|
OBPgp279
OBPgp279 (OBP genome protein 279) is an endolysin that hydrolyzes peptidoglycan, a major constituent in bacterial membrane. OBPgp279 is found in ''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' phage OBP, which belongs in the ''Myoviridae'' family of bacteriophages. Because of its role in hydrolyzing the peptidoglycan layer, OBPgp279 is a key enzyme in the lytic cycle of the OBP bacteriophage; it allows the bacteriophage to lyse its host internally to escape. Unlike other endolysins, OBPgp279 does not rely on holins to perforate the inner bacterial membrane in order to reach the peptidoglycan layer. Although OBPgp279 is not a well-studied enzyme, it has garnered interest as a potential antibacterial protein due to its activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Predicted enzyme mechanism The mechanism of OBPgp279 is predicted to be part of glycoside hydrolase family 19 (GH19) due to the presence of a conserved sequence motif (general sequence motif = HYG-R-G- Pζ-Q- L T HYW N Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolysin
Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target one of the five bonds in peptidoglycan (murein), the main component of bacterial cell walls, which allows the release of progeny virions from the lysed cell. Cell-wall-containing Archaea are also lysed by specialized pseudomurein-cleaving lysins, while most archaeal viruses employ alternative mechanisms. Similarly, not all bacteriophages synthesize lysins: some small single-stranded DNA and RNA phages produce membrane proteins that activate the host's autolytic mechanisms such as autolysins. Lysins are being used as antibacterial agents due to their high effectiveness and specificity in comparison with antibiotics, which are susceptible to bacterial resistance. Structure Double-stranded DNA phage lysins tend to lie within the 25 to 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysin
Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target one of the five bonds in peptidoglycan (murein), the main component of bacterial cell walls, which allows the release of progeny virions from the lysed cell. Cell-wall-containing Archaea are also lysed by specialized pseudomurein-cleaving lysins, while most archaeal viruses employ alternative mechanisms. Similarly, not all bacteriophages synthesize lysins: some small single-stranded DNA and RNA phages produce membrane proteins that activate the host's autolytic mechanisms such as autolysins. Lysins are being used as antibacterial agents due to their high effectiveness and specificity in comparison with antibiotics, which are susceptible to bacterial resistance. Structure Double-stranded DNA phage lysins tend to lie within the 25 to 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyre2
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as 'fire') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable accurac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophages
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Model
An animal model (short for animal disease model) is a living, non-human, often genetic-engineered animal used during the research and investigation of human disease, for the purpose of better understanding the disease process without the risk of harming a human. Although biological activity in an animal model does not ensure an effect in humans, many drugs, treatments and cures for human diseases are developed in part with the guidance of animal models. Animal models representing specific taxonomic groups in the research and study of developmental processes are also referred to as model organisms. There are three main types of animal models: Homologous, Isomorphic and Predictive. Homologous animals have the same causes, symptoms and treatment options as would humans who have the same disease. Isomorphic animals share the same symptoms and treatments, only. Predictive models are similar to a particular human disease in only a couple of aspects. However, these are useful in isolating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
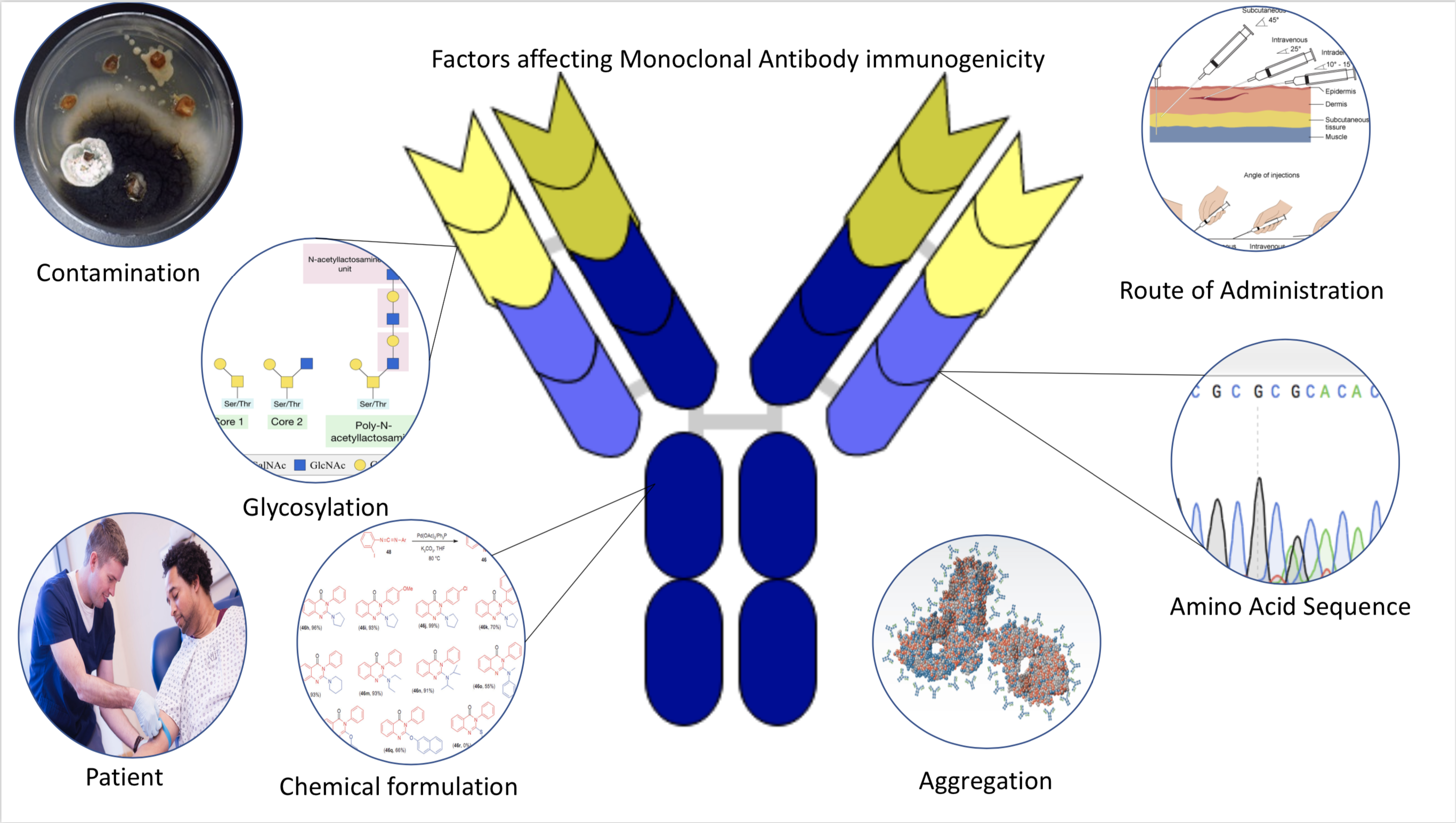
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehringer Ingelheim
C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. is the parent company of the Boehringer Ingelheim group, which was founded in 1885 by Albert Boehringer in Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany. As of 2018, Boehringer Ingelheim is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies, and the largest private one. Headquartered in Ingelheim, it operates globally with 146 affiliates and more than 47,700 employees. Unlike most large pharmaceutical companies which are listed, the company is private and fully owned by the Boehringer, Liebrecht and von Baumbach families. The company's key areas of interest are: respiratory diseases, metabolism, immunology, oncology and diseases of the central nervous system. Boehringer Ingelheim is a full member of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). The corporate logo of Boehringer Ingelheim depicts a stylized rendition of the central section of the imperial palace of Charlemagne. History 1885–1999 *1885: Albert Boehringer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterility Assurance Level
In microbiology, sterility assurance level (SAL) is the probability that a single unit that has been subjected to sterilization nevertheless remains nonsterile. It is never possible to prove that all organisms have been destroyed, as the likelihood of survival of an individual microorganism is never zero. So SAL is used to express the probability of the survival. For example, medical device manufacturers design their sterilization processes for an extremely low SAL, such as 10−6, which is a 1 in 1,000,000 chance of a non-sterile unit. SAL also describes the killing efficacy of a sterilization process. A very effective sterilization process has a very low SAL. Terminology Mathematically, SALs are probabilities, often very small but (by definition) always lying between zero and one. So when they are expressed in scientific notation their exponents are negative, as for instance, "The SAL of this process is 10−6". But the term ''SAL'' is sometimes also used to refer to a sterili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
KU Leuven (or Katholieke Universiteit Leuven) is a Catholic research university in the city of Leuven, Belgium. It conducts teaching, research, and services in computer science, engineering, natural sciences, theology, humanities, medicine, law, canon law, business, and social sciences. In addition to its main campus in Leuven, it has satellite campuses in Kortrijk, Antwerp, Ghent, Bruges, Ostend, Geel, Diepenbeek, Aalst, Sint-Katelijne-Waver, and in Belgium's capital Brussels. KU Leuven is the largest university in Belgium and the Low Countries. In 2017–18, more than 58,000 students were enrolled. Its primary language of instruction is Dutch, although several programs are taught in English, particularly graduate and postgraduate degrees. KU Leuven consistently ranks among the top 100 universities in the world by major ranking tables. As of 2021, it ranks 42nd in the ''Times Higher Education'' rankings, 70th according QS World University Rankings, 87th according to the Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Drug Resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasites (resistant to multiple antifungal, antiviral, and antiparasitic drugs of a wide chemical variety). Recognizing different degrees of MDR in bacteria, the terms extensively drug-resistant (XDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) have been introduced. Extensively drug-resistant (XDR) is the non-susceptibility of one bacteria species to all antimicrobial agents except in two or less antimicrobial categories. Within XDR, pandrug-resistant (PDR) is the non-susceptibility of bacteria to all antimicrobial agents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |