|
Novorybnaya
Novorybnaya is a village and former camp in the administrative and municipal district of Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District, established as a city on January 23, 1931. The current population is 627, the highest of the three villages in the northern reindeer settlement of Khatanga. Electricity is provided by a diesel power plant. Internet was established here on April 26, 2021. Geography The city is located on the Taymyr peninsula and near the mouth of the Khatanga River, in what was once an okrug but is now a district. It is in the far arctic north of Krasnoyarsk Krai, where indigenous people, such as Nenets, live in the northern taiga, tree line, and tundra eco-regions. The scenery is open tundra, as far as the eye can see. Climate Though this town is well within the arctic tundra ecoregion (~ 73 N), its climate is '' Dfc'' (taiga), with long, cold winters and short summers. The average high in July is 62 F (17 C), and the average lows in January and February are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District
Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District (russian: Таймы́рский Долга́но-Не́нецкий райо́н) is an administrativeLaw #10-4765 and municipalLaw #2-54 district (raion), one of the forty-three in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is located in the north of the krai above the Arctic Circle on the Taymyr Peninsula and borders with Laptev and Kara Seas in the north, the Sakha Republic in the east, Evenkiysky and Turukhansky Districts in the south, and with Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug in the west. The area of the district is .Official website of Krasnoyarsk KraiInformation about Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District Its administrative center is the town of Dudinka, which accounts for 64.4% of the district's total population. The 2010 Russian census counted 34,432 people in the whole district, as opposed to 39,786 ( 2002 Census) in 2002, and in 1989. Norilsk is an enclave surrounded by, but independent from, Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District. In 2005, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east. The sea is named after the Russian explorers Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev; formerly, it had been known under various names, the last being Nordenskiöld Sea (russian: link=no, мо́ре Норденшёльда), after explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The sea has a severe climate with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) over more than nine months per year, low water salinity, scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, and low depths (mostly less than 50 meters) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of Siberia
Siberia, including the Russian Far East, is a vast region spanning the northern part of the Asian continent, and forming the Asiatic portion of Russia. As a result of the Russian conquest of Siberia (17th to 19th centuries) and of the subsequent population movements during the Soviet era (1917-1991), the modern-day demographics of Siberia is dominated by ethnic Russians ( Siberiaks) and other Slavs. However, there remains a slowly increasing number of indigenous groups, between them, accounting for about 10% of the total Siberian population (about 4,500,000), some of which are closely genetically related to indigenous peoples of the Americas. History In Kamchatka, the Itelmens' uprisings against Russian rule in 1706, 1731, and 1741, were crushed. During the first uprising the Itelmen were armed with only stone weapons, but in later uprisings they used gunpowder weapons. The Russian Cossacks faced tougher resistance from the Koryaks, who revolted with bows and guns from 1745 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru , image = , caption = , population = , popplace = 118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate) , region1 = , pop1 = approx. 7,500,000 (including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 7,170,000 (2018) ''including Crimea'' , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 3,512,925 (2020) , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 3,072,756 (2009)(including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 1,800,000 (2010)(Russian ancestry and Russian Germans and Jews) , ref5 = 35,000 (2018)(born in Russia) , region6 = , pop6 = 938,500 (2011)(including Russian Jews) , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 809,530 (2019) , ref7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nganasan People
The Nganasans (; Nganasan: ''ŋənəhsa(nəh)'', ''ńæh'') are a Uralic people of the Samoyedic branch native to the Taymyr Peninsula in north Siberia. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as one of the indigenous peoples of the Russian North. They reside primarily in the settlements of Ust-Avam, Volochanka, and Novaya in the Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai, with smaller populations residing in the towns of Dudinka and Norilsk as well. The Nganasans are thought to be the direct descendants of proto-Uralic peoples. However there is some evidence that they absorbed local Paleo-Siberian population. The Nganasans were traditionally a semi-nomadic people whose main form of subsistence was wild reindeer hunting, in contrast to the Nenets, who herded reindeer. Beginning in the early 17th century, the Nganasans were subjected to the yasak system of Czarist Russia. They lived relatively independently, until the 1970s, when they were settled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolgans
Dolgans (; Dolgan: , , (Sakha); Yakut: ) are an ethnic group who mostly inhabit Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. They are descended from several groups, particularly Evenks, one of the indigenous peoples of the Russian North. They adopted a Turkic language sometime after the 18th century. The 2010 Census counted 7,885 Dolgans. This number includes 5,517 in former Taymyr Autonomous Okrug. Dolgans speak the Dolgan language, which is closely related to the Yakut language. History In the 17th century, the Dolgans lived in the basins of the Olenyok River and Lena River. They moved to their current location, Taymyr, in the 18th century. The Dolgan identity began to emerge during the 19th and early 20th centuries, under the influence of three groups who migrated to the Krasnoyarsk area from the Lena River and Olenyok River region: Evenks, Yakuts, Enets, and so-called tundra peasants (). Culture and livelihood Originally, the Dolgans were nomadic hunters and reindeer herders. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
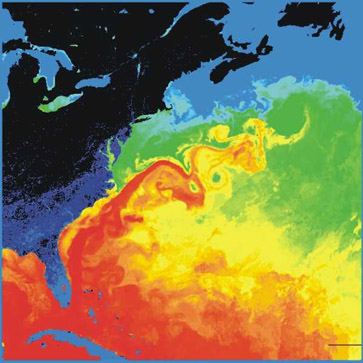
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States then veers east near 36 latitude (North Carolina) and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of Boundary current, western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northwards accelerating current off the east coast of North America. At about , it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the coastal areas of the east coast of the United States from Florida to southeast Virginia (near 36 north latitude), and to a greater degree the climate of Northwest Europe. There is consensus that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sápmi
(, smj, Sábme / Sámeednam, sma, Saepmie, sju, Sábmie, , , sjd, Са̄мь е̄ммьне, Saam' jiemm'n'e) is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sámi people. Sápmi is in Northern and Eastern Europe and includes the northern parts of Fennoscandia, also known as the "Cap of the North". The region stretches over four countries: Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia. On the north it is bounded by the Barents Sea, on the west by the Norwegian Sea, and on the east by the White Sea."Lapland." Encyclopædia Britannica. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2009. Web. 24 November 2009 http://search.eb.com/eb/article-9047170. The area is historically referred to as Lapland () in English, although the term "Lapp" for its inhabitants is now considered pejorative.; ; Norwegian Sápmi was historically called ''Finnmǫrk'', a name used for the former county Finnmark, now Troms og Finnmark. Sápmi refers to the areas where the Sámi people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rovaniemi
Rovaniemi ( , ; sme, Roavvenjárga ; smn, Ruávinjargâ; sms, Ruäʹvnjargg) is a city and municipality of Finland. It is the administrative capital and commercial centre of Finland's northernmost province, Lapland, and its southern part Peräpohjola. The city centre is situated about south of the Arctic Circle and is between the hills of Ounasvaara and Korkalovaara, at the confluence of the river Kemijoki and its tributary, the Ounasjoki. It is the second-largest city of Northern Finland after Oulu, and, together with the capital city Helsinki, it is one of Finland's most significant tourist cities in terms of foreign tourism. The city and the surrounding (Rural municipality of Rovaniemi) were consolidated into a single entity on 1 January 2006. Rovaniemi municipality has an approximate population of . The urban area of Rovaniemi has a population of 53,361, in an area of about . Rovaniemi is a unilingual Finnish-speaking municipality and, uncommonly for larger Finnish to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiruna
(; se, Giron ; fi, Kiiruna ) is the northernmost Stad (Sweden), city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland, Sweden, Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The city was originally built in the 1890s to serve the Kiruna Mine. The Esrange Space Center was established in Kiruna in the 1960s. Also in Kiruna are the Institute of Space Physics (Sweden), Institute of Space Physics and Luleå University of Technology's Department of Space Science. History Origins Archaeological findings have shown that the region around Kiruna has been inhabited for at least 6,000 years. Centuries before Kiruna was founded in 1900, the presence of iron ore at Kiirunavaara and Luossavaara had been known by the local Sami people, Sami population. In 1696, Samuel Mört, a bookkeeper of the Kengis works, wrote on rumours about the presence of iron in the two hills.Kummu 1997, p. 96. The ore became b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; iu, ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the Inuit of Quebec and part of the wider Inuit Nunangat. Almost all of the 14,045 inhabitants ( 2021 census) of the region, of whom 90% are Inuit, live in fourteen northern villages on the coast of Nunavik and in the Cree reserved land (TC) of Whapmagoostui, near the northern village of Kuujjuarapik. means "great land" in the local dialect of Inuktitut and the Inuit inhabitants of the region call themselves . Until 1912, the region was part of the District of Ungava of the Northwest Territories. Negotiations for regional autonomy and resolution of outstanding land claims took place in the 2000s. The seat of government would be Kuujjuaq. Negotiations on better empowering Inuit political rights in their land are still ongoing. A flag for N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)