|
Nirjara
''Nirjara'' is one of the seven fundamental principles, or Tattva in Jain philosophy, and refers to the shedding or removal of accumulated karmas from the atma (soul), essential for breaking free from samsara, the cycle of birth-death and rebirth, by achieving moksha, liberation. Singh, p. 4525 Literally meaning "falling off", the concept is described first in chapter 9 of the classical Jain text, Tattvartha Sutra (True nature of Reality) written by Acharya Umasvati, in 2nd century CE, the only text authoritative in both Svetambara and Digambara sects of Jainism. Later it also finds mention in Dravyasamgraha (Compendium of substances), a 10th-century Jain text by Acharya Nemichandra. Nemichandra, p. 93 Preparation Nirjara is preceded by stoppage of karma accumulation, or '' samvara'', thereby ending '' asrava'' or influx of karma which leads to '' bandha'' or bondage due '' kasaya'' or passions of the soul, namely, ''krodha'' (anger), ''lobha'' (greed), ''mana'' (ego) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
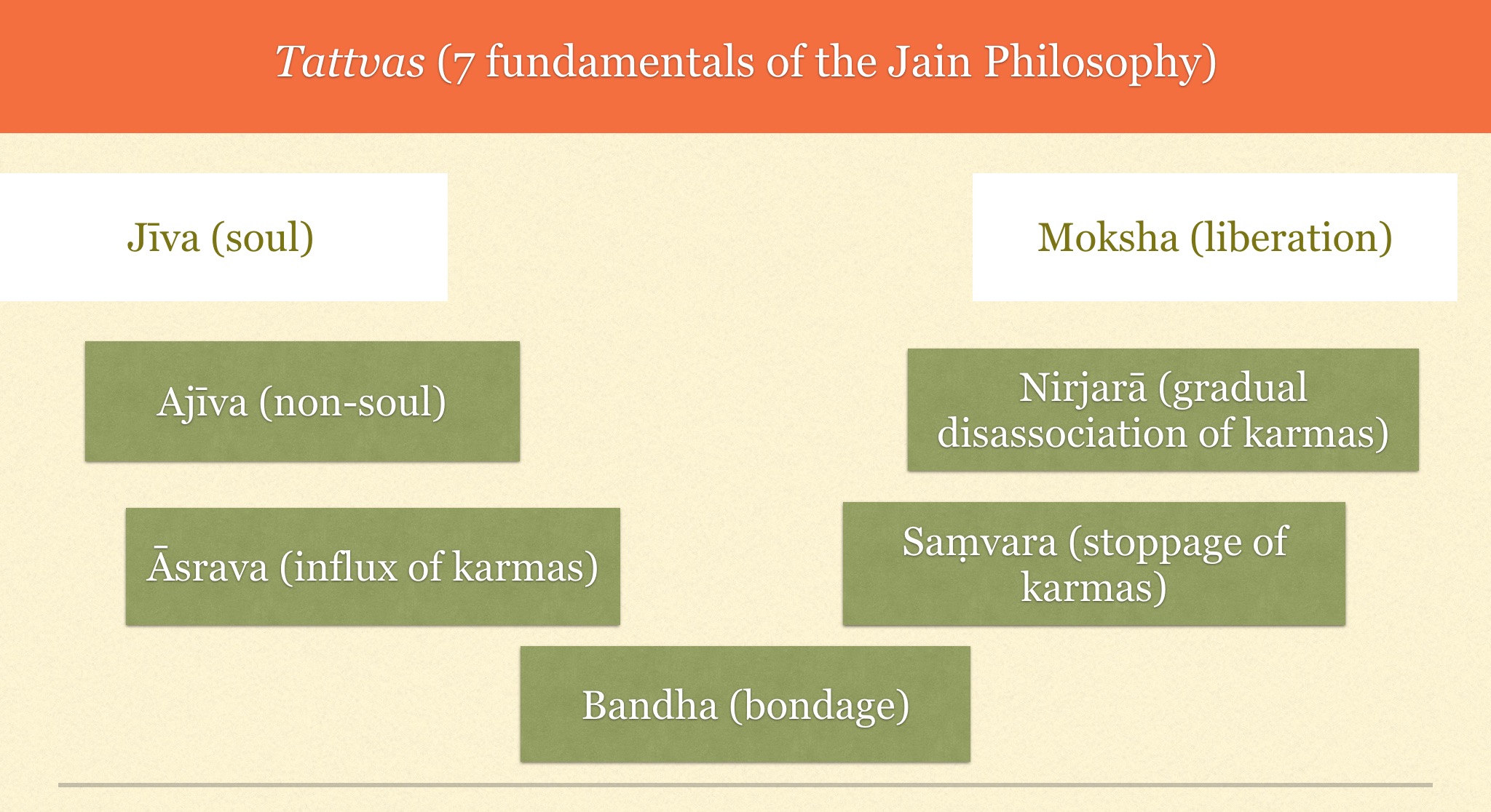
Tattva (Jainism)
Jain philosophy explains that seven ''tattva'' (truths or fundamental principles) constitute reality. These are:— #'' jīva''- the soul which is characterized by consciousness #''ajīva''- the non-soul #''āsrava'' (influx)- inflow of auspicious and evil karmic matter into the soul. #''bandha'' (bondage)- mutual intermingling of the soul and ''karmas''. #''samvara'' (stoppage)- obstruction of the inflow of karmic matter into the soul. #''nirjara'' (gradual dissociation)- separation or falling-off of part of karmic matter from the soul. #''mokṣha'' (liberation)- complete annihilation of all karmic matter (bound with any particular soul). The knowledge of these reals is said to be essential for the liberation of the soul. However, as per one sect of Jain i.e. Shwetamber (Sthanakwasi), there are total nine tattva (truths or fundamental principles). Seven tattva are same as above but 2 more tattva are there namely: Overview The first two are the two ontological catego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratnatraya
Jainism emphasises that ratnatraya (triple gems of Jainism) — the right faith (''Samyak Darshana''), right knowledge (''Samyak Gyana'') and right conduct (''Samyak Charitra'') — constitutes the path to liberation. These are known as the triple gems (or jewels) of Jainism and hence also known as ''Ratnatraya'' The Path to liberation According to Jainism, purification of soul and liberation can be achieved through the path of three jewels: ''Samyak darśana'' (Correct View), meaning faith, acceptance of the truth of soul (''jīva''); ''Samyak jnana'' (Correct Knowledge), meaning undoubting knowledge of the ''tattvas''; and ''Samyak charitra'' (Correct Conduct), meaning behavior consistent with the Five vows. Jain texts often add ''samyak tap'' (Correct Asceticism) as a fourth jewel, emphasizing belief in ascetic practices as the means to liberation (moksha). The four jewels are called ''moksha marg''. According to Jain texts, the liberated pure soul (''Siddha'') goes up to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattvartha Sutra
''Tattvārthasūtra'', meaning "On the Nature nowiki/>''artha''">artha.html" ;"title="nowiki/>''artha">nowiki/>''artha''of Reality [''tattva'']" (also known as ''Tattvarth-adhigama-sutra'' or ''Moksha-shastra'') is an ancient Jain text written by ''Acharya (Jainism), Acharya'' Umaswami in Sanskrit, sometime between the 2nd- and 5th-century CE. The ''Tattvārthasūtra'' is regarded as one of the earliest, most authoritative texts in Jainism. It is accepted as authoritative in both its major sub-traditions – ''Digambara'' and '' Śvētāmbara'' – as well as the minor sub-traditions. It is a philosophical text, and its importance in Jainism is comparable with that of the ''Brahma Sutras'' and ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' in Hinduism. In an aphoristic sutra style of ancient Indian texts, it presents the complete Jainism philosophy in 350 sutras over 10 chapters. The text has attracted numerous commentaries, translations and interpretations since the 5th-century. One of its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Gems Of Jainism
Jainism emphasises that ratnatraya (triple gems of Jainism) — the right faith (''Samyak Darshana''), right knowledge (''Samyak Gyana'') and right conduct (''Samyak Charitra'') — constitutes the path to liberation. These are known as the triple gems (or jewels) of Jainism and hence also known as ''Ratnatraya'' The Path to liberation According to Jainism, purification of soul and liberation can be achieved through the path of three jewels: ''Samyak darśana'' (Correct View), meaning faith, acceptance of the truth of soul (''jīva''); ''Samyak jnana'' (Correct Knowledge), meaning undoubting knowledge of the ''tattvas''; and ''Samyak charitra'' (Correct Conduct), meaning behavior consistent with the Five vows. Jain texts often add ''samyak tap'' (Correct Asceticism) as a fourth jewel, emphasizing belief in ascetic practices as the means to liberation (moksha). The four jewels are called ''moksha marg''. According to Jain texts, the liberated pure soul (''Siddha'') goes up to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Philosophy
Jain philosophy refers to the ancient Indian philosophical system found in Jainism. One of the main features of Jain philosophy is its dualistic metaphysics, which holds that there are two distinct categories of existence, the living, conscious or sentient being (''jiva'') and the non-living or material (''ajiva''). Jain texts discuss numerous philosophical topics such as epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, cosmology and soteriology. Jain thought is primarily concerned with understanding the nature of living beings, how these beings are bound by karma (which are seen as fine material particles) and how living beings may be liberated ('' moksha'') from the cycle of reincarnation. Also notable is the Jain belief in a beginning-less and cyclical universe and a rejection of a Creator deity. From the Jain point of view, Jain philosophy is eternal and has been taught numerous times in the remote past by the great enlightened tirthankaras ("ford-makers"). Historians trace the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karma In Jainism
Karma is the basic principle within an overarching psycho-cosmology in Jainism. Human moral actions form the basis of the transmigration of the soul ('). The soul is constrained to a cycle of rebirth, trapped within the temporal world ('), until it finally achieves liberation ('). Liberation is achieved by following a path of purification. Jains believe that karma is a physical substance that is everywhere in the universe. Karma particles are attracted to the soul by the actions of that soul. Karma particles are attracted when we do, think, or say things, when we kill something, when we lie, when we steal and so on. Karma not only encompasses the causality of transmigration, but is also conceived of as an extremely subtle matter, which infiltrates the soul—obscuring its natural, transparent and pure qualities. Karma is thought of as a kind of pollution, that taints the soul with various colours ('' leśyā''). Based on its karma, a soul undergoes transmigration and reincar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Monasticism
Jain monasticism refers to the order of monks and nuns in the Jain community and can be divided into two major denominations: the ''Digambara'' and the '' Śvētāmbara''. The monastic practices of the two major sects vary greatly, but the major principles of both are identical. Five ''mahāvratas'' (Great Vows), from Mahavira's teachings, are followed by all Jain ascetics. Historians believe that a united Jain ''sangha'' (community) existed before 367 BCE, about 160 years after the ''moksha'' (liberation) of Mahavira. The community then gradually divided into the major denominations. Terminology ''Digambaras'' use the word ' for male monastics and '' aryika'' for female monastics. ''Digambara monks'' are also called ''nirgrantha'' (without bonds). '' Śvētāmbaras'' use the word ''sadhvi''s for female monastics. History Mahavira had 11 chief disciples, Indrabhuti Gautama being the most senior. Each chief disciple was made responsible for 250 to 500 monks. The Jain sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahavrata
Jain ethical code prescribes two '' dharmas'' or rules of conduct. One for those who wish to become ascetic and another for the '' śrāvaka'' (householders). Five fundamental vows are prescribed for both votaries. These vows are observed by '' śrāvakas'' (householders) partially and are termed as ''anuvratas'' (small vows). Ascetics observe these fives vows more strictly and therefore observe complete abstinence. These five vows are: * '' Ahiṃsā'' (Non-violence) * ''Satya'' (Truth) * ''Asteya'' (Non-stealing) * ''Brahmacharya'' (Chastity) * ''Aparigraha'' (Non-possession) According to Jain text, '' Puruşārthasiddhyupāya'': Apart from five main vows, a householder is expected to observe seven supplementary vows (''śeelas'') and last '' sallekhanā'' vow. ''Maha vratas'' (major vows) ''Mahavrata'' (lit. major vows) are the five fundamental observed by the Jain ascetics. According to Acharya Samantabhadra’s Ratnakaraņdaka śrāvakācāra: Ahiṃsā Ahimsa (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raaga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each ''rāga'' is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience. Each ''rāga'' provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the ''rāga'' in keeping with rules specific to the ''rāga''. ''Rāga''s range from small ''rāga''s like Bahar and Shahana that are not much more than songs to big ''rāga''s like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances can last over an hour. ''Rāga''s may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhyana
Dhyana may refer to: Meditative practices in Indian religions * Dhyana in Buddhism (Pāli: ''jhāna'') * Dhyana in Hinduism * Jain Dhyāna, see Jain meditation Other *''Dhyana'', a work by British composer John Tavener (1944-2013) * ''Dhyana'' (MaYaN album), 2018 * Hygon Dhyana, a x86 compatible microprocessor {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atonement
Atonement (also atoning, to atone) is the concept of a person taking action to correct previous wrongdoing on their part, either through direct action to undo the consequences of that act, equivalent action to do good for others, or some other expression of feelings of remorse. From the Middle English ''attone'' or ''atoon'' ("agreed", literally "at one"), now meaning to be "at one", in harmony, with someone. Atonement "is closely associated to forgiveness, reconciliation, sorrow, remorse, repentance, reparation, and guilt".Ruth Williams, "Atonement", in David A. Leeming, Kathryn Madden, Stanton Marlan, ''Encyclopedia of Psychology and Religion: L-Z'' (2009), p. 83. It can be seen as a necessary step on a path to redemption.Linda Radzik, ''Making Amends: Atonement in Morality, Law, and Politics'' (2009). In law and society In the legal systems, the concept of atonement plays an important role with respect to criminal justice, where it is considered one of the primary goals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |