|
Nicanor Of Syria
Nicanor (; el, Nικάνωρ ''Nīkā́nōr'') was a Syrian Greek who lived in the 3rd century BC under Seleucid Empire. Together with a Gaul named Apaturius, he assassinated Seleucus III Ceraunus during his expedition into Asia against Attalus I in 222 BC. He was immediately seized and executed by order of the general Achaeus. (Polybius 4.48; Eusebius Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian ... Armenian text 165.) References * {{SmithDGRBM Ancient Syria 222 BC deaths Year of birth unknown 3rd-century BC Greek people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
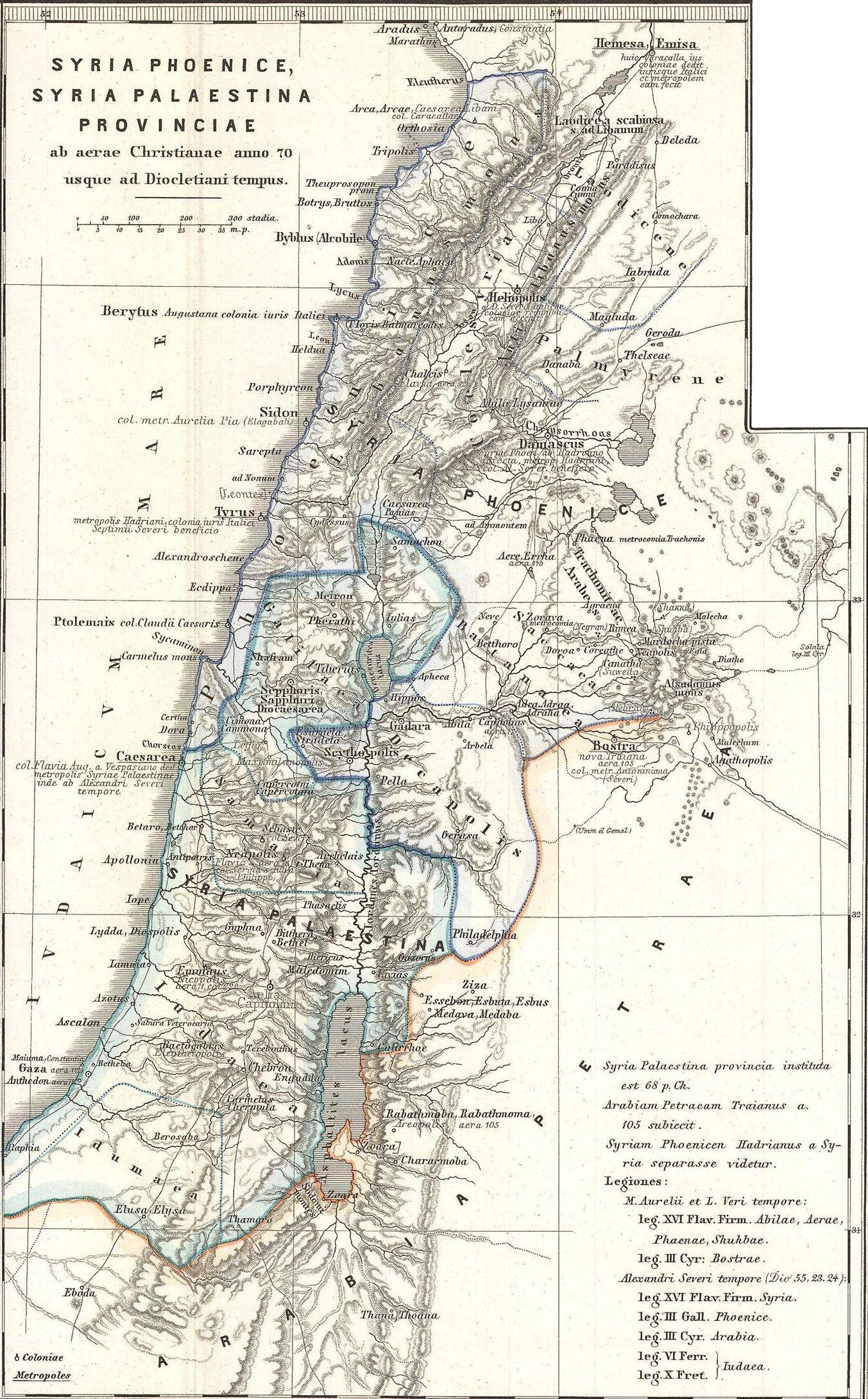
Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria (region), Syria in classical antiquity. It probably derived from the Aramaic word for all of the Syria (region), region of Syria, but it was most often applied to the Beqaa Valley between the Mount Lebanon, Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. The area is now part of the modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ''kul'', meaning "all, the entire", such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apaturius
Apaturius ( grc, Ἀπατούριος) of Alabanda was a scene-painter of ancient Greece, whose mode of painting the scene of the little theatre at Tralles is described by Vitruvius, with the criticism made upon it by Licinius.Vitruvius, ''De architectura'' 7.5. §§ 5, 6 A different, unrelated Apaturius was a Gaul who, with Nicanor of Syria, assassinated Seleucus III Ceraunus Seleucus III Soter, called Seleucus Ceraunus (Greek: ; c. 243 BC – April/June 223 BC, ruled December 225 – April/June 223 BC), was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Kingdom, the eldest son of Seleucus II Callinicus and Laodice II. Biograph ... in the 3rd century BCE. Notes Ancient Greek painters Gaulish people 3rd-century BC people 3rd-century BC painters {{Greece-painter-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus III Ceraunus
Seleucus III Soter, called Seleucus Ceraunus (Greek: ; c. 243 BC – April/June 223 BC, ruled December 225 – April/June 223 BC), was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Kingdom, the eldest son of Seleucus II Callinicus and Laodice II. Biography His birth name was Alexander and he was named after his great uncle the Seleucid official Alexander. Alexander changed his name to Seleucus after he succeeded his father as King. After a brief reign of less than two years (225–223 BC), during which he unsuccessfully continued his father's war in Asia Minor against Attalus I of Pergamon of Pergamum, Seleucus was assassinated in Anatolia Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ... by members of his army. His official byname ''Soter'' means "Saviour", while his nickname ''Cerau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the first cousin once removed and the adopted son of Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king in 238 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis. Attalus won Battle of the Caecus River, an important victory over the