|
Nodularia (bivalve)
''Nodularia'' is a genus of filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae. They occur mainly in brackish or salinic waters, such as the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans, the Peel-Harvey Estuary in Western Australia or the Baltic Sea. ''Nodularia'' cells occasionally form heavy algal blooms. Some strains produce a cyanotoxin called nodularin R, which is harmful to humans. The type species for the genus is ''Nodularia spumigena'' Mertens ex Bornet & Flahault, 1886. Morphology ''Nodularia'' may form solitary filaments or groups of filaments. They reproduce by the formation of hormogonia, filament breakage, and by akinetes An akinete is an enveloped, thick-walled, non-motile, dormant cell formed by filamentous, heterocyst-forming cyanobacteria under the order Nostocales and Stigonematales. Akinetes are resistant to cold and desiccation. They also accumulate and stor ... .Martin Dworkin and Stanley Falkow, 2006 See also Kruger, T., Oelmuller, R., and Luckas, B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Carl Mertens
Franz Carl Mertens (3 April 1764 – 19 June 1831) was a German botanist who was a native of Bielefeld. He specialized in the field of phycology. Mertens studied theology and languages at the University of Halle, and after graduation taught classes at Bremen Polytechnic College. In his spare time he studied botany, and through a mutual friend met German botanist Albrecht Wilhelm Roth (1757–1834). With Roth, he took scientific expeditions throughout Europe, including Scandinavia. From these trips, Mertens described a number of species of algae. He also performed illustrative work on Volume 3 of Roth's ''Catalecta botanica''. With Erlangen professor Wilhelm Daniel Joseph Koch (1771–1849), he published the third edition of Johann Christoph Röhling's ''Deutschlands flora'', a five volume treatise on German flora. The plant genus ''Mertensia'' from the family Boraginaceae is named after him, while the ctenophore genus ''Mertensia'' is named after his son Karl Heinrich Merten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
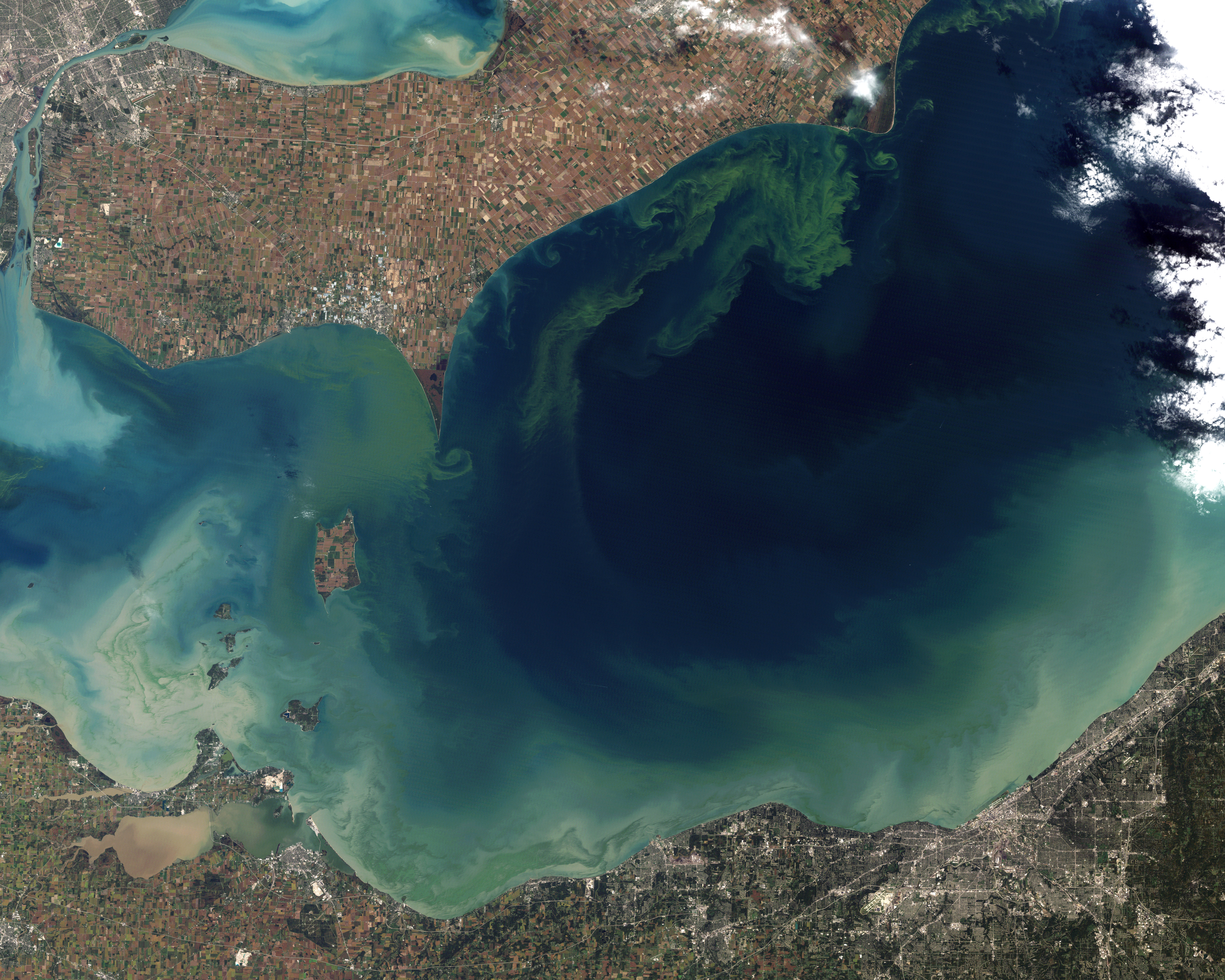
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinetes
An akinete is an enveloped, thick-walled, non-motile, dormant cell formed by filamentous, heterocyst-forming cyanobacteria under the order Nostocales and Stigonematales. Akinetes are resistant to cold and desiccation. They also accumulate and store various essential material, both of which allows the akinete to serve as a survival structure for up to many years. However, akinetes are not resistant to heat. Akinetes usually develop in strings with each cell differentiating after another and this occurs next to heterocysts if they are present. Development usually occurs during stationary phase and is triggered by unfavorable conditions such as insufficient light or nutrients, temperature, and saline levels in the environment. Once conditions become more favorable for growth, the akinete can then germinate back into a vegetative cell. Increased light intensity, nutrients availability, oxygen availability, and changes in salinity are important triggers for germination. In comparison t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormogonia
Hormogonia are motile filaments of cells formed by some cyanobacteria in the order Nostocales and Stigonematales. They are formed during vegetative reproduction in unicellular, filamentous cyanobacteria, and some may contain heterocysts and akinetes. Cyanobacteria differentiate into hormogonia when exposed to an environmental stress or when placed in new media. Hormogonium differentiation is crucial for the development of nitrogen-fixing plant cyanobacteria symbioses, in particular that between cyanobacteria of the genus ''Nostoc'' and their hosts. In response to a hormogonium-inducing factor (HIF) secreted by plant hosts, cyanobacterial symbionts differentiate into hormogonia and then dedifferentiate back into vegetative cells after about 96 hours. Hopefully, they have managed to reach the plant host by this time. The bacteria then differentiate specialized nitrogen-fixing cells called heterocysts and enter into a working symbiosis with the plant. Depending on species, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Flahault
Charles Henri Marie Flahault (3 October 1852 – 3 February 1935) was a French botanist, among the early pioneers of phytogeography, phytosociology, and forest ecology. The word '' relevé'' for a plant community sample is his invention. Early life and education Flahault was born in Bailleul, Nord, and received his Baccalauréat de Lettres at Douai in 1872, after which he became a gardener at the Jardin des Plantes de Paris. He was noticed by Joseph Decaisne (1807–1882), who gave him private lessons, after which he entered the Sorbonne in 1874 to study in the laboratory of Philippe Van Tieghem (1839–1914), obtaining his doctoral degree in biology in 1878. He continued his studies at Uppsala University in 1879 together with Gaston Bonnier. Career In 1881 joined the University of Montpellier where in 1883 he became professor of botany, and in 1890 he founded the ''Institut de Botanique''. The Swiss botanist Josias Braun-Blanquet was one of his students In 1888 Flahault was ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Édouard Bornet
Jean-Baptiste Édouard Bornet (September 2, 1828, Guérigny – December 18, 1911, Paris) was a French botanist. Life Bornet studied medicine in Paris, and in 1886 became a member of the French Académie des sciences. With Gustave Thuret, he was co-author of ''Notes algologiques'' (1876-1880) and the ''Études phycologiques'' (1878), both works being published after Thuret's death in 1875. He helped establish the nature of lichens and was the first to find the reproductive process of red algae. In the field of lichenology, he wrote ''Recherches sur les gonidies des lichens'' (1873). With Charles Flahault, he published on Nostocaceae: ''Revision des Nostocacées héterocystées'' (1886–88). Awards and honours In 1877, botanist Munier-Chalmas published '' Bornetella'' is a genus of green algae in the family Dasycladaceae and named in Jean-Baptiste Édouard Bornet's honor. Bornet was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1888. He was awarded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodularin R
Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium ''Nodularia spumigena'', among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of ''Nodularia spumigena'' are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins. Nodularin-R is the predominant toxin variant, though 10 variants of nodularin have been discovered to date. Nodularins are cyclic nonribosomal pentapeptides and contain several unusual non-proteinogenic amino acids such as N-methyl-didehydroaminobutyric acid and the β-amino acid ADDA. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they exponential growth, reproduce exponentially to form Algal bloom, blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The " Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodularia Armorica
''Nodularia'' is a genus of filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae. They occur mainly in brackish or salinic waters, such as the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans, the Peel-Harvey Estuary in Western Australia or the Baltic Sea. ''Nodularia'' cells occasionally form heavy algal blooms. Some strains produce a cyanotoxin called nodularin R, which is harmful to humans. The type species for the genus is ''Nodularia spumigena'' Mertens ex Bornet & Flahault, 1886. Morphology ''Nodularia'' may form solitary filaments or groups of filaments. They reproduce by the formation of hormogonia, filament breakage, and by akinetes An akinete is an enveloped, thick-walled, non-motile, dormant cell formed by filamentous, heterocyst-forming cyanobacteria under the order Nostocales and Stigonematales. Akinetes are resistant to cold and desiccation. They also accumulate and stor ... .Martin Dworkin and Stanley Falkow, 2006 See also Kruger, T., Oelmuller, R., and Luckas, B. (200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makgadikgadi Pans
The Makgadikgadi Pan (Tswana pronunciation ), a salt pan situated in the middle of the dry savanna of north-eastern Botswana, is one of the largest salt flats in the world. The pan is all that remains of the formerly enormous Lake Makgadikgadi, which once covered an area larger than Switzerland, but dried up tens of thousands of years ago. Recent studies of human mitochondrial DNA suggest that modern ''Homo sapiens'' first began to evolve in this region some 200,000 years ago, when it was a vast, exceptionally fertile area of lakes, rivers, marshes, woodlands and grasslands especially favorable for habitation by evolving hominins and other mammals. Location and description Lying southeast of the Okavango Delta and surrounded by the Kalahari Desert, Makgadikgadi is technically not a single pan, but many pans with sandy desert in between, the largest being the Sua (Sowa), Ntwetwe and Nxai Pans. The largest individual pan is about . In comparison, Salar de Uyuni in Bolivia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)




_(2).jpg)