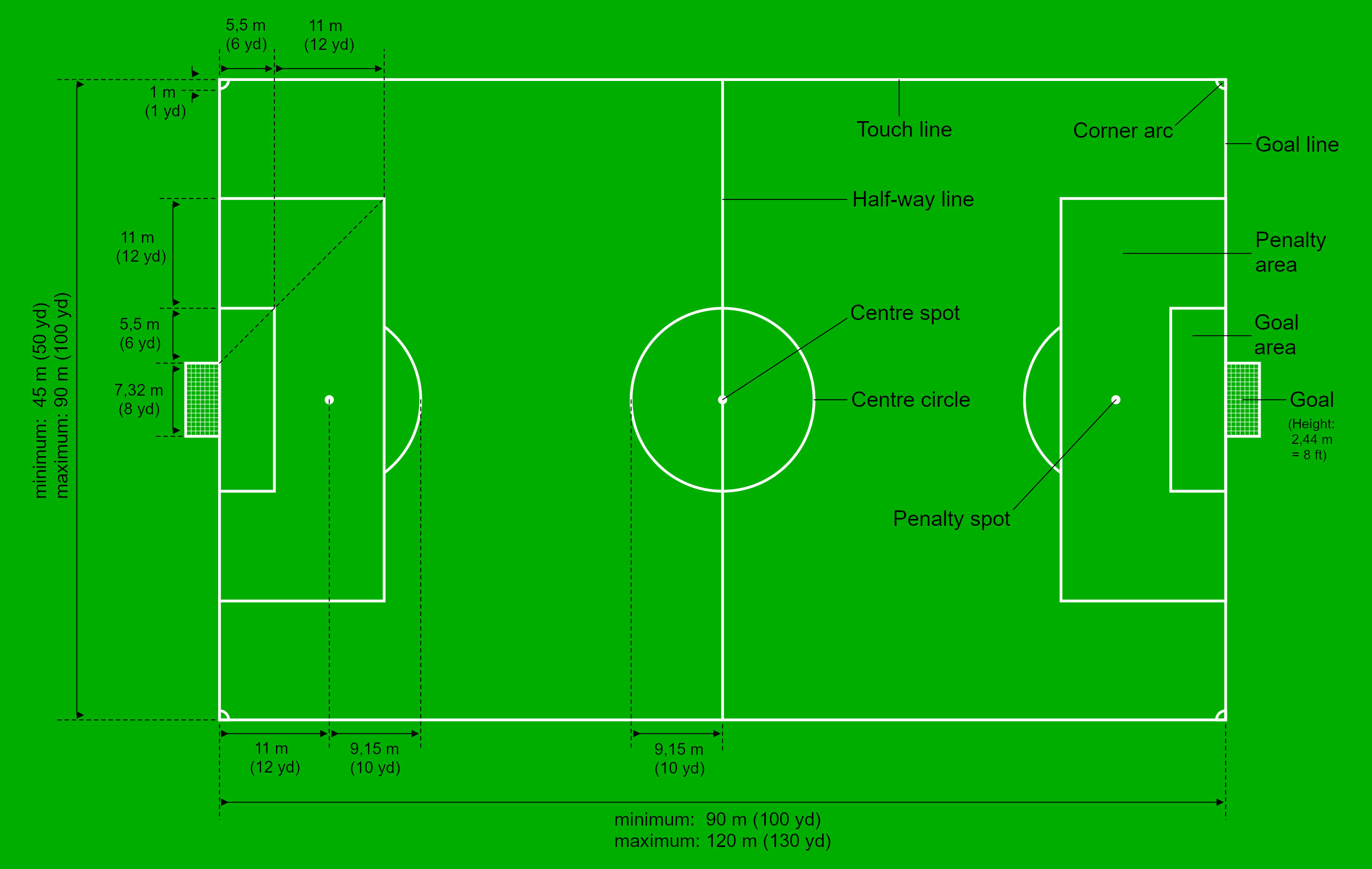
Association Football Pitch
A football pitch (also known as soccer field) is the playing surface for the game of association football. Its dimensions and markings are defined by Law 1 of the Laws of the Game, "The Field of Play". The pitch is typically made of natural turf or artificial turf, although amateur and recreational teams often play on dirt fields. Artificial surfaces are allowed only to be green in colour. All line markings on the pitch form part of the area which they define. For example, a ball on or above the touchline is still on the field of play, and a foul committed over the line bounding the penalty area results in a penalty. Therefore, a ball has to completely cross the touchline to be out of play, and a ball has to wholly cross the goal line (between the goal posts) in order for a goal to be scored; if any part of the ball is still on or above the line, a goal is not scored and the ball is still in play. The field descriptions that apply to adult matches are described below. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcides Ghiggia
Alcides Edgardo Ghiggia Pereyra (; 22 December 1926 – 16 July 2015) was a Uruguayan-Italian football player, who played as a right winger. He achieved lasting fame for his decisive role in the final match of the 1950 World Cup, and at the time of his death exactly 65 years later, he was also the last surviving player from that game. Career Ghiggia's family was of Ticinese descent originally from Sonvico. He played for the national sides of both Uruguay and Italy during his career. He also played for Peñarol and Danubio in Uruguay and A.S. Roma and A.C. Milan in Italy. In 1950, Ghiggia, then playing for Uruguay, scored the winning goal against Brazil in the final match of that year's World Cup. Roberto Muylaert compares the black and white film of the goal with Abraham Zapruder's chance images of the assassination of John F. Kennedy in Dallas: he says that the goal and the shot that killed the U.S. president have "the same dramatic pattern ... the same movement .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Reader
George Reader (22 November 1896 – 13 July 1978) was the fourth man to referee a FIFA World Cup Final, the first Englishman (one of only 10 match officials from the United Kingdom) to do so, and the oldest match official at any World Cup in history. He hailed from Nuneaton, Warwickshire. Early career By profession he was a schoolmaster, going to St Luke's teacher training college (the same one that Ken Aston was to attend) just after the First World War in Exeter. St. Luke's is now part of Exeter University. Finding work in Exeter as a young teacher, Reader first played as an amateur for Exeter City in the Southern Football League, in the 1919–20 season. It was with that club that he played in a friendly against Southampton on 3 January 1920, a week before the third round of the FA Cup. Reader scored and impressed the visiting side so much that they signed him for a fee of £50, as a handy replacement centre-forward to Bill Rawlings, who was a mainstay of the Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan López (football Manager, Born 1908)
Juan López Fontana (15 March 1908 – 4 October 1983) was a Uruguayan professional football manager who won the 1950 FIFA World Cup as the head coach of the Uruguay national team. Biography López was born in the Barrio Palermo of Montevideo, Uruguay's capital on 15 March 1908. His hometown is the home of Estadio Centenario where Uruguay had won the 1930 FIFA World Cup under head coach at the time Alberto Suppici. López started out in coaching as a medical assistant at local club Central Fútbol Club, managed by Suppici, who taught López the fundamentals of coaching. López was appointed head coach of Uruguay in 1946. Uruguay won the 1950 FIFA World Cup in Brazil under López's management. His side beat Bolivia 8–0 in their only first-round game, earning a spot in a four-team final group in the absence of a traditional cup final. Uruguay drew Spain and beat Sweden going into a final match at the Estádio do Maracanã with Brazil, who only needed a draw to win their first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSSSF
The Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation (RSSSF) is an international organization dedicated to collecting statistics about association football. The foundation aims to build an exhaustive archive of football-related information from around the world. History This enterprise, according to its founders, was created in January 1994 by three regulars of the Rec.Sport.Soccer (RSS) Usenet newsgroup: Lars Aarhus, Kent Hedlundh, and Karel Stokkermans. It was originally known as the "North European Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation", but the geographical reference was dropped as its membership from other regions grew. The RSSSF has members and contributors from all around the world and has spawned seven spin-off projects to more closely follow the leagues of that project's home country. The spin-off projects are dedicated to Albania, Brazil, Denmark, Norway, Poland (90minut.pl), Romania, Uruguay, Venezuela, and Egypt Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lima, Peru
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaside city of Callao, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area. With a population of more than 9.7 million in its urban area and more than 10.7 million in its metropolitan area, Lima is one of the largest cities in the Americas. Lima was named by natives in the agricultural region known by native Peruvians as ''Limaq''. It became the capital and most important city in the Viceroyalty of Peru. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru (República del Perú). Around one-third of the national population now lives in its metropolitan area. The city of Lima is considered to be the political, cultural, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile National Football Team
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández Islands, Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas Islands, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish language, Spanish. Conquest of Chile, Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Incas in Central Chile, Inca rule, but Arauco War, fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montevideo Wanderers
Montevideo Wanderers Fútbol Club, usually known simply as Wanderers, is a Uruguayan professional football club based in Montevideo. The club are currently members of the Primera División and play at the Estadio Viera. Beside football, the club also has teams playing basketball, volleyball, athletics, futsal, pool and pelota. History Origin 1898 - 1931 The Montevideo Wanderers was founded in the end of the 19th century, made up of a group of idealistic young people who wanted to express their sporting principles in a club where they were truly the protagonists of their own decisions. Led by the Sardeson brothers, the community quickly became a well-known group in their neighborhood of origin, El Prado. Its name was born as a result of a trip by Enrique Sardeson and Juan Sardeson to England. In England at that time The Wanderers were a prominent team, although it was not the only Club with that name playing in the English tournament, since it coexisted with Wolverhampton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deportivo Juventud
''Deportivo'' (Spanish, 'sporting') may refer to: * Deportivo de La Coruña, commonly known as simply Deportivo, a Spanish football club * Déportivo, a French rock band * Deportivo (Mexicable) Mexicable is a aerial lift line in Ecatepec de Morelos, in Greater Mexico City. It was created by the Government of the State of Mexico. The first part of this project was inaugurated on October 4, 2016. The line is long and runs between San ..., an aerial lift station in Ecatepec, Mexico * Deportivo station, in San Juan agglomeration, Puerto Rico See also * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defender (association Football)
In the sport of association football, a defender is an Glossary of association football terms#O, outfield position whose primary role is to stop attacks during the game and prevent the opposition from scoring. Centre-backs are usually positioned in pairs, with one full-back on either side to their left and right, but can be played in threes with or without full-backs. Defenders fall into four main categories: centre-back, sweeper, full-back, and wing-back. The centre-back and full-back positions are essential in most modern formations. The sweeper and wing-back roles are more specialised for certain formations dependent on the manager's style of play and tactics. Centre-backs are usually tall and positioned for their ability to win duels in the air. Centre-back The centre-back (also known as a central defender or centre-half, as the modern role of the centre-back arose from the Midfielder#Centre-half, centre-half position) defends in the area directly in front of the goal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holding Midfielder
A midfielder is an outfield position in association football. Midfielders may play an exclusively defensive role, breaking up attacks, and are in that case known as defensive midfielders. As central midfielders often go across boundaries, with mobility and passing ability, they are often referred to as deep-lying midfielders, play-makers, box-to-box midfielders, or holding midfielders. There are also attacking midfielders with limited defensive assignments. The size of midfield units on a team and their assigned roles depend on what formation is used; the unit of these players on the pitch is commonly referred to as the midfield. Its name derives from the fact that midfield units typically make up the in-between units to the defensive units and forward units of a formation. Managers frequently assign one or more midfielders to disrupt the opposing team's attacks, while others may be tasked with creating goals, or have equal responsibilities between attack and defence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Guamán_Poma%2C_1616.jpg)