Galatians, newly arrived Celtic tribes from Thrace, who had been, for more than a generation, plundering and exacting tribute throughout most of Asia Minor without any serious check. This victory, celebrated by the triumphal monument at Pergamon (famous for its ''Dying Gaul'') and the liberation from the Gallic "terror" which it represented, earned for Attalus the name of "Soter", and the title of "basileus, king". A courageous and capable general and loyal ally of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaeus (general)
Achaeus ( grc, Ἀχαιός, ''Akhaios''; died 213 BC) was a general and later a separatist ruler of part of the Greek Seleucid kingdom. He was the son of Andromachus, whose sister Laodice II married Seleucus Callinicus, the father of Antiochus III the Great He accompanied Seleucus Ceraunus, the son of Callinicus, in his expedition across mount Taurus against Attalus I, and after the assassination of Seleucus Ceraunus revenged his death; and though he might easily have assumed the royal power, he remained faithful to the family of Seleucus. In 223 BC Antiochus III, the successor of Seleucus Ceraunus, appointed him to the command of all Asia Minor on the western side of Mount Taurus. Achaeus recovered all the districts which Attalus had gained on the Seleucids once more; but being falsely accused by Hermeias, the minister to Antiochus, of intending to revolt, Achaeus assumed the title of king in self-defence, and ruled over the whole of Asia on the western side of the Tauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail. Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed constitution or the separation of powers in government, his in-depth discussion of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", which influenced Montesquieu's ''The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's ''Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909–2008), who published studies related to him for 50 years, including a long commentary of his ''Histories'' and a biography. Early life Polybius was born around 200 BC in Megalopolis, Greece, Megalopolis, Arcadia (region), Arcadia, when it was an active member of the Achaean League. The town was revived, along with other Achaean states, a century before he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima in the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. Together with Pamphilus, he was a scholar of the biblical canon and is regarded as one of the most learned Christians during late antiquity. He wrote ''Demonstrations of the Gospel'', '' Preparations for the Gospel'' and ''On Discrepancies between the Gospels'', studies of the biblical text. As "Father of Church History" (not to be confused with the title of Church Father), he produced the ''Ecclesiastical History'', ''On the Life of Pamphilus'', the ''Chronicle'' and ''On the Martyrs''. He also produced a biographical work on Constantine the Great, the first Christian Roman emperor, who was ''augustus'' between AD 306 and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |