|
OPML
OPML (Outline Processor Markup Language) is an XML format for outlines (defined as "a tree, where each node contains a set of named attributes with string values"). Originally developed by UserLand as a native file format for the outliner application in its Radio UserLand product, it has since been adopted for other uses, the most common being to exchange lists of web feeds between web feed aggregators. The OPML specification defines an outline as a hierarchical, ordered list of arbitrary elements. The specification is fairly open which makes it suitable for many types of list data. Support for importing and exporting RSS feed lists in OPML format is available in Mozilla Thunderbird, and many other RSS reader web sites and applications. XML format The XML elements in an OPML document are: ; <opml version="1.0"> : This is the root element. It must contain the version attribute and one ''head'' and one ''body'' element. ; <head> : Contains metadata. May include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dave Winer
Dave Winer (born May 2, 1955, in Queens, New York City) is an American software developer, entrepreneur, and writer who resides in New York City. Winer is noted for his contributions to outliners, scripting, content management, and web services, as well as blogging and podcasting. He is the founder of the software companies Living Videotext, Userland Software and Small Picture Inc., a former contributing editor for the Web magazine HotWired, the author of the ''Scripting News'' weblog, a former research fellow at Harvard Law School, and current visiting scholar at New York University's Arthur L. Carter Journalism Institute. Early life and education Winer was born on May 2, 1955, in Queens, New York City, the son of Eve Winer, PhD, a school psychologist, and Leon Winer, PhD, a former professor of the Columbia University Graduate School of Business. Winer is also the grandnephew of German novelist Arno Schmidt and a relative of Hedy Lamarr. He graduated from the Bronx High Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
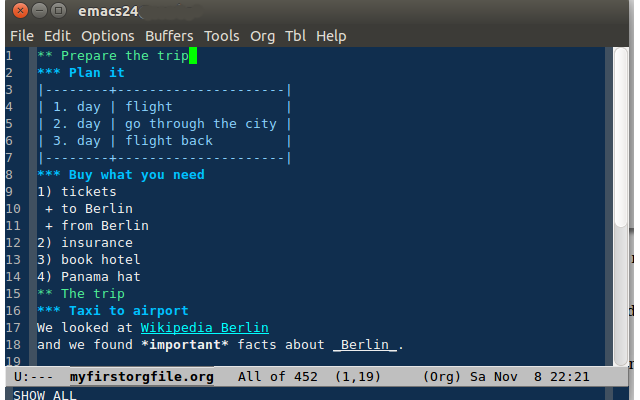
Outliner
An outliner (or outline processor) is a specialized type of text editor (word processor) used to create and edit outlines, which are text files which have a tree structure, for organization. Textual information is contained in discrete sections called "nodes", which are arranged according to their topic–subtopic (parent–child) relationships, like the members of a family tree. When loaded into an outliner, an outline may be collapsed or expanded to display as few or as many levels as desired. Outliners are used for storing and retrieving textual information, with terms, phrases, sentences, or paragraphs attached to a tree. So rather than being arranged by document, information is arranged by topic or content. An outline in an outliner may contain as many topics as desired. This eliminates the need to have separate documents, as outlines easily include other outlines just by adding to the tree. The main difference between a hand-written outline and a digital one is that the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outliner
An outliner (or outline processor) is a specialized type of text editor (word processor) used to create and edit outlines, which are text files which have a tree structure, for organization. Textual information is contained in discrete sections called "nodes", which are arranged according to their topic–subtopic (parent–child) relationships, like the members of a family tree. When loaded into an outliner, an outline may be collapsed or expanded to display as few or as many levels as desired. Outliners are used for storing and retrieving textual information, with terms, phrases, sentences, or paragraphs attached to a tree. So rather than being arranged by document, information is arranged by topic or content. An outline in an outliner may contain as many topics as desired. This eliminates the need to have separate documents, as outlines easily include other outlines just by adding to the tree. The main difference between a hand-written outline and a digital one is that the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UserLand Software
UserLand Software is a US-based software company, founded in 1988, that sells web content management, as well as blogging software packages and services. Company history Dave Winer founded the company in 1988 after leaving Symantec in the spring of 1988. Jean-Louis Gassée, who resigned in 1990 as chief of Apple's product development, came to serve on UserLand's board of directors. Frontier UserLand's first product release of April 1989 was UserLand IPC, a developer tool for interprocess communication that was intended to evolve into a cross-platform RPC tool. In January 1992 UserLand released version 1.0 of Frontier, a scripting environment for the Macintosh which included an object database and a scripting language named ''UserTalk''. At the time of its original release, Frontier was the only system-level scripting environment for the Macintosh, but Apple was working on its own scripting language, AppleScript, and started bundling it with the MacOS 7 system software. As a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XBEL
The XML Bookmark Exchange Language (XBEL), is an open XML standard for sharing Internet URIs, also known as ''bookmarks'' (or ''favorites'' in Internet Explorer). An example of XBEL use is thXBELiciousapplication, which stores Del.icio.us bookmarks in XBEL format. The Galeon, Konqueror, Arora and Midori web browsers use XBEL as the format for storing user bookmarks. ThFloccussynchronization client can store XBEL on WebDAV servers. ThSiteBarbookmark server can import and export bookmarks in XBEL format. XBEL was created by the Pythonbr>XML Special Interest Group"to create an interesting, fun project which was both useful and would demonstrate the Python XML processing software which was being developed at the time". It is also used by Nautilus and gedit of the GNOME desktop environment. See also * Internet bookmark * XOXO (eXtensible Open XHTML Outlines), an XML microformat for outlines built on top of XHTML. * OPML (Outline Processor Markup Language), an XML format for outli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share Icon
A share icon is a user interface icon intended to convey to the user a button for performing a share action. Content platforms such as YouTube often include a share icon so that users can forward the content onto social media platforms or embed videos into their websites, thus increasing its view count. Share Icon WordPress developer Alex King created the original Share Icon in 2006. ShareThis acquired the rights to this icon a year later, and eventually licensed it under four licenses: the share-alike GPL and LGPL, and the permissive BSD license and Creative Commons Attribution 2.5. ShareThis produces widgets for accessing social networking services from a single pop-up menu. This icon is trademarked and was cause for controversy due to it being subject to legal take-down notices despite its license. Open Share Icon The Open Share Icon (or Shareaholic icon) is designed to help users easily identify shareable content. The icon aims to convey the act of sharing visually by rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Profiling Mark-up Language
Attention Profiling Mark-up Language (APML) is an XML-based markup language for documenting a person's interests and dislikes. Overview APML allows people to share their own personal attention profile in much the same way that OPML allows the exchange of reading lists between news readers. The idea behind APML is to compress all forms of attention data into a portable file format containing a description of the user's rated interests. The APML Workgroup The APML Workgroup is tasked with maintaining and refining the APML specification. The APML Workgroup is made up of industry experts and leaders and was founded by Chris Saad and Ashley Angell. The workgroup allows public recommendations and input, and actively evangelises the public’s "Attention Rights". The workgroup also adheres to the principles of Media 2.0 Best Practices. Services ''Services that have adopted APML'' * Bloglines was an RSS reader. It was one of the major RSS readers on the web, with its main competitor b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XOXO (microformat)
XOXO (eXtensible Open XHTML Outlines) for web syndication is an XML microformat for outlines built on top of XHTML. Developed by several authors as an attempt to reuse XHTML building blocks instead of inventing unnecessary new XML elements/attributes, XOXO is based on existing conventions for publishing outlines, lists, and blogrolls on the Web. The XOXO specification defines an outline as a hierarchical, ordered list of arbitrary elements. The specification is fairly open which makes it suitable for many types of list data. E.g. the more semantic version of the S5 presentation file format is based upon XOXO. XML format The XML elements in an XOXO document are: ; <ol class="xoxo"> ; <ul class="xoxo"> : The ordered list and unordered list are the root elements of XOXO. They may contain the class attribute with the value xoxo. They are also used as containers for outline items. They may have the attribute compact="compact" to indicate state of whether child items ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML And MIME
There are two MIME assignments for XML data. These are: *application/xml (RFC 7303, previously RFC 3023) *text/xml (RFC 7303, previously RFC 3023) However, since the introduction of RFC 7303, these are to be regarded as the same in all aspects except name. Because of the wide variety of documents that can be expressed using an XML syntax, additional MIME types are needed to differentiate between languages. XML-based formats add a suffix of ''+xml'' to their own MIME type; this convention is defined in (RFC 7303). ''The following are some examples of common XML media types:'' *Registered ** Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML): application/xhtml+xml (RFC 3236) ** Atom: application/atom+xml (RFC 4287) ** Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations (XSLT): 'application/xslt+xml'' ** Scalable Vector Graphics ( SVG): 'image/svg+xml'' ** Mathematical Markup Language (MathML): application/mathml+xml *Registration-In-Progress ** application/akn+xml ** application/rif+xml *Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Syndication Formats
Web most often refers to: * Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal * World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to: Computing * WEB, a literate programming system created by Donald Knuth * GNOME Web, a Web browser * Web.com, a web-design company * Webs (web hosting), a Web hosting and website building service Engineering * Web (manufacturing), continuous sheets of material passed over rollers ** Web, a roll of paper in offset printing * Web, the vertical element of an I-beam or a rail profile * Web, the interior beams of a truss Films * ''Web'' (2013 film), a documentary * ''Webs'' (film), a 2003 science-fiction movie * ''The Web'' (film), a 1947 film noir * Charlotte's Web (2006 film) Literature * ''Web'' (comics), a MLJ comicbook character (created 1942) * ''Web'' (novel), by John Wyndham (1979) * The Web (series), a science fiction series (1997–1999) * World English Bible, a public-domain Bible t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Icon
On the World Wide Web, a web feed (or news feed) is a data format used for providing users with frequently updated content. Content distributors ''syndicate'' a web feed, thereby allowing users to ''subscribe'' a channel to it by adding the feed resource address to a news aggregator client (also called a ''feed reader'' or a ''news reader''). Users typically subscribe to a feed by manually entering the URL of a feed or clicking a link in a web browser or by dragging the link from the web browser to the aggregator, thus "RSS and Atom files provide news updates from a website in a simple form for your computer." The kinds of content delivered by a web feed are typically (webpage content) or links to webpages and other kinds of digital media. Often when websites provide web feeds to notify users of content updates, they only include summaries in the web feed rather than the full content itself. Many news websites, weblogs, schools, and podcasters operate web feeds. As web feeds a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |