|
Norman Lockyer Observatory
The Norman Lockyer Observatory, the Lockyer Technology Centre, and the Planetarium (jointly NLO), is a public access optical observatory east of Sidmouth, East Devon in South West England. It houses a number of historical optical telescopes, including the Lockyer Telescope, and is operated by Norman Lockyer Observatory Society (NLOS). History The observatory was founded by Joseph Norman Lockyer in 1912 when he retired to Sidmouth following the closure of the South Kensington Observatory, of which Lockyer was Director. Originally known as Hill Observatory, the observatory was renamed Norman Lockyer Observatory after his death in 1920. Mary Thomasina Browne, ''a.k.a.'' "Lady Lockyer", took a strong interest in the observatory and made gifts to it. She was elected to the Royal Astronomical Society in 1923. The Observatory's historic instruments are associated with Lockyer's pioneering work on star temperature which led to theories of stellar evolution and the foundation of as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Observatory
A public observatory is an astronomical observatory mainly dedicated to public and educational purposes. It is often supported by a municipality, a school or an astronomical society. The primary purpose of public observatories is to offer extensive programs for public education in astronomy. A second purpose may be to serve as a center for local hobby astronomers, or for interested astro-tourists. Some sites also are engaged in special research programs, e.g. on meteors or asteroids. Public observatories are equipped with several optical telescope An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electro ...s that are housed within a dome or similar structure to protect the instruments from the elements. The domes have a slit in the roof that can be opened during observing and closed when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Physics Observatory
The Institute of Astronomy (IoA) is the largest of the three astronomy departments in the University of Cambridge, and one of the largest astronomy sites in the United Kingdom. Around 180 academics, postdocs, visitors and assistant staff work at the department. Research at the department is made in a number of scientific areas, including exoplanets, stars, star clusters, cosmology, gravitational-wave astronomy, the high-redshift universe, AGN, galaxies and galaxy clusters. This is a mixture of observational astronomy, over the entire electromagnetic spectrum, computational theoretical astronomy, and analytic theoretical research. The Kavli Institute for Cosmology is also located on the department site. This institute has an emphasis on ''The Universe at High Redshifts''. The Cavendish Astrophysics Group are based in the Battcock Centre, a building in the same grounds. History The institute was formed in 1972 from the amalgamation of earlier institutions: * The Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science History
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Eastern Roman (or Byzantine) Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are monitored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Current
In meteorology, air currents are concentrated areas of winds. They are mainly due to differences in atmospheric pressure or temperature. They are divided into horizontal and vertical currents; both are present at mesoscale while horizontal ones dominate at synoptic scale. Air currents are not only found in the troposphere, but extend to the stratosphere and mesosphere. Horizontal currents A difference in air pressure causes an air displacement and generates the wind. The Coriolis Force deflects the air movement to the right in the northern hemisphere and the left in the southern one, which makes the winds parallel to the isobars on an elevation in pressure card. It's called the geostrophic wind. Pressure differences depend, in turn, on the average temperature in the air column. As the sun does not heat the Earth evenly, there is a temperature difference between the poles and the equator, creating air masses with more or less homogeneous temperature with latitude. Differences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial Visible spectrum, lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light pollution can be understood not only as a phenomenon resulting from a specific source or kind of pollution, but also as a contributor to the wider, collective impact of various sources of pollution. Although this type of pollution can exist throughout the day, its effects are magnified during the night with the contrast of darkness. It has been estimated that 83 percent of the world's people live under light-polluted skies and that 23 percent of the world's land area is affected by skyglow. The area affected by artificial illumination continues to increase. A major side-effect of urbanization, light pollution is blamed for compromising health, disrupting ecosystems, and spoiling aesthetic environments. Globally, it has incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Seeing
In astronomy, seeing is the degradation of the image of an astronomical object due to turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth that may become visible as blurring, twinkling or variable distortion. The origin of this effect are rapidly changing variations of the optical refractive index along the light path of the object. Seeing is a major limitation to the angular resolution in astronomical observations with telescopes that would otherwise be limited through diffraction by the size of the telescope aperture. Today, many large scientific ground-based optical telescopes include adaptive optics to overcome seeing. The strength of seeing is often characterized by the angular diameter of the long-exposure image of a star (''seeing disk'') or by the Fried parameter ''r''0. The diameter of the seeing disk is the full width at half maximum of its optical intensity. An exposure time of several tens of milliseconds can be considered ''long'' in this context. The Fried parameter describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
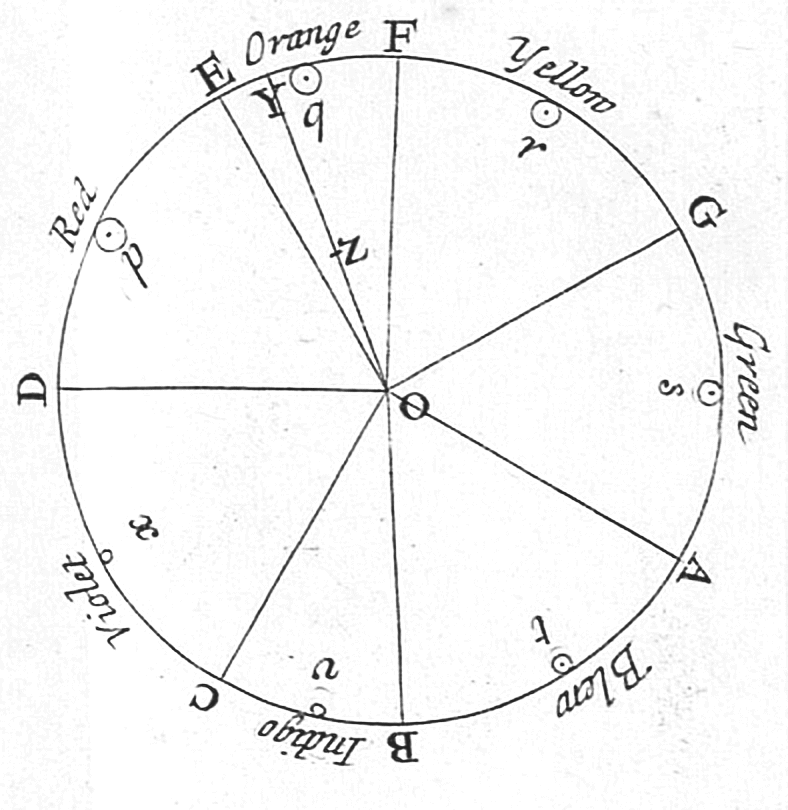
Optical Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. '' Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or purple variations like magenta, for example, are absen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |