|
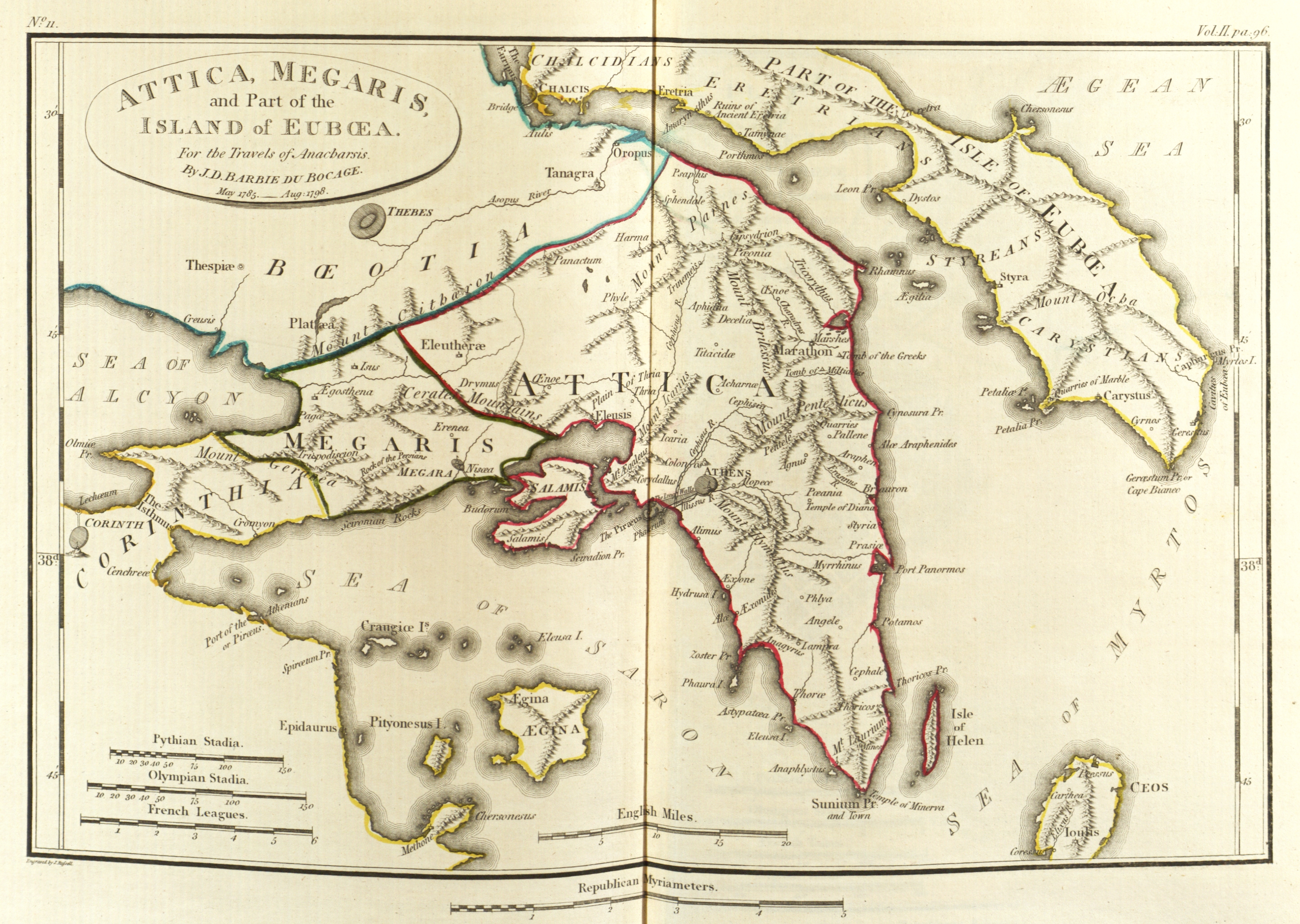
Nisa (Megaris)
Nisa ( grc, Νίσα) was a city in ancient Megaris mentioned by Strabo who wrote that its inhabitants had emigrated to form a colony near the Mount Citheron, and did not exist in his time. In one of the foundation myths of Megara, which was preserved by the Boeotians and adopted by the rest of Greece, Nisa was a prior name of Megara itself and its port-town. In the reign of Pylas, Pandion II being expelled from Athens by the Metionidae, fled to Megara, married the daughter of Pylas, and succeeded his father-in-law in the kingdom. The Metionidae were in their turn driven out of Athens, and when the dominions of Pandion were divided among his four sons, Nisus, the youngest, obtained Megaris. The city was called after him Nisa, and the same name was given to the port-town which he built. When Minos attacked Nisus, Megareus, son of Poseidon, came from Onchestus in Boeotia to assist the latter, and was buried in the city, which was called after him Megara. The name of Nisa, subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Megaris
:''This is also the ancient Greek name of a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.'' Megaris ( grc, Μεγαρίς) was a small but populous state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabitants were adventurous seafarers, credited with deceitful propensities. The capital, Megara, was famous for white marble and fine clay. Mount Geraneia dominates the center of the region. The island of Salamis was originally under the control of Megara, before it was lost to Athens in the late 7th century BCE. Province The province of Megaris or Megarida ( el, Επαρχία Μεγαρίδας or ) was one of the provinces of the East Attica Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aspropyrgos, Eleusis, Mandra-Eidyllia and Megara Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minos
In Greek mythology, Minos (; grc-gre, Μίνως, ) was a King of Crete, son of Zeus and Europa. Every nine years, he made King Aegeus pick seven young boys and seven young girls to be sent to Daedalus's creation, the labyrinth, to be eaten by the Minotaur. After his death, Minos became a judge of the dead in the underworld. The Minoan civilization of Crete was named after him by the archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. Etymology "Minos" is often interpreted as the Cretan word for "king", or, by a euhemerist interpretation, the name of a particular king that was subsequently used as a title. According to La Marle's reading of Linear A, which has been heavily criticised as arbitrary, we should read ''mwi-nu ro-ja'' (Minos the king) on a Linear A tablet. La Marle suggests that the name'' mwi-nu'' (Minos) is expected to mean 'ascetic' as Sanskrit ''muni'', and fits this explanation to the legend about Minos sometimes living in caves on Crete. The royal title ''ro-ja'' is read o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Megaris
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theocritus
Theocritus (; grc-gre, Θεόκριτος, ''Theokritos''; born c. 300 BC, died after 260 BC) was a Greek poet from Sicily and the creator of Ancient Greek pastoral poetry. Life Little is known of Theocritus beyond what can be inferred from his writings. We must, however, handle these with some caution, since some of the poems ('' Idylls''; ) commonly attributed to him have little claim to authenticity. It is clear that at a very early date two collections were made: one consisting of poems whose authorship was doubtful yet formed a corpus of bucolic poetry, the other a strict collection of those works considered to have been composed by Theocritus himself. Theocritus was from Sicily, as he refers to Polyphemus, the Cyclops in the ''Odyssey'', as his "countryman." He also probably lived in Alexandria for a while, where he wrote about everyday life, notably '' Pharmakeutria''. It is also speculated that Theocritus was born in Syracuse, lived on the island of Kos, and lived in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megara Hyblaea
Megara Hyblaea ( grc, Μέγαρα Ὑβλαία) – perhaps identical with Hybla Major – is an ancient Greek colony in Sicily, situated near Augusta on the east coast, north-northwest of Syracuse, Italy, on the deep bay formed by the Xiphonian promontory. There were at least three (and possibly as many as five) cities named "Hybla" in ancient accounts of Sicily which are often confounded with each other, and among which it is sometimes very difficult to distinguish. History It was unquestionably a Greek colony, deriving its origin from the Megara in Greece; and the circumstances attending its foundation are related in detail by Thucydides. He tells us that a colony from Megara, under the command of a leader named Lamis ( grc, Λάμις), arrived in Sicily about the time that Leontini was founded by the Chalcidic colonists, and settled themselves first near the mouth of the river Pantagias, at a place called Trotilon (Latin: Trotilus, modern Brucoli). From there they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisaea
Nisaea or Nisaia ( grc, Νίσαια or Νισαία) was the Saronic Gulf, Saronic port town of the ancient polis Megara. In Greek mythology, Nisaea was founded by one of Pandion II's sons, Nisos, who named the region given to him by his father Nisaea, after himself. Control of Nisaea slipped back and forth between Athens and Megara both before and during the Peloponnesian War, Peloponessian War. Athenian allies of the Megarians built long walls which connected Nisaea to Megaris. According to Thucydides, the length of the walls that connected the port to Megara were eight Greek Stadion (unit), stadia, while Strabo claims the walls to have been 18 stadia in length. A temple of Demeter was located on the road near Nisaea, and a temple of Poseidon located within the port town. Nisaean Megara is thought to have been the birthplace of poet Theognis of Megara, Theognis, but his birthplace is not known for certain The location of the ancient port town remains in debate by historians. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onchestus (Boeotia)
Onchestos or Onchestus ( el, Ογχηστός) was a Greek town in ancient Boeotia northwest of Thebes. In ancient times it was famous for its sanctuary of Poseidon. The site has been excavated intermittently since the 1960s. It was in the territory of Haliartus, said to have been founded by Onchestos, a son of Poseidon. History Onchestos is mentioned in the famous "Catalogue of Ships" in Homer's ''Iliad'' where it is referred to as Poseidon’s "bright grove."Strabon, ''Geōgraphiká'' 9.2.33. The town was a meeting place for the Boeotian League in the Macedonian period. The town was burned by the Persians under Xerxes I, and probably again by the Romans in 171 BC when nearby Haliartus was destroyed. In the early 1st century AD Strabo wrote that the temple was standing although Poseidon's sacred grove was "devoid of trees". In the 2nd century Pausanias wrote that he was still able to see Poseidon’s temple, cult image, and grove. Archaeology Its site is located nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes. He also had the cult title "earth shaker". In the myths of isolated Arcadia he is related with Demeter and Persephone and he was venerated as a horse, however, it seems that he was originally a god of the waters.Seneca quaest. Nat. VI 6 :Nilsson Vol I p.450 He is often regarded as the tamer or father of horses, and with a strike of his trident, he created springs which are related to the word horse.Nilsson Vol I p.450 His Roman equivalent is Neptune. Poseidon was the protector of seafarers, and of many Hellenic cities and colonies. Homer and Hesiod suggest that Poseidon became lord of the sea when, following the overthrow of his father Cronus, the world was divided by lot among Cronus' three sons; Zeus w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megareus Of Onchestus
In Greek mythology, Megareus (Ancient Greek: Μεγαρεύς) may refer to: *Megareus, king of Onchestus in Boeotia and father of Hippomenes. *Megareus, son of Eurydice of Thebes, and a defender of Thebes during the war of the Seven against Thebes. Notes References * Aeschylus, translated in two volumes. 1. ''Seven Against Thebes'' by Herbert Weir Smyth, Ph. D. Cambridge, MA. Harvard University Press. 1926Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * Gaius Julius Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisos
In Greek mythology, Nisos or Nisus (Ancient Greek: Νῖσος) was a King of Megara. Family Nisos was one of the four sons of Pandion II, King of Athens, and Pylia, daughter of King Pylas of Megara. He was the brother of Aegeas, Pallas, Lykos and the wife of Sciron. According to Hyginus, Nisus's father was the god Ares while other authors affirmed that he was the offspring of Deion.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'198/ref> Nisos was married to Abrota, sister of Megareus, and when she died, Nisos commanded that the Megarian women should wear clothes like she had. His daughter Eurynome, with Poseidon, had the famous son Bellerophon. The second daughter Iphinoe married Megareus, her maternal uncle. Lastly, the third princess Scylla was responsible for Nisos' death. Mythology Early days Metion, the uncle of Nisos, had seized the throne from Pandion II. However, upon their father's death, Nisos and his brothers returned to Athens and took back control. They drove out the sons of Metion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



