|
Niles Firebrick
Niles Firebrick was manufactured by the Niles Fire brick Company since it was created in 1872 by John Rhys Thomas until the company was sold in 1953 and completely shutdown in 1960. Capital to establish the company was provided by Lizzie B. Ward to construct a small plant across from the Old Ward Mill which was run by her husband James Ward. Thomas immigrated in 1868 from Carmarthenshire in Wales with his wife and son W. Aubrey Thomas who served as secretary of the company until he was appointed as representative to the U. S. Congress in 1904. The company was managed by another son, Thomas E. Thomas, after J.R. Thomas died unexpectedly in 1898. The Thomases returned the favor of their original capitalization by purchasing an iron blast furnace from James Ward when he went bankrupt in 1879. Using their knowledge of firebrick they were able to make this small furnace profitable. Later they used it to showcase the value of adding hot blast to a furnace using 3 ovens packed full of fireb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Brick
A fire brick, firebrick, or refractory is a block of ceramic material used in lining furnaces, kilns, fireboxes, and fireplaces. A refractory brick is built primarily to withstand high temperature, but will also usually have a low thermal conductivity for greater energy efficiency. Usually dense firebricks are used in applications with extreme mechanical, chemical, or thermal stresses, such as the inside of a wood-fired kiln or a furnace, which is subject to abrasion from wood, fluxing from ash or slag, and high temperatures. In other, less harsh situations, such as in an electric- or natural gas-fired kiln, more porous bricks, commonly known as "kiln bricks", are a better choice. They are weaker, but they are much lighter and easier to form and insulate far better than dense bricks. In any case, firebricks should not spall, and their strength should hold up well during rapid temperature changes. Manufacture In the making of firebrick, fireclay is fired in the kiln until it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire ( cy, Sir Gaerfyrddin; or informally ') is a county in the south-west of Wales. The three largest towns are Llanelli, Carmarthen and Ammanford. Carmarthen is the county town and administrative centre. The county is known as the "Garden of Wales" and is also home to the National Botanic Garden of Wales. Carmarthenshire has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The county town was founded by the Romans, and the region was part of the Kingdom of Deheubarth in the High Middle Ages. After invasion by the Normans in the 12th and 13th centuries it was subjugated, along with other parts of Wales, by Edward I of England. There was further unrest in the early 15th century, when the Welsh rebelled under Owain Glyndŵr, and during the English Civil War. Carmarthenshire is mainly an agricultural county, apart from the southeastern part which was once heavily industrialised with coal mining, steel-making and tin-plating. In the north of the county, the woollen industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Weston Young
William Weston Young (1776–1847) was a British Quaker entrepreneur, artist, botanist, wreck-raiser, surveyor, potter, and inventor of the firebrick. Biography William Weston Young was born on 20 April 1776 at Lewin's Mead, Bristol, England, into a devout Quaker family, the third son of Edward Young, a Bristolian merchant and Sarah (Sally) Young (née Weston). He was educated at Gildersome Quaker boarding school in Yorkshire, which among other things gave him a rudimentary knowledge of science which he was later to apply in his invention of the silica firebrick. After a flustered attempt to emigrate to America in 1794, involving his ship being captured by a fleet of French men-of-war, his ultimate escape from captivity and arduous journey home, Young settled back in Bristol, found employment and married fellow Quaker, Elizabeth Davis, in April 1795. In 1798, Young had acquired the financial backing (with notable help from his uncle Thomas Young, father of the physicist, ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neath Valley
The Vale of Neath (or Neath Valley, Welsh: ''Cwm Nedd''), one of the South Wales Valleys, encompasses the upper reaches of the River Neath in southwest Wales. In addition to the River Neath, it is traversed by the Neath Canal and the A465 dual carriageway. Settlements in the valley include Neath, Cadoxton, Tonna, Aberdulais, Resolven, Blaengwrach, Glynneath and Pontneddfechan. Coal mining was an industry in the valley with mining operations being located at Aberpergwm and Pentreclwydau near Glynneath. Waterfall Country " Waterfall Country" is a nickname given to the Vale of Neath due to the diverse number of waterfalls in the valley. In the upper reaches of the valley, at the foothills of the Brecon Beacons, are the waterfalls of four or five rivers: the Afon Hepste, Nedd Fechan, Afon Pyrddin, Afon Mellte and Afon Sychryd. In the lower valley, waterfalls can be found at Melincourt and Aberdulais. Vale of Neath Railway Currently partly used as a goods line the Vale of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperateness, north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff. Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a Kingdom of Wales, kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanelli
Llanelli ("St Elli's Parish"; ) is a market town and the largest community in Carmarthenshire and the preserved county of Dyfed, Wales. It is located on the Loughor estuary north-west of Swansea and south-east of the county town, Carmarthen. The town had a population of 25,168 in 2011, estimated in 2019 at 26,225. The local authority was Llanelli Borough Council when the county of Dyfed existed, but it has been under Carmarthenshire County Council since 1996. Name Spelling The anglicised spelling “Llanelly” was used until 1966, when it was changed to Llanelli after a local public campaign. It remains in the name of a local historic building, Llanelly House. It should not be confused with the village and parish of Llanelly, in south-east Wales near Abergavenny. Llanelly in Victoria, Australia was named after this town of Llanelli, using the spelling current at that time. History The beginnings of Llanelli can be found on the lands of present-day Parc Howard. An Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory Materials
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to Thermal decomposition, decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, Inorganic compound, inorganic, Nonmetal, non-metallic, Porosity, porous, and heterogeneous. They are typically composed of oxides or carbides, nitrides etc. of the following materials: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. ASTM International, ASTM C71 defines refractories as "...non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, or as components of systems, that are exposed to environments above ." Refractory materials are used in Metallurgical furnace, furnaces, kilns, incinerators, and Nuclear reactor technology, reactors. Refractories are also used to make crucibles and moulds for casting glass and metals and for surfacin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
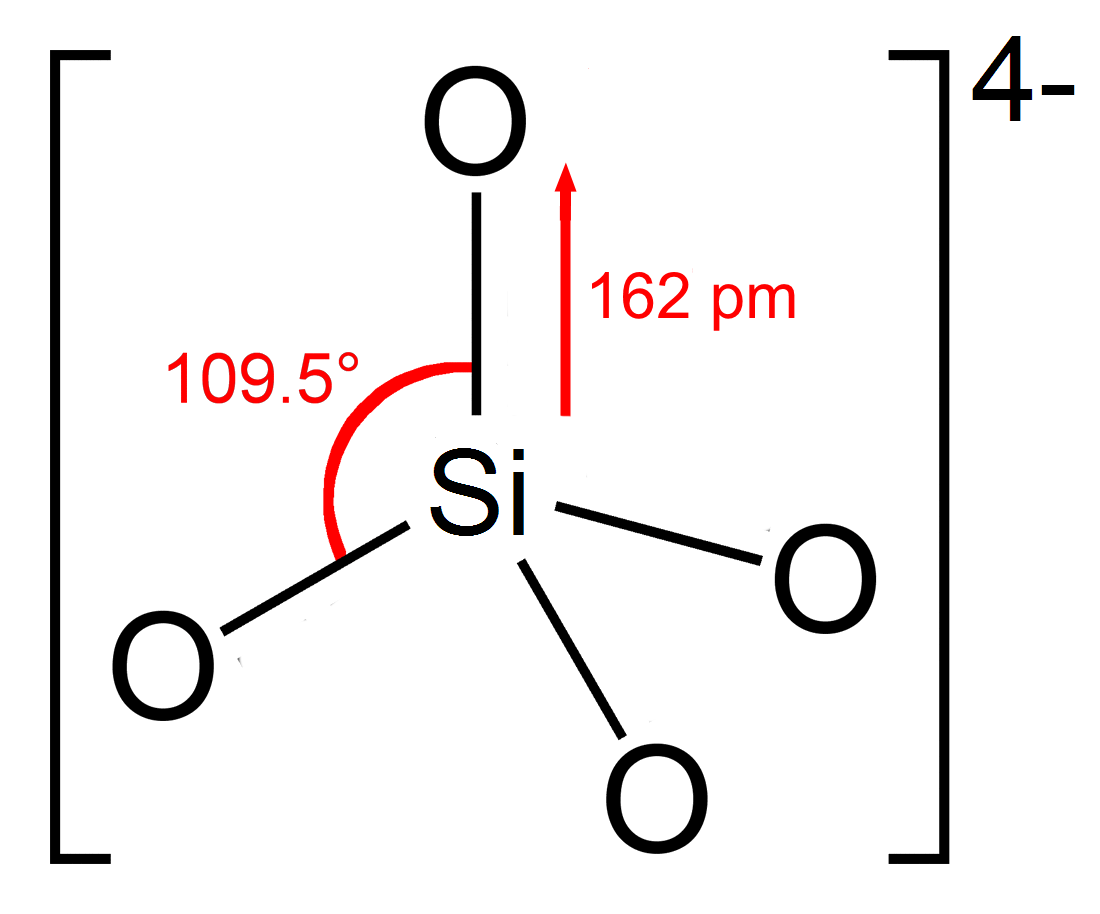
Silicates
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bricks
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using mortar, adhesives or by interlocking them. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region and time period, and are produced in bulk quantities. ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of similar materials, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since circa 4000 BC. Air-dried bricks, also known as mud-bricks, have a history older than fired bricks, and have an additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)