|
Nihilist
Nihilism (; ) is a philosophy, or family of views within philosophy, that rejects generally accepted or fundamental aspects of human existence, such as objective truth, knowledge, morality, values, or meaning. The term was popularized by Ivan Turgenev, and more specifically by his character Bazarov in the novel '' Fathers and Sons''. There have been different nihilist positions, including that human values are baseless, that life is meaningless, that knowledge is impossible, or that some set of entities do not exist or are meaningless or pointless. Pratt, Alan.Nihilism" ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. . Scholars of nihilism may regard it as merely a label that has been applied to various separate philosophies, or as a distinct historical concept arising out of nominalism, skepticism, and philosophical pessimism, as well as possibly out of Christianity itself. Contemporary understanding of the idea stems largely from the Nietzschean 'crisis of nihilism', from which d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fathers And Sons (novel)
''Fathers and Sons'' (russian: «Отцы и дети»; ''Otcy i deti'', ; archaic spelling Отцы и дѣти), also translated more literally as ''Fathers and Children'', is an 1862 novel by Ivan Turgenev, published in Moscow by Grachev & Co. It is one of the most acclaimed Russian novels of the 19th century. Plot Arkady Kirsanov has just graduated from the University of Petersburg. He returns with a friend, Bazarov, to his father's modest estate in an outlying province of Russia. His father, Nikolay, gladly receives the two young men at his estate, called Marino, but Nikolay's brother, Pavel, soon becomes upset by the strange new philosophy called "nihilism" which the young men, especially Bazarov, advocate. Nikolay, initially delighted to have his son return home, slowly begins to feel uneasy. A certain awkwardness develops in his regard toward his son, as Arkady's radical views, much influenced by Bazarov, make Nikolay’s own beliefs feel dated. Nikolay has always tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nietzschean
Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) developed his philosophy during the late 19th century. He owed the awakening of his philosophical interest to reading Arthur Schopenhauer's ''Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung'' (''The World as Will and Representation'', 1819, revised 1844) and said that Schopenhauer was one of the few thinkers that he respected, dedicating to him his essay ''Schopenhauer als Erzieher'' (''Schopenhauer as Educator''), published in 1874 as one of his ''Untimely Meditations''. Since the dawn of the 20th century, the philosophy of Nietzsche has had great intellectual and political influence around the world. Nietzsche applied himself to such topics as morality, religion, epistemology, poetry, ontology, and social criticism. Because of Nietzsche's evocative style and his often outrageous claims, his philosophy generates passionate reactions running from love to disgust. Nietzsche noted in his autobiographical '' Ecce Homo'' that his philosophy developed and evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Turgenev
Ivan Sergeyevich Turgenev (; rus, links=no, Ива́н Серге́евич Турге́невIn Turgenev's day, his name was written ., p=ɪˈvan sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ tʊrˈɡʲenʲɪf; 9 November 1818 – 3 September 1883 (Old Style dates: 28 October 1818 – 22 August 1883) was a Russian novelist, short story writer, poet, playwright, translator and popularizer of Russian literature in the West. His first major publication, a short story collection titled ''A Sportsman's Sketches'' (1852), was a milestone of Russian realism. His novel '' Fathers and Sons'' (1862) is regarded as one of the major works of 19th-century fiction. Life Ivan Sergeyevich Turgenev was born in Oryol (modern-day Oryol Oblast, Russia) to noble Russian parents Sergei Nikolaevich Turgenev (1793–1834), a colonel in the Russian cavalry who took part in the Patriotic War of 1812, and Varvara Petrovna Turgeneva (née Lutovinova; 1787–1850). His father belonged to an old, but impoverished Turge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postmodernity
Postmodernity (post-modernity or the postmodern condition) is the economic or cultural state or condition of society which is said to exist ''after'' modernity. Some schools of thought hold that modernity ended in the late 20th century – in the 1980s or early 1990s – and that it was replaced by postmodernity, and still others would extend modernity to cover the developments denoted by postmodernity. The idea of the postmodern condition is sometimes characterized as a culture stripped of its capacity to function in any linear or autonomous state like regressive isolationism, as opposed to the progressive mind state of modernism. Postmodernity can mean a personal response to a postmodern society, the conditions in a society which make it postmodern or the state of being that is associated with a postmodern society as well as a historical epoch. In most contexts it should be distinguished from postmodernism, the adoption of Postmodern philosophy, postmodern philosophies or traits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Institutions
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions and norms are all examples of institutions. Institutions vary in their level of formality and informality. Institutions are a principal object of study in social sciences such as political science, anthropology, economics, and sociology (the latter described by Émile Durkheim as the "science of institutions, their genesis and their functioning"). Primary or meta-institutions are institutions such as the family or money that are broad enough to encompass sets of related institutions. Institutions are also a central concern for law, the formal mechanism for political rule-making and enforcement. Historians study and document the founding, growth, decay and development of institutions as part of political, economic and cultural history. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History By Period
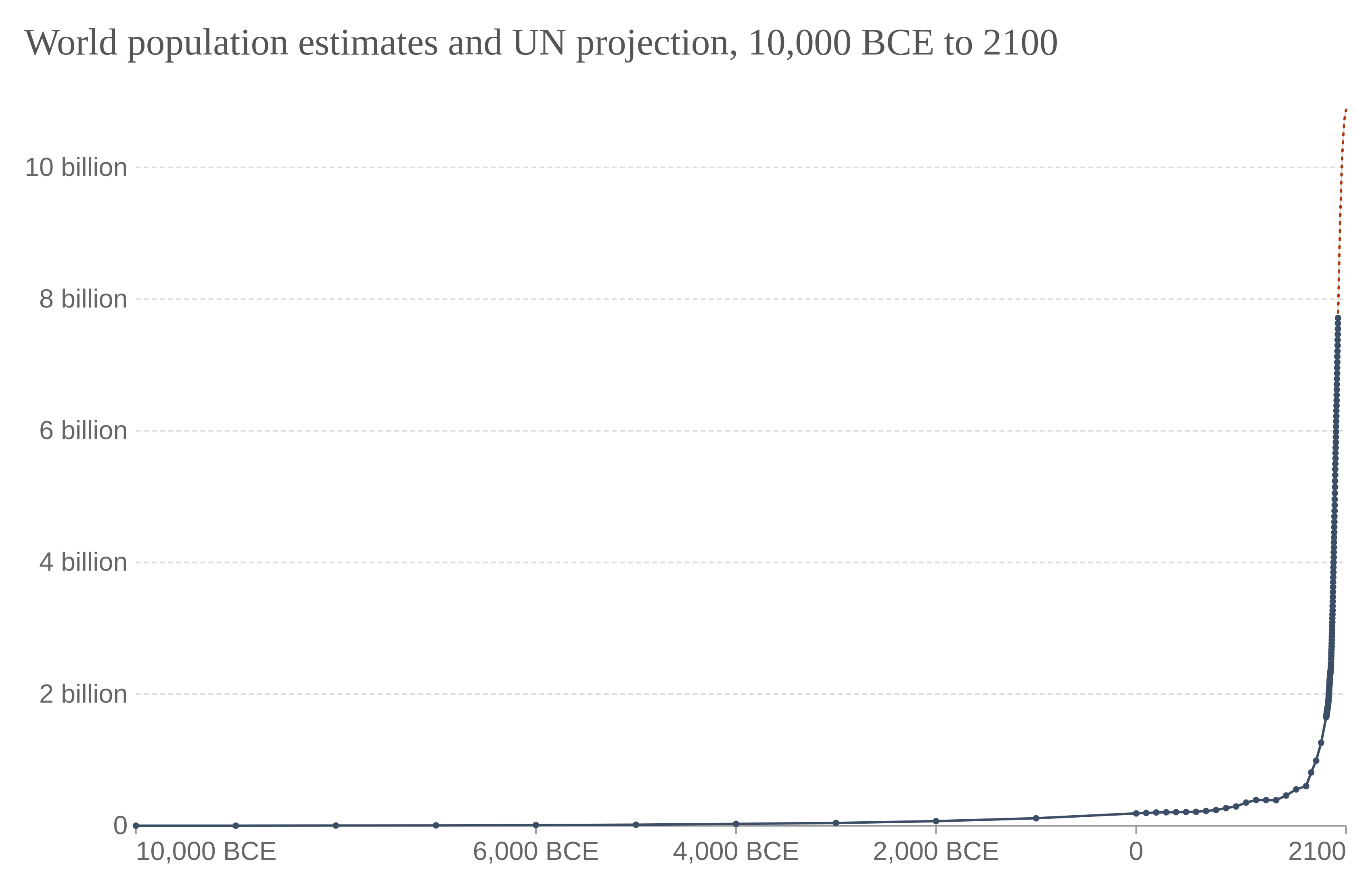
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied through primary and secondary source documents. Humanity's written history was preceded by its prehistory, beginning with the Paleolithic ("Old Stone Age") era. This was followed by the Neolithic ("New Stone Age") era, which saw the Agricultural Revolution begin in the Middle East around 10,000 BCE. During this period, humans began the systematic husbandry of plants and animals. As agriculture advanced, most humans transitioned from a nomadic to a settled lifestyle as farmers in permanent settlements. The relative security and increased productivity provided by farming allowed communities to expand into increasingly larger units, fostered by advances in transportation. The earliest complex societies appeared in fertile river valleys. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baudrillard
Jean Baudrillard ( , , ; 27 July 1929 – 6 March 2007) was a French sociologist, philosopher and poet with interest in cultural studies. He is best known for his analyses of media, contemporary culture, and technological communication, as well as his formulation of concepts such as simulation and hyperreality. Baudrillard wrote about diverse subjects, including consumerism, gender relations, critique of economy, economics, social history, art, Western foreign policy, and popular culture. Among his best known works are ''Seduction'' (1978), ''Simulacra and Simulation'' (1981), ''America'' (1986), and '' The Gulf War Did Not Take Place'' (1991). His work is frequently associated with postmodernism and specifically post-structuralism. Baudrillard: "I have nothing to do with postmodernism."MLA Brennan, Eugene. Review of Pourquoi la guerre aujourd’hui?, by Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Derrida. French Studies: A Quarterly Review, vol. 71 no. 3, 2017, p. 449-449. Project MUSE mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulacra And Simulation
''Simulacra and Simulation'' (french: Simulacres et Simulation) is a 1981 philosophical treatise by the philosopher and cultural theorist Jean Baudrillard, in which the author seeks to examine the relationships between reality, symbols, and society, in particular the significations and symbolism of culture and media involved in constructing an understanding of shared existence. Simulacra are copies that depict things that either had no original, or that no longer have an original. Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Summary Definition ''Simulacra and Simulation'' is most known for its discussion of symbols, signs, and how they relate to contemporaneity (simultaneous existences). Baudrillard claims that our current society has replaced all reality and meaning with symbols and signs, and that human experience is a simulation of reality. Moreover, these simulacra are not merely mediations of reality, nor even deceptive media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methods include questioning, critical discussion, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Newton's 1687 ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'' later became classified as a book of physics. In the 19th century, the growth of modern research universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold J
Arnold may refer to: People * Arnold (given name), a masculine given name * Arnold (surname), a German and English surname Places Australia * Arnold, Victoria, a small town in the Australian state of Victoria Canada * Arnold, Nova Scotia United Kingdom * Arnold, East Riding of Yorkshire * Arnold, Nottinghamshire United States * Arnold, California, in Calaveras County * Arnold, Carroll County, Illinois * Arnold, Morgan County, Illinois * Arnold, Iowa * Arnold, Kansas * Arnold, Maryland * Arnold, Mendocino County, California * Arnold, Michigan * Arnold, Minnesota * Arnold, Missouri * Arnold, Nebraska * Arnold, Ohio * Arnold, Pennsylvania * Arnold, Texas * Arnold, Brooke County, West Virginia * Arnold, Lewis County, West Virginia * Arnold, Wisconsin * Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Massachusetts * Arnold Township, Custer County, Nebraska Other uses * Arnold (automobile), a short-lived English car * Arnold of Manchester, a former English coachbuilder * Arnold (band), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Study Of History
''A Study of History'' is a 12-volume universal history by the British historian Arnold J. Toynbee, published from 1934 to 1961. It received enormous popular attention but according to historian Richard J. Evans, "enjoyed only a brief vogue before disappearing into the obscurity in which it has languished." Toynbee's goal was to trace the development and decay of 19 or 21 world civilizations in the historical record, applying his model to each of these civilizations, detailing the stages through which they all pass: genesis, growth, time of troubles, universal state, and disintegration. The 19 (or 21) major civilizations, as Toynbee sees them, are: Egyptian, Andean, Sumerian, Babylonic, Hittite, Minoan, Indic, Hindu, Syriac, Hellenic, Western, Orthodox Christian (having two branches: the main or Byzantine body and the Russian branch), Far Eastern (having two branches: the main or Chinese-Korean body and the Japanese branch), Islamic (having two branches which later merged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)