|
Northern Local Supervoid
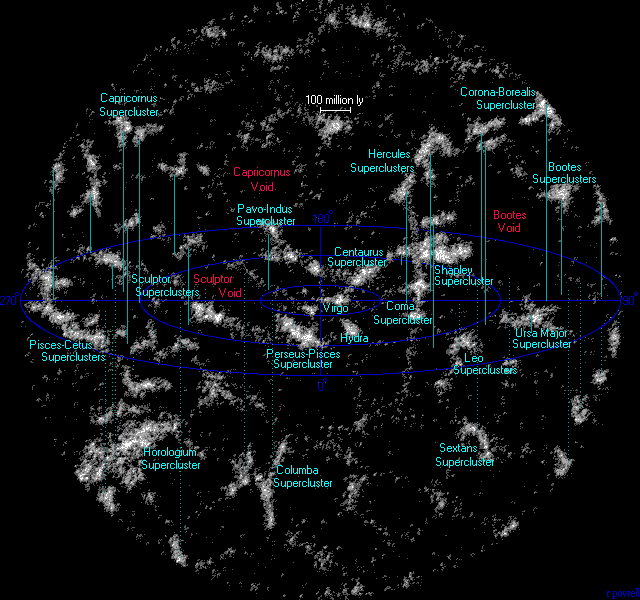
The Northern Local Supervoid is a region of space devoid of rich clusters of galaxy, galaxies, known as a Void (astronomy), void. It is the closest supervoid and is located between the Virgo supercluster, Virgo (Local), Coma supercluster, Coma and Hercules Supercluster, Hercules superclusters. On the sky, it is located between Boötes (constellation), Boötes, Virgo (constellation), Virgo, and Serpens, Serpens Caput constellations. It contains a few small galaxy, galaxies (primarily spiral galaxy, spirals) and galaxy clusters, but is mostly empty. The faint galaxies within this void divide the region into smaller voids, which are 3–10 times smaller than the supervoid. The center is located away at approximately (, ) and it is in diameter across its narrowest width. See also * KBC Void References Voids (astronomy) {{astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Void (astronomy)
Cosmic voids (also known as dark space) are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. The cosmological evolution of the void regions differs drastically from the evolution of the Universe as a whole: there is a long stage when the curvature term dominates, which prevents the formation of galaxy clusters and massive galaxies. Hence, although even the emptiest regions of voids contain more than ~15% of the average matter density of the Universe, the voids look almost empty for an observer. Voids typically have a diameter of 10 to 100 megaparsecs (30 to 300 million light-years); particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich superclusters, are sometimes called supervoids. They were first discovered in 1978 in a pioneering study by Stephen Gregory and Laird A. Thompson at the Kitt Peak National Observatory. Voids are believed to have been formed by baryon acoustic oscillations in the Big Bang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters are located within its diameter of 33 megaparsecs (110 million light-years). The Virgo SC is one of about 10 million superclusters in the observable universe and is in the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex, a galaxy filament. A 2014 study indicates that the Virgo Supercluster is only a lobe of an even greater supercluster, Laniakea, a larger, competing referent of the term Local Supercluster centered on the Great Attractor. Background Beginning with the first large sample of nebulae published by William and John Herschel in 1863, it was known that there is a marked excess of nebular fields in the constellation Virgo (near the north galactic pole). In the 1950s, French–American astronomer Gérard de Vau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma Supercluster
The Coma Supercluster (SCl 117) is a nearby supercluster of galaxies comprising the Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) and the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367). Located 300 million light-years from Earth, it is in the center of the Great Wall and a part of the Coma Filament. The Coma Supercluster is the nearest massive cluster of galaxies to our own Virgo Supercluster. It is roughly spherical, about 20 million light-years in diameter and contains more than 3,000 galaxies. It is located in the constellation Coma Berenices. Being one of the first superclusters to be discovered, the Coma Supercluster helped astronomers understand the large scale structure of the universe. See also * Abell catalogue * Large-scale structure of the universe * List of Abell clusters The Abell catalogue is a catalogue of approximately 4,000 galaxy clusters with at least 30 members, almost complete to a redshift of ''z'' = 0.2. It was originally compiled by the American astronomer George O. Abell in 1958 using plates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules Supercluster
The Hercules Superclusters (SCl 160) refers to a set of two nearby superclusters of galaxies. Relative to other local superclusters, Hercules is considered particularly large, being approximately 330 Mly in diameter. The Northern Local Supervoid lies in front of the superclusters, and is as big as the superclusters themselves. The redshifts of the member galaxies lie between 0.0304 and 0.0414. The region includes Abell 2147, Hercules Cluster, Abell 2151 (Hercules Cluster), and Abell 2152 galaxy clusters. An extremely long filament of galaxies has been found, that connects this group of clusters to the Abell 2197 and Abell 2199 pair. Abell 2162 in the nearby constellation Corona Borealis is also a member. The Hercules Superclusters are near the Coma Supercluster, helping make up part of the CfA2 Great Wall. In the 1930s, Harlow Shapley studied the structure of the distribution of galaxies in the Hercules (constellation), constellation of Hercules, and was probably first to discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea ''Nature (journal), Nature'' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boötes (constellation)
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from la, Boōtēs, which comes from grc-gre, Βοώτης, Boṓtēs ' herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, ' ox-driver'; from ''boûs'' 'cow'). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth-brightest star in the night sky, the orange giant Arcturus. Epsilon Boötis, or Izar, is a colourful multiple star popular with amateur astronomers. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye. History and mythology In ancient Babylon, the stars of Boötes were known as SHU.PA. They were apparently depicted as the god Enlil, who was the leader of the Babylonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo (constellation)
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for maiden, and its old astronomical symbol is (♍︎). Lying between Leo (constellation), Leo to the west and Libra (constellation), Libra to the east, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky (after Hydra (constellation), Hydra) and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica. Location Virgo is prominent in the spring sky in the Northern Hemisphere, visible all night in March and April. As the largest zodiac constellation, the Sun takes 44 days to pass through it, longer than any other. From 1990 and until 2062, this will take place from September 16 to October 30. It is located in the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpens
Serpens ( grc, , , the Serpent) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in ''Serpens Caput'' and Nu Serpentis in ''Serpens Cauda''. The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Alt URL pp. 124–151) and, as such, form part of the . Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating containing s, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the |
Astronomy And Astrophysics
''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. The journal is run by a Board of Directors representing 27 sponsoring countries plus a representative of the European Southern Observatory. The journal is published by EDP Sciences and the editor-in-chief is . History Origins ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'' (A&A) was created as an answer to the publishing scenario found in Europe in the 1960s. At that time, multiple journals were being published in several countries around the continent. These journals usually had a limited number of subscribers, and published articles in languages other than English, resulting in a small number of citations compared to American and British journals. Starting in 1963, conversations between astronomers from European countries assessed the need for a common astronomical journal. On 8 April 1968, leading astronomers from Belgium, Denmark, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |