|
Nonhypotenuse Number
In mathematics, a nonhypotenuse number is a natural number whose square ''cannot'' be written as the sum of two nonzero squares. The name stems from the fact that an edge of length equal to a nonhypotenuse number ''cannot'' form the hypotenuse of a right angle triangle with integer sides. The numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4 are all nonhypotenuse numbers. The number 5, however, is ''not'' a nonhypotenuse number as 52 equals 32 + 42. The first fifty nonhypotenuse numbers are: :1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 16, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 27, 28, 31, 32, 33, 36, 38, 42, 43, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 54, 56, 57, 59, 62, 63, 64, 66, 67, 69, 71, 72, 76, 77, 79, 81, 83, 84 Although nonhypotenuse numbers are common among small integers, they become more-and-more sparse for larger numbers. Yet, there are infinitely many nonhypotenuse numbers, and the number of nonhypotenuse numbers not exceeding a value ''x'' scales asymptotically with ''x''/. The nonhypotenuse numbers are those numbers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are those numbers used for counting (as in "there are ''six'' coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country"). Numbers used for counting are called ''Cardinal number, cardinal numbers'', and numbers used for ordering are called ''Ordinal number, ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are sometimes used as labels, known as ''nominal numbers'', having none of the properties of numbers in a mathematical sense (e.g. sports Number (sports), jersey numbers). Some definitions, including the standard ISO/IEC 80000, ISO 80000-2, begin the natural numbers with , corresponding to the non-negative integers , whereas others start with , corresponding to the positive integers Texts that exclude zero from the natural numbers sometimes refer to the natural numbers together with zero as the whole numbers, while in other writings, that term is used instead for the integers (including negative integers). The natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotenuse
In geometry, a hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle. The length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. For example, if one of the other sides has a length of 3 (when squared, 9) and the other has a length of 4 (when squared, 16), then their squares add up to 25. The length of the hypotenuse is the square root of 25, that is, 5. Etymology The word ''hypotenuse'' is derived from Greek (sc. or ), meaning " idesubtending the right angle" (Apollodorus), ''hupoteinousa'' being the feminine present active participle of the verb ''hupo-teinō'' "to stretch below, to subtend", from ''teinō'' "to stretch, extend". The nominalised participle, , was used for the hypotenuse of a triangle in the 4th century BCE (attested in Plato, ''Timaeus'' 54d). The Greek term was loaned into La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Triple
A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers , , and , such that . Such a triple is commonly written , and a well-known example is . If is a Pythagorean triple, then so is for any positive integer . A primitive Pythagorean triple is one in which , and are coprime (that is, they have no common divisor larger than 1). For example, is a primitive Pythagorean triple whereas is not. A triangle whose sides form a Pythagorean triple is called a Pythagorean triangle, and is necessarily a right triangle. The name is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, stating that every right triangle has side lengths satisfying the formula a^2+b^2=c^2; thus, Pythagorean triples describe the three integer side lengths of a right triangle. However, right triangles with non-integer sides do not form Pythagorean triples. For instance, the triangle with sides a=b=1 and c=\sqrt2 is a right triangle, but (1,1,\sqrt2) is not a Pythagorean triple because \sqrt2 is not an integer. Moreover, 1 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Of Computation
''Mathematics of Computation'' is a bimonthly mathematics journal focused on computational mathematics. It was established in 1943 as ''Mathematical Tables and other Aids to Computation'', obtaining its current name in 1960. Articles older than five years are available electronically free of charge. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Mathematical Reviews, Zentralblatt MATH, Science Citation Index, CompuMath Citation Index, and Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.417. References External links * Delayed open access journals English-language journals Mathematics journals Publications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Factor
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow method of checking the primality of a given number n, called trial division, tests whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and \sqrt. Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error, and the AKS primality test, which always pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Prime
A Pythagorean prime is a prime number of the Pythagorean primes are exactly the odd prime numbers that are the sum of two squares; this characterization is Fermat's theorem on sums of two squares. Equivalently, by the Pythagorean theorem, they are the odd prime numbers p for which \sqrt p is the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with integer legs, and they are also the prime numbers p for which p itself is the hypotenuse of a primitive Pythagorean triangle. For instance, the number 5 is a Pythagorean prime; \sqrt5 is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs 1 and 2, and 5 itself is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs 3 and 4. Values and density The first few Pythagorean primes are By Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions, this sequence is infinite. More strongly, for each n, the numbers of Pythagorean and non-Pythagorean primes up to n are approximately equal. However, the number of Pythagorean primes up to n is frequently somewhat smaller tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibonacci Quarterly
The ''Fibonacci Quarterly'' is a scientific journal on mathematical topics related to the Fibonacci numbers, published four times per year. It is the primary publication of The Fibonacci Association, which has published it since 1963. Its founding editors were Verner Emil Hoggatt Jr. and Alfred Brousseau; by Clark Kimberling the present editor is Professor Curtis Cooper of the Mathematics Department of the . The ''Fibonacci Quarterly'' has an editorial board of nineteen members an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition Chain
In mathematics, an addition chain for computing a positive integer can be given by a sequence of natural numbers starting with 1 and ending with , such that each number in the sequence is the sum of two previous numbers. The ''length'' of an addition chain is the number of sums needed to express all its numbers, which is one less than the cardinality of the sequence of numbers. Examples As an example: (1,2,3,6,12,24,30,31) is an addition chain for 31 of length 7, since :2 = 1 + 1 :3 = 2 + 1 :6 = 3 + 3 :12 = 6 + 6 :24 = 12 + 12 :30 = 24 + 6 :31 = 30 + 1 Addition chains can be used for addition-chain exponentiation. This method allows exponentiation with integer exponents to be performed using a number of multiplications equal to the length of an addition chain for the exponent. For instance, the addition chain for 31 leads to a method for computing the 31st power of any number using only seven multiplications, instead of the 30 multiplications that one would get from repeated multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIAM Journal On Computing
The ''SIAM Journal on Computing'' is a scientific journal focusing on the mathematical and formal aspects of computer science. It is published by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM). Although its official ISO abbreviation is ''SIAM J. Comput.'', its publisher and contributors frequently use the shorter abbreviation ''SICOMP''. SICOMP typically hosts the special issues of the IEEE Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS) and the Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC), where about 15% of papers published in FOCS and STOC each year are invited to these special issues. For example, Volume 48 contains 11 out of 85 papers published in FOCS 2016. References * External linksSIAM Journal on Computing on |
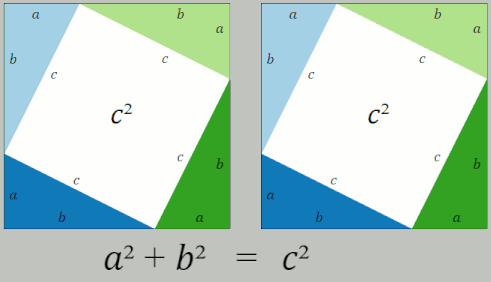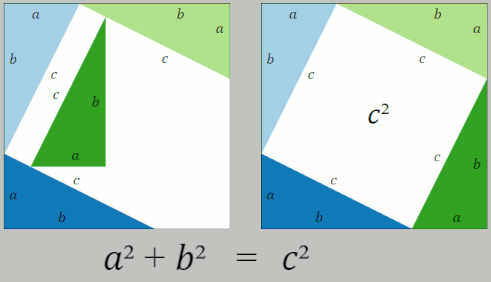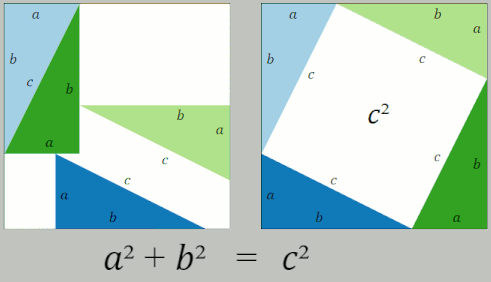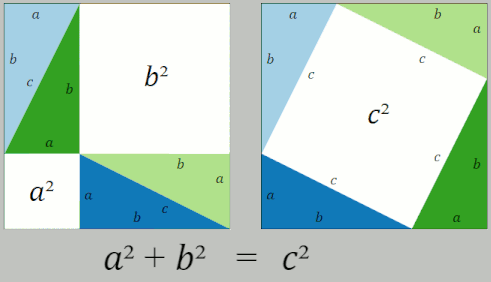
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides ''a'', ''b'' and the hypotenuse ''c'', often called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 , The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proven numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies the Pythagorean relation: the squared dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |