|
New South Wales Tulloch Suburban Carriage Stock
The New South Wales Tulloch suburban carriage stock were a type of electric multiple unit operated by the New South Wales Government Railways and its successors between 1940 and 1992. In their later years, they were nicknamed ''Red Rattlers''. History In 1940, 24 first series power cars and 24 trailer cars were built by Tulloch Limited for the New South Wales Government Railways. These differed from the 1920s built carriages in having a pillar between the doors to increase passenger circulation space."Rolling Stock" ''Railway Digest'' January 1992 page 31"Sydney's Electric Trains from 1926 to 1960" '' ARHS Bulletin'' issue 761 March 2001 pages 90-93T4554 - Tulloch 1940 Suburban Trailer Car NSW Environment & Heritage In 1951, a further three first seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulloch Limited
Tulloch Limited was an Australian engineering and railway rolling stock manufacturer, located at Rhodes, New South Wales. History In 1885 Robert Tulloch founded Phoenix Iron Works in Pyrmont, New South Wales, Pyrmont. In 1913 the business was incorporated as Tulloch's Phoenix Iron Works and relocated to Rhodes, New South Wales, Rhodes. It primarily built freight wagons for the New South Wales Government Railways but also built Rail rolling stock in New South Wales#1926–1960 single-deck steel cars, single deck electric carriages for the Railways in Sydney, Sydney suburban network from 1926 until the 1957. During World War II a number of boats were built for the Royal Australian Navy including some 120ft Motor Lighters. In April 1948 the first of four seven-carriage New South Wales HUB type carriage stock, HUB sets was delivered. In the 1950s it commenced building locomotives with 27 Victorian Railways Victorian Railways W class (diesel-hydraulic), W class diesel hydraulic shunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
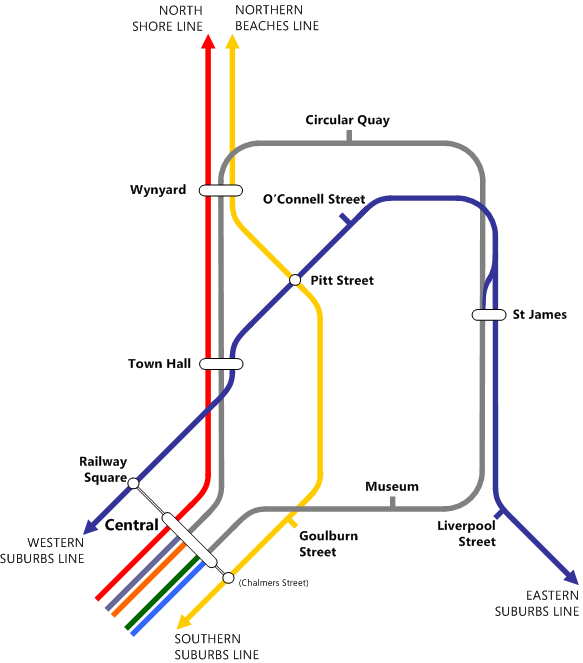
Electric Multiple Units Of New South Wales
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Railway History
''Australian Railway History'' is a monthly magazine covering railway history in Australia, published by the New South Wales Division of the Australian Railway Historical Society on behalf of its state and territory Divisions. Australian Railway Historical Society History and profile It was first published in 1937 as the ''Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society Bulletin'', being renamed ''ARHS Bulletin'' in 1952. In January 2004, the magazine was re-branded as ''Australian Railway History''. Historically, the magazine had a mix of articles dealing with historical material and items on current events drawn from its affiliate publications. Today, it contains only historical articles, two or three of them being in-depth.Parameters * Size : A4; ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Digest
''Railway Digest'' is a monthly magazine, published in Sydney, covering contemporary railways of Australia. Overview The magazine's publisher is the Australian Railway Historical Society (ARHS), NSW Division. The first issue was published in March 1963 under the name ''New South Wales Digest'' and regular publication commenced with the May 1963 edition. It was renamed in January 1983. In January 1985 it changed paper size from SRA5 to A4. Originally an enthusiast magazine mainly focusing on reporting day-to-day workings of the New South Wales Government Railways and it successors, it was produced by volunteers using a hand-operated duplicator at the home of one of its members. In May 1993, a paid editor was appointed and the magazine's focus gradually shifted to reporting news from across Australia. It has evolved into a professional full-colour production directed at the wider community and commercially distributed to newsagents throughout Australia."Adapt or disappear - the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales Standard Suburban Carriage Stock
The New South Wales Standard suburban carriage stock are a class of electric multiple units that were operated by the New South Wales Government Railways and its successors between 1926 and 1992. They served on the Sydney suburban network. In the years before their withdrawal, they were nicknamed ''Red Rattlers''.This term was imported from Victoria and was never a contemporaneous colloquialism. History To provide rolling stock for the electrification of Sydney's suburban rail network, steel carriages were ordered."Sydney's Electric Trains from 1926 to 1960" '' ARHS Bulletin'' issue 761 March 2001 pages 90-93 The initial 50 power cars were built in England by Leeds Forge Company and shipped to Australia in knocked-down condition. They were assembled by Eveleigh Carriage Workshops (10) and Clyde Engineering (40) between April and October 1925. Initially numbered 2213-2262, they entered service being inserted into sets with Bradfield carriages for haulage by steam locomotives un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Air Brake
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted. The Westinghouse system uses air pressure to charge air reservoirs (tanks) on each car. Full air pressure causes each car to release the brakes. A subsequent reduction or loss of air pressure causes each car to apply its brakes, using the compressed air stored in its reservoirs. Overview Straight air brake In the air brake's simplest form, called the ''straight air system'', compressed air pushes on a piston in a cylinder. The piston is connected through mechanical linkage to brake shoes that can rub on the train wheels, using the resulting friction to slow the train. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Air Brake Company
The Westinghouse Air Brake Company (sometimes nicknamed or abbreviated WABCO although this was also confusingly used for spinoffs) was founded on September 28, 1869 by George Westinghouse in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Earlier in the year he had invented the railway air brake in New York state. After having manufactured equipment in Pittsburgh for a number of years, he began to construct facilities and plants east of the city where homes for his employees were built. In 1889, the air brake manufacturing facility was moved to Wilmerding, Pennsylvania, and the company's general office building was built there in 1890. In 1921 the company began manufacturing a modified air brake system for installation in trucks and heavy vehicles. In 1953 WABCO entered the heavy equipment marketplace, buying the assets of leading equipment designer R.G LeTourneau. An entity known as LeTourneau-Westinghouse sold a range of innovative products, including scrapers, cranes and bulldozers until 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantograph (rail)
A pantograph (or "pan" or "panto") is an apparatus mounted on the roof of an electric train, tram or electric bus to collect power through contact with an overhead line. By contrast, battery electric buses and trains are charged at charging stations. The pantograph is a common type of current collector; typically, a single or double wire is used, with the return current running through the rails. The term stems from the resemblance of some styles to the mechanical pantographs used for copying handwriting and drawings. Invention The pantograph, with a low-friction, replaceable graphite contact strip or "shoe" to minimise lateral stress on the contact wire, first appeared in the late 19th century. Early versions include the bow collector, invented in 1889 by Walter Reichel, chief engineer at Siemens & Halske in Germany, and a flat slide-pantograph first used in 1895 by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad The familiar diamond-shaped roller pantograph was devised and patented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Line
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as: * Overhead catenary * Overhead contact system (OCS) * Overhead equipment (OHE) * Overhead line equipment (OLE or OHLE) * Overhead lines (OHL) * Overhead wiring (OHW) * Traction wire * Trolley wire This article follows the International Union of Railways in using the generic term ''overhead line''. An overhead line consists of one or more wires (or rails, particularly in tunnels) situated over rail tracks, raised to a high electrical potential by connection to feeder stations at regular intervals. The feeder stations are usually fed from a high-voltage electrical grid. Overview Electric trains that collect their current from overhead lines use a device such as a pantograph, bow collector or trolley pole. It presses against the underside of the lowest overhead wire, the contact wire. Current collectors ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Suburbs Railway Line
The Eastern Suburbs Railway is a commuter railway line in Sydney constructed in the 1970s. It is operated by Sydney Trains and has stations at Martin Place, Kings Cross, Edgecliff and Bondi Junction. In addition, it has dedicated platforms at Town Hall, Central and Redfern stations. All of these stations are underground. The Eastern Suburbs railway connects with the Illawarra line at Erskineville, forming the Eastern Suburbs & Illawarra Line. The line features turnbacks at Central, Martin Place and Bondi Junction. There was also previously a rarely used cross-over or 'turnout' at Edgecliff. It operates a service every 3 to 5 minutes during weekday peak hours and 8 to 10 minutes at all other times. Design The twin-track Eastern Suburbs line consists of eight stations connected mainly by viaduct and tunnel. The stations are finished in terrazzo and colourful tiles. Alignment From a tunnel portal north of Erskineville, the Eastern Suburbs line runs north to Redfern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)