|
Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy
Noncompaction cardiomyopathy (NCC) is a rare congenital disease of heart muscle that affects both children and adults. It results from abnormal prenatal development of heart muscle. During development, the majority of the heart muscle is a sponge-like meshwork of interwoven myocardial fibers. As normal development progresses, these trabeculated structures undergo significant compaction that transforms them from spongy to solid. This process is particularly apparent in the ventricles, and particularly so in the left ventricle. Noncompaction cardiomyopathy results when there is failure of this process of compaction. Because the consequence of non-compaction is particularly evident in the left ventricle, the condition is also called left ventricular noncompaction. Other hypotheses and models have been proposed, none of which is as widely accepted as the noncompaction model. Symptoms range greatly in severity. Most are a result of a poor pumping performance by the heart. The dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. Originally formed in New York City in 1924, it is currently headquartered in Dallas, Texas. The American Heart Association is a national voluntary health agency. They are known for publishinguidelineson cardiovascular disease and prevention, standards on basic life support, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), and pediatric advanced life support (PALS), and in 2014 issued its first guidelines for preventing strokes in women. They are known also for operating a number of highly visible public service campaigns starting in the 1970s, and also operate a number of fundraising events. In 1994, the ''Chronicle of Philanthropy'', an industry publication, released a study that showed the American H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart, with or without both lungs, from a recently deceased organ donor ( brain death is the standard) and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart ( orthotopic procedure) or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart (heterotopic, or "piggyback", transplant procedure). Approximately 3,500 heart transplants are performed each year worldwide, more than half of which are in the US. Post-operative survival periods average 15 years. Heart transplantation is not considered to be a cure for heart disease; rather it is a life-saving treatment intended to improve the quality and duration of life for a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. One common adverse effect is an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart attack (preventative healthcare, secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines Adrenaline, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on beta receptor, adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Some block activation of all types of β-adrenergic receptors and others are selective for one of the three known types of beta receptors, designated β1, β2 and β3 receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (), or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. Therefore, ACE indirectly increases blood pressure by causing blood vessels to constrict. ACE inhibitors are widely used as pharmaceutical drugs for treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Other lesser known functions of ACE are degradation of bradykinin, substance P and amyloid beta-protein. Nomenclature ACE is also known by the following names: * dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I * peptidase P * dipeptide hydrolase * peptidyl dipeptidase * angiotensin converting enzyme * kininase II * angiotensin I-converting enzyme * carboxycathepsin * dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase * "hypertensin converting enzyme" peptidyl dipeptidase I * peptidyl-dipeptide hydrolase * peptidyldipeptide hydrolase * endothelial cell peptidyl dipeptidas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertensive Heart Disease
Hypertensive heart disease includes a number of complications of high blood pressure that affect the heart. While there are several definitions of hypertensive heart disease in the medical literature, the term is most widely used in the context of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) coding categories. The definition includes heart failure and other cardiac complications of hypertension when a causal relationship between the heart disease and hypertension is stated or implied on the death certificate. In 2013 hypertensive heart disease resulted in 1.07 million deaths as compared with 630,000 deaths in 1990. According to ICD-10, hypertensive heart disease (I11), and its subcategories: hypertensive heart disease with heart failure (I11.0) and hypertensive heart disease without heart failure (I11.9) are distinguished from chronic rheumatic heart diseases (I05-I09), other forms of heart disease (I30-I52) and ischemic heart diseases (I20-I25). However, since high blood p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
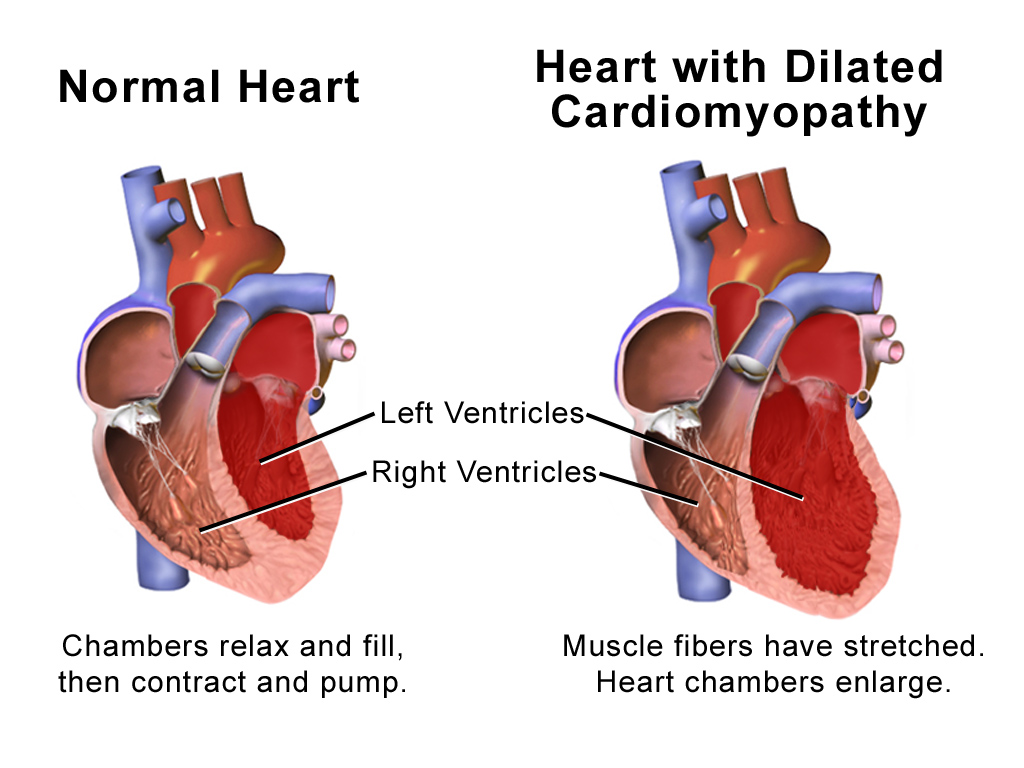
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Risk factors include certain infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)