|
Niğde Belediyespor
Niğde (; grc, Νίγδη; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and the capital of Niğde province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey at an elevation of 1,299 m. In 2017 the city population was 141,010 people. The city is small with plenty of green space and gardens around the houses. Its people generally tend to be religious and conservative. Medieval monuments are scattered about the centre of the town, especially around the market place. The nearest airport is Nevşehir Kapadokya Airport (NAV) which is 90.6 km (50.6 miles) away. History Niğde is located near a number of ancient trade routes, particularly the road from Kayseri (ancient Caesarea Mazaca) to the Cilician Gates and thence to the Mediterranean coast. The area has been settled by Hittites, Assyrians, Greeks, Armenians, Romans, Byzantines and Turks. In the early Middle Ages, it was known as Magida ( el, Μαγίδα), and was settled by the remaining inhabitants of nearby Tyana after it fell to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the governing body of a given municipality. A municipality is a general-purpose administrative subdivision, as opposed to a special-purpose district. The term is derived from French and Latin . The English word ''municipality'' derives from the Latin social contract (derived from a word meaning "duty holders"), referring to the Latin communities that supplied Rome with troops in exchange for their own incorporation into the Roman state (granting Roman citizenship to the inhabitants) while permitting the communities to retain their own local governments (a limited autonomy). A municipality can be any political jurisdiction, from a sovereign state such as the Principality of Monaco, to a small village such as West Hampton Dunes, New York. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Greek-speaking Eastern Romans of Orthodox Christianity throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia Minor (modern Turkey), the Greek islands, Cyprus, and portions of the southern Balkans, and formed large minorities, or pluralities, in the coastal urban centres of the Levant and northern Egypt. Throughout their history, the Byzantine Greeks self-identified as ''Romans'' ( gr, Ῥωμαῖοι, Rhōmaîoi), but are referred to as "Byzantine Greeks" in modern historiography. Latin speakers identified them simply as Greeks or with the term Romei. The social structure of the Byzantine Greeks was primarily supported by a rural, agrarian base that consisted of the peasantry, and a small fraction of the poor. These peasants lived within three kinds of settlements: the ''chorion'' or village, the ''agridion'' or hamlet, and the ''proast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ) * Armenian language, Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province") * Bulgarian language, Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region") * el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province") or επαρχία (''eparchia'', meaning "eparchy") * lad, sancak , group=note (; ota, ; Modern Turkish: ''Sancak'', ) were administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire. ''Sanjak'', and the variant spellings ''sandjak'', ''sanjaq'' and ''sinjaq'', are English language, English or French language, French transliterations of the Turkish language, Turkish word ''sancak'', meaning "district", "banner (country subdivision), banner" or "flag". Sanjaks were also called by the Arabic language, Arabic word for ''banner'' or ''flag'': ''Liwa (Arabic), liwa (Liwā or Liwā’)''. Ottoman provinces (eyalets, later vilayets) were divided into sanjaks (also called ''livas'') governed by sanjakbeys (also calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914 Population Statistics For The Ottoman Empire
The 1914 Ottoman census was collected and published as the ''Memalik-i Osmaniyyenin 1330 Senesi Nütus Istatistiki''. These statistics were prepared by using the figures from the 1905–06 census of the Ottoman Empire and reflecting births and deaths registered in six years from last. The register states that birth and mortality rate used on "nomads" such as the nomadic Nestorians. The 1914 census list reflected major changes in the territorial boundaries and administrative division of the Ottoman state. The population statistics and 1914 Ottoman general election were major population sources. The empire's total population was provided as 18,520,015. The grand total for 1914 showed a "net gain" of 1,131,454 from the 1905-06 Ottoman census survey. The data reflects the loss of territory and population in Europe due to Balkan Wars, as the total net gain figure would be 3,496,068. The census underestimated non-Muslim populations. For example, in Diyarbekir the Armenian population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niğde Prodromos Church 1311
Niğde (; grc, Νίγδη; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and the capital of Niğde province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey at an elevation of 1,299 m. In 2017 the city population was 141,010 people. The city is small with plenty of green space and gardens around the houses. Its people generally tend to be religious and conservative. Medieval monuments are scattered about the centre of the town, especially around the market place. The nearest airport is Nevşehir Kapadokya Airport (NAV) which is 90.6 km (50.6 miles) away. History Niğde is located near a number of ancient trade routes, particularly the road from Kayseri (ancient Caesarea Mazaca) to the Cilician Gates and thence to the Mediterranean coast. The area has been settled by Hittites, Assyrians, Greeks, Armenians, Romans, Byzantines and Turks. In the early Middle Ages, it was known as Magida ( el, Μαγίδα), and was settled by the remaining inhabitants of nearby Tyana after it fell to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim world. He travelled more than any other explorer in pre-modern history, totalling around , surpassing Zheng He with about and Marco Polo with . Over a period of thirty years, Ibn Battuta visited most of southern Eurasia, including Central Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, China, and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, he dictated an account of his journeys, titled ''A Gift to Those Who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling'', but commonly known as ''The Rihla''. Name Ibn Battuta is a patronymic literally meaning "son of the duckling". His most common full name is given as Kunya (Arabic), Abu Abdullah (name), Abdullah Muhammad (name), Muhammad ibn Battuta. In his travel literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
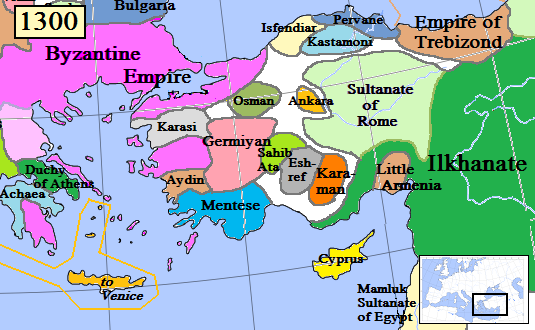
Eretna Beylik
The Eretnids ( tr, Eretna Beyliği) were an Anatolian beylik that succeeded the Ilkhanid governors in Anatolia and that ruled in a large region extending between Caesarea (Kayseri), Sebastea (Sivas) and Amaseia (Amasya) in Central Anatolia between 1328 and 1381. The dynasty was founded by Eretna, an officer of Uyghurs, Uyghur origin in the service of Ilkhanid governors of Anatolia. Although short-lived, the Beylik of Eretna left important works of architecture. The name of Eretna may be derived from Sanskrit word ''Ratna'' "Jewel" or Tuvan language, Tuvan (Turkic) "Ertine" (эртине) "treasure, jewel, value, esteem, appreciate, dignify, treasure, cherish". The dynasty's founder, Eretna, was a Mongol officer of Uyghur origin in the service of Timurtash, the Ilkhanid governor of Anatolia. After his master unsuccessfully revolted in 1327 to ally with the Mamluks in response to the fate of his father Chupan, Ilkhan Abu Sa'id (Ilkhanid dynasty), Abu Said appointed Eretna a governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaman Beylik
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the middle 1300s until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu and others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jones-Williams (New York: Taplinger, 1968), pp. 281–2. which participated in the Babai Revolt, revolt led by Baba Ishak and af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolian Beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A second more extensive period of foundations took place as a result of the decline of the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm in the second half of the 13th century. One of the beyliks, that of the Osmanoğlu from the Kayi tribe of the Oghuz Turks, from its capital in Bursa completed its conquest of other beyliks by the late 15th century, becoming the Ottoman Empire. The word "beylik" denotes a territory under the jurisdiction of a bey, equivalent in other European societies to a lord. History Following the 1071 Seljuq victory over the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert and the subsequent conquest of Anatolia, Oghuz clans began settling in present-day Turkey. The Seljuq Sultanate's central power established in Konya was largely the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Rûm
fa, سلجوقیان روم () , status = , government_type = Hereditary monarchy Triarchy (1249–1254)Diarchy (1257–1262) , year_start = 1077 , year_end = 1308 , p1 = Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynastyByzantine Empire , p2 = Seljuk Empire , p3 = Danishmends , p4 = Mengujekids , p5 = Saltukids , p6 = Artuqids , s1 = Anatolian beyliks , s2 = Ilkhanate, , event_pre = Battle of Manzikert , date_pre = 1071 , event_start = Division from the Seljuk Empire , event1 = Battle of Köse Dağ , date_event1 = 1243 , event_end = Karamanid conquest , image_flag = Double-headed eagle of the Sultanate of Rum.svg , flag_size = 100px , flag_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tyana
The siege of Tyana was carried out by the Umayyad Caliphate in 707–708 or 708–709 in retaliation for a heavy defeat of an Umayyad army under Maimun the Mardaite by the Byzantine Empire in c. 706. The Arab army invaded Byzantine territory and laid siege to the city in summer 707 or 708. The date is uncertain, as virtually each of the extant Greek, Arabic, and Syriac parallel sources has in this respect a different date. Tyana initially withstood the siege with success, and the Arab army faced great hardship during the ensuing winter and was on the point of abandoning the siege in spring, when a relief army sent by Emperor Justinian II arrived. Quarrels among the Byzantine generals, as well as the inexperience of a large part of their army, contributed to a crushing Umayyad victory. Thereupon the inhabitants of the city were forced to surrender. Despite the agreement of terms, the city was plundered and largely destroyed, and according to Byzantine sources its people were made c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |